New research shows that long-term memory is not stored by a single molecular switch, but by a sequence of timed genetic programs unfolding across different brain regions.

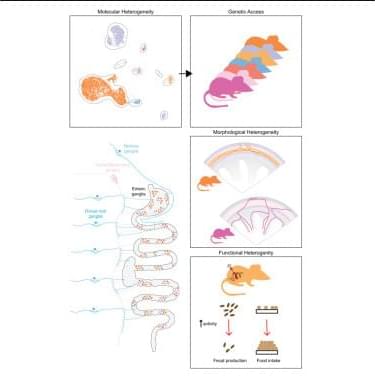
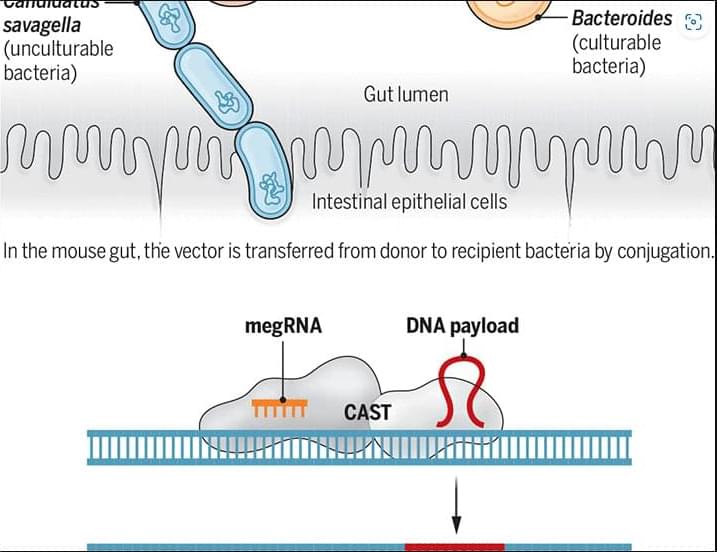
In a new Science study, researchers describe MetaEdit, a strategy that enables targeted insertion of large DNA sequences into the genome of bacteria within the mouse gut environment.
Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
A gene-editing approach enables modification of bacteria within the mouse gut.
Amandine Maire and David Bikard Authors Info & Affiliations
Science
Vol 390, Issue 6774


This ‘fundamental’ study uncovers how directing pyruvate into mitochondria can shrink cells by shifting their metabolism away from building amino acids and proteins.
This fundamental work demonstrates that compartmentalized cellular metabolism is a dominant input into cell size control in a variety of mammalian cell types and in Drosophila. The authors show that increased pyruvate import into the mitochondria in liver-like cells and in primary hepatocytes drives gluconeogenesis but reduces cellular amino acid production, suppressing protein synthesis. The evidence supporting the conclusions is compelling, with a variety of genetic and pharmacologic assays rigorously testing each step of the proposed mechanism. This work will be of interest to cell biologists, physiologists, and researchers interested in cell metabolism, and is significant because stem cells and many cancers exhibit metabolic rewiring of pyruvate metabolism.

A new pill for treating dementia is delivering promising “topline” results in early-stage clinical trials, according to a recent press release by its makers.
The treatment, called VES001 after its developer Vesper Bio, is designed to tackle frontotemporal dementia (FTD) – the most common type of dementia in the under-60s.
In a two-part preliminary safety trial at two medical centres in the Netherlands and the UK, VES001 was given to people showing no signs of FTD, including six volunteers with an increased genetic risk for the condition.
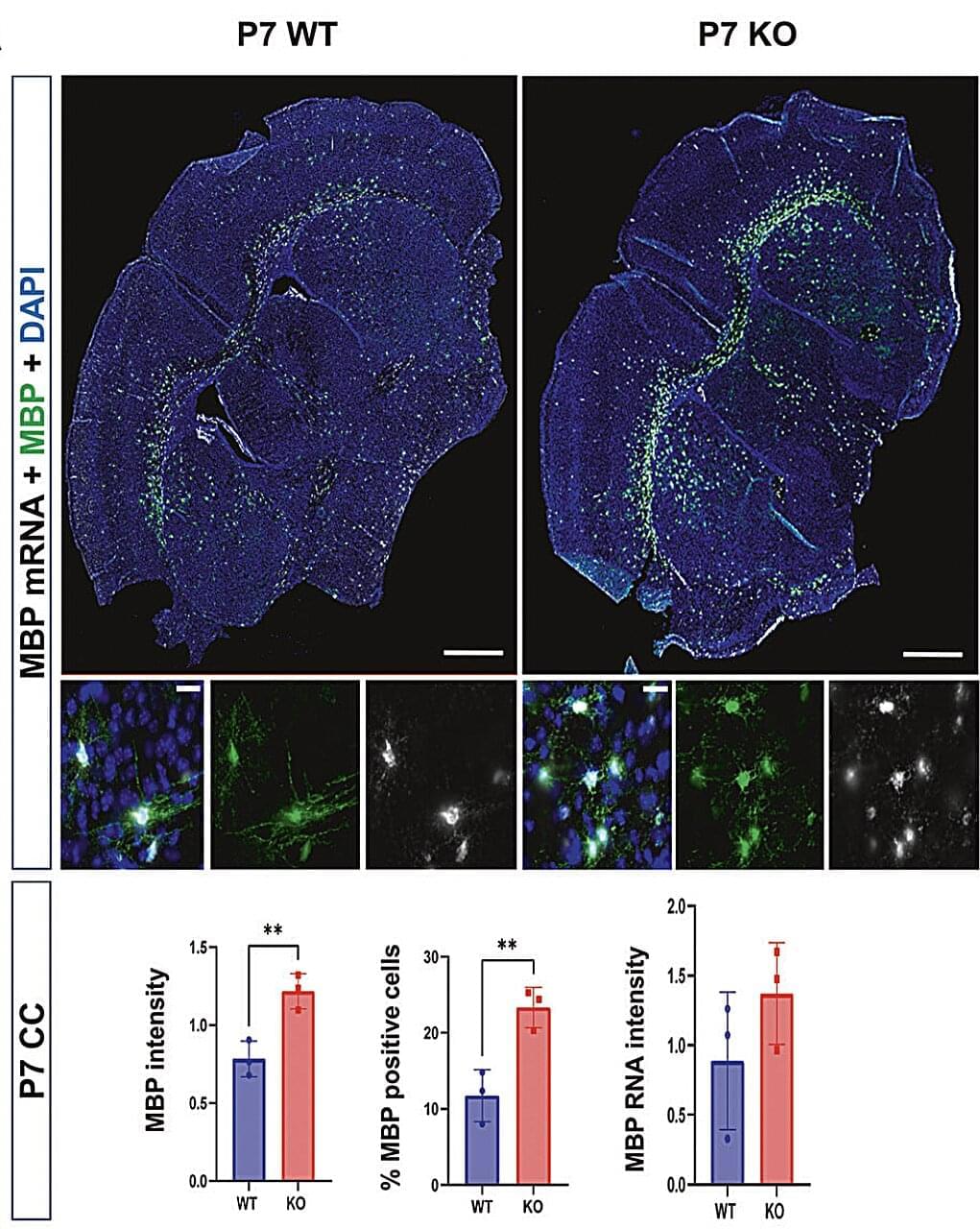
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by differences in communication, behavior and the processing of sensory information. Past research has shown that some individuals diagnosed with ASD exhibit specific genetic variants or differences in the regulation of genes.
In some patients, the Shank3 gene was found to be mutated, partially or fully deleted, or not expressed as much. This gene is known to support the creation of junctions at which connected neurons communicate with each other, known as synapses.
Past findings suggest that people diagnosed with ASD who exhibit variants in Shank3 also present abnormalities in the volume, structure and function of white matter. White matter is a brain region filled with a fatty substance known as myelin, which insulates nerves and allows signals to travel faster within the nervous system.