However, more recent research suggests there are likely countless other possibilities for how life might emerge through potential chemical combinations. As the British chemist Lee Cronin, the American theoretical physicist Sara Walker and others have recently argued, seeking near-miraculous coincidences of chemistry can narrow our ability to find other processes meaningful to life. In fact, most chemical reactions, whether they take place on Earth or elsewhere in the Universe, are not connected to life. Chemistry alone is not enough to identify whether something is alive, which is why researchers seeking the origin of life must use other methods to make accurate judgments.
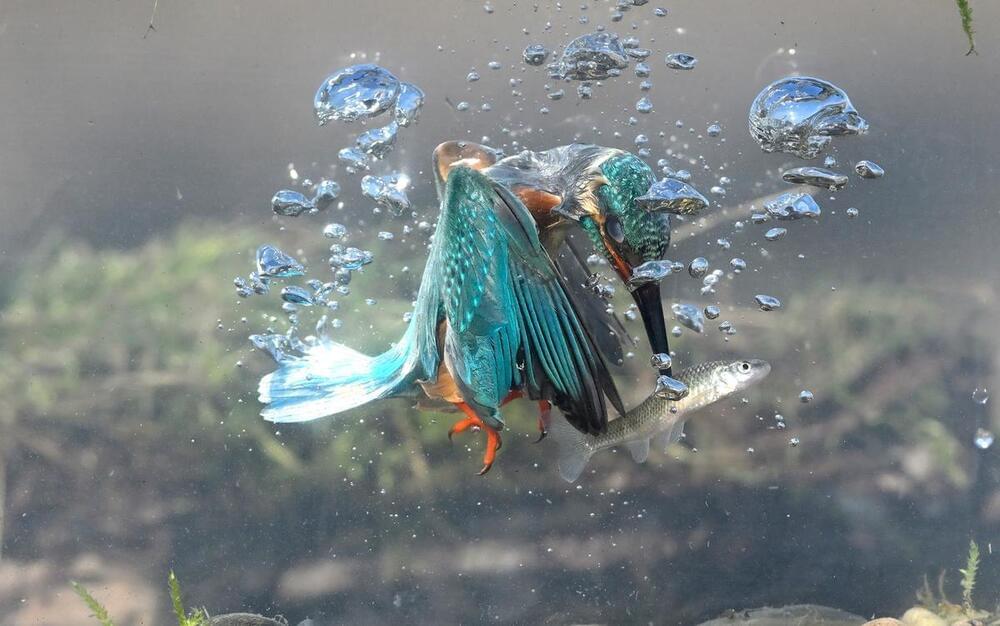
Today, ‘adaptive function’ is the primary criterion for identifying the right kinds of biotic chemistry that give rise to life, as the theoretical biologist Michael Lachmann (our colleague at the Santa Fe Institute) likes to point out. In the sciences, adaptive function refers to an organism’s capacity to biologically change, evolve or, put another way, solve problems. ‘Problem-solving’ may seem more closely related to the domains of society, culture and technology than to the domain of biology. We might think of the problem of migrating to new islands, which was solved when humans learned to navigate ocean currents, or the problem of plotting trajectories, which our species solved by learning to calculate angles, or even the problem of shelter, which we solved by building homes. But genetic evolution also involves problem-solving. Insect wings solve the ‘problem’ of flight. Optical lenses that focus light solve the ‘problem’ of vision. And the kidneys solve the ‘problem’ of filtering blood. This kind of biological problem-solving – an outcome of natural selection and genetic drift – is conventionally called ‘adaptation’. Though it is crucial to the evolution of life, new research suggests it may also be crucial to the origins of life.
This problem-solving perspective is radically altering our knowledge of the Universe. Life is starting to look a lot less like an outcome of chemistry and physics, and more like a computational process.