Using DNA and proteins, scientists have created new synthetic cells that act like living cells. Blurring the line between artificial and living materials, these cells can be reprogrammed to perform multiple functions, opening the door to new synthetic biology tech that goes beyond nature’s abilities.
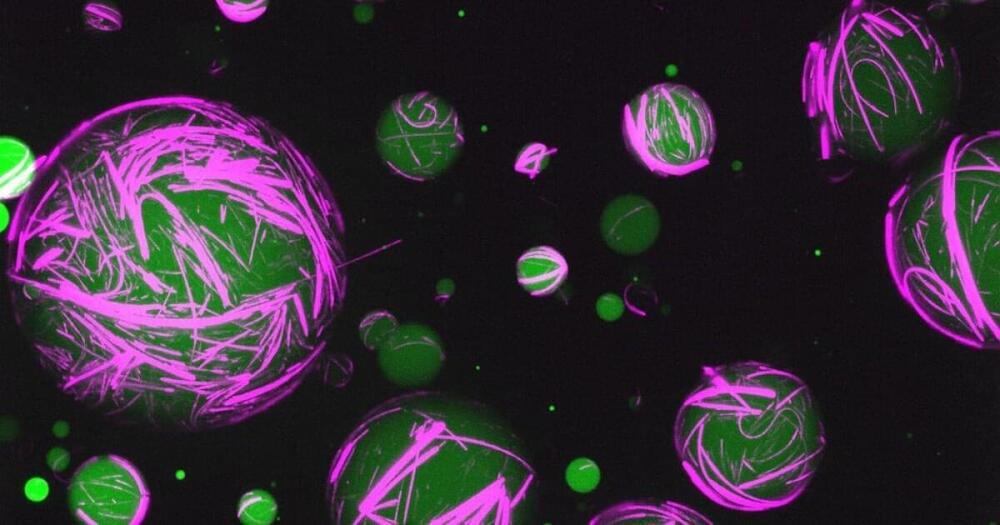
Cells get their structure and stability from their cytoskeleton, a crosslinked framework of proteins that encases and protects other components. Depending on the type of cell, this cytoskeleton can be flexible to different degrees and respond in different ways to their environment, giving cells their specialized abilities.
For the new study, scientists from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill developed synthetic, self-assembling cytoskeletons, built out of DNA, peptides and other genetic material.