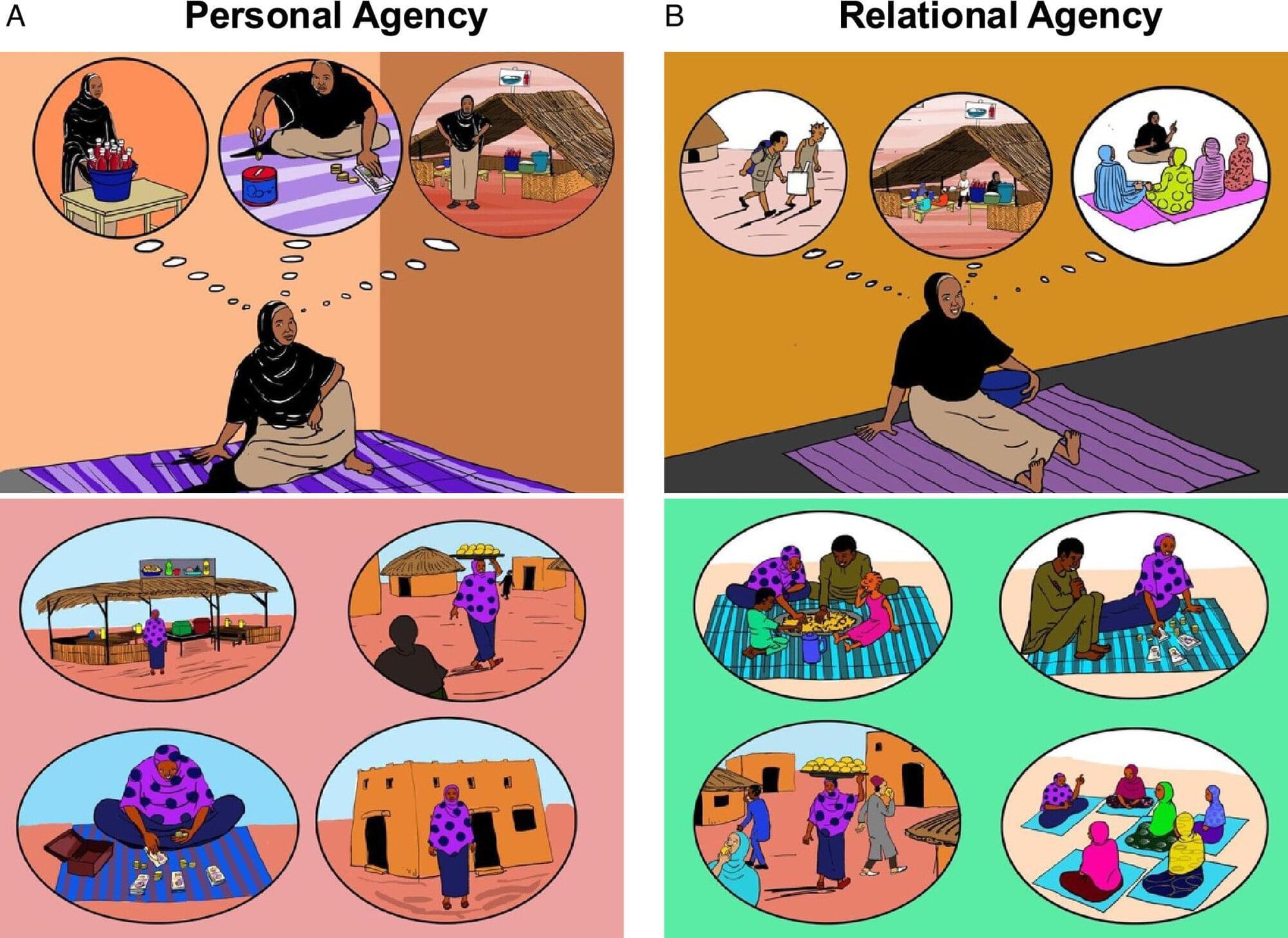
Most poverty-fighting efforts focus on meeting basic material needs, such as food and shelter. But this overlooks the psychological and cultural factors that shape how people take action in their lives.
University of Michigan researchers found that psychosocial programs designed to support women’s agency in Niger, West Africa, were effective in promoting women’s economic empowerment when grounded in local values—such as social harmony, respectfulness and collective progress—but not a Western-style program grounded in individual ambition.
The new study highlights how culturally attuned approaches to empowerment can offer a powerful pathway for reducing global poverty. The research, published in the latest issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, introduces a “culturally wise” approach: psychosocial programs that honor diverse worldviews and community values.