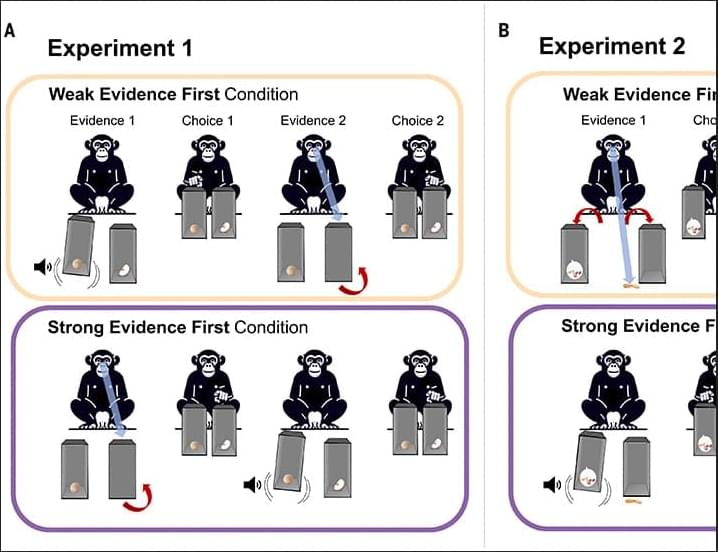
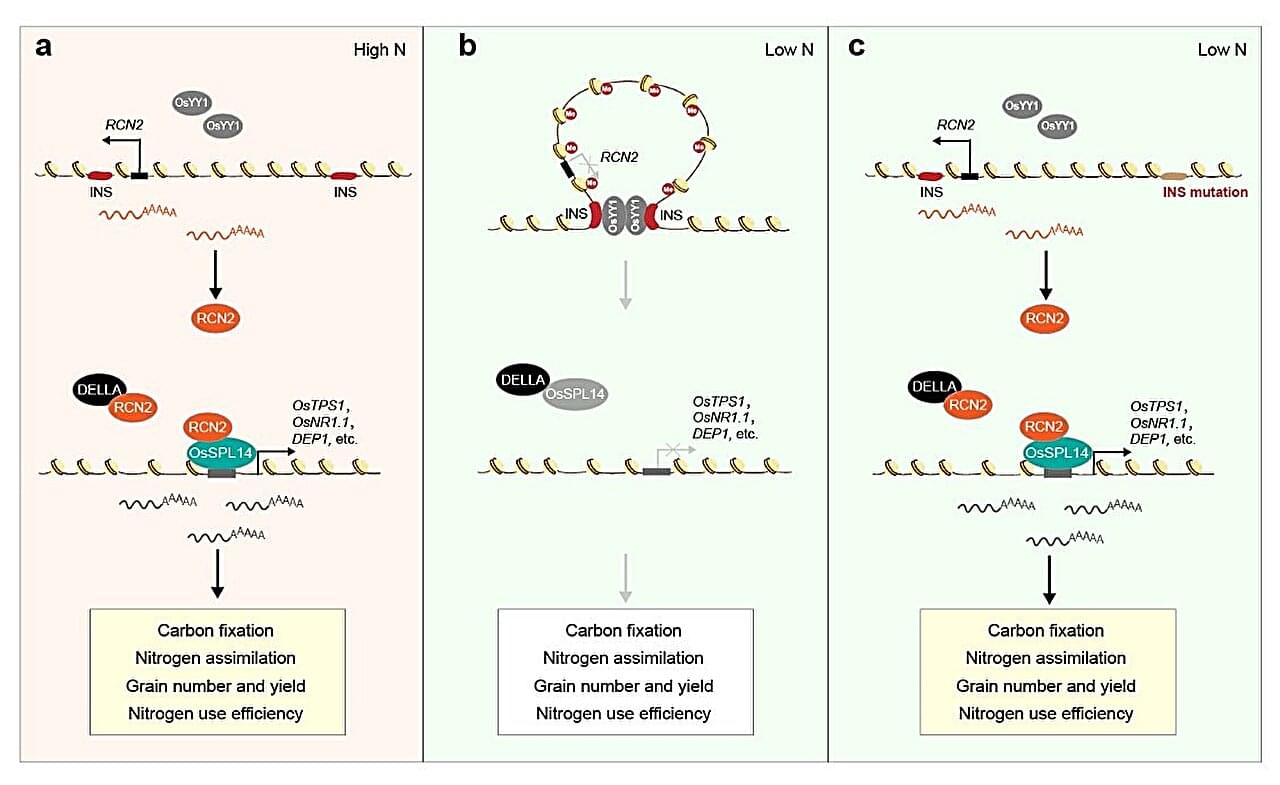
The study, titled “,” was conducted by a large research team that included UC Berkeley Psychology Postdoctoral Researcher Emily Sanford, UC Berkeley Psychology Professor Jan Engelmann and Utrecht University Psychology Professor Hanna Schleihauf. Their findings showed that chimpanzees — like humans — can change their minds based on the strength of available evidence, a key feature of rational thought.
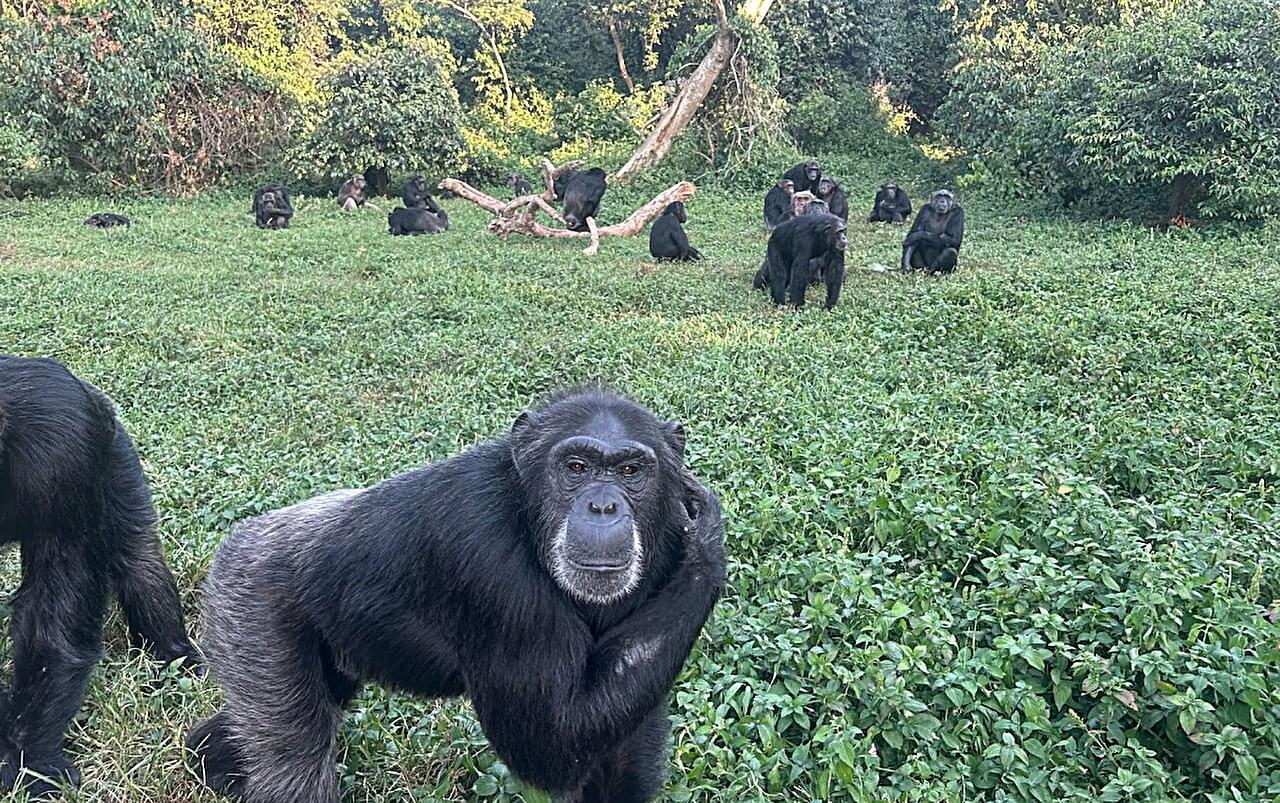
Working at the Ngamba Island Chimpanzee Sanctuary in Uganda, the researchers presented chimps with two boxes, one containing food. Initially, the animals received a clue suggesting which box held the reward. Later, they were given stronger evidence pointing to the other box. The chimps frequently switched their choices in response to the new clues.
“Chimpanzees were able to revise their beliefs when better evidence became available,” said Sanford, who is a researcher in the UC Berkeley Social Origins Lab. “This kind of flexible reasoning is something we often associate with 4-year-old children. It was exciting to show that chimps can do this too.”
To ensure the findings reflected genuine reasoning rather than instinct, the team incorporated tightly controlled experiments and computational modeling. These analyses ruled out simpler explanations, such as the chimps favoring the latest signal (recency bias) or reacting to the most obvious cue. The models confirmed that the chimps’ decision-making aligned with rational strategies of belief revision.
“We recorded their first choice, then their second, and compared whether they revised their beliefs,” Sanford said. “We also used computational models to test how their choices matched up with various reasoning strategies.”
The study challenges the traditional view that rationality — the ability to form and revise beliefs based on evidence — is exclusive to humans.
“The difference between humans and chimpanzees isn’t a categorical leap. It’s more like a continuum,” Sanford said.