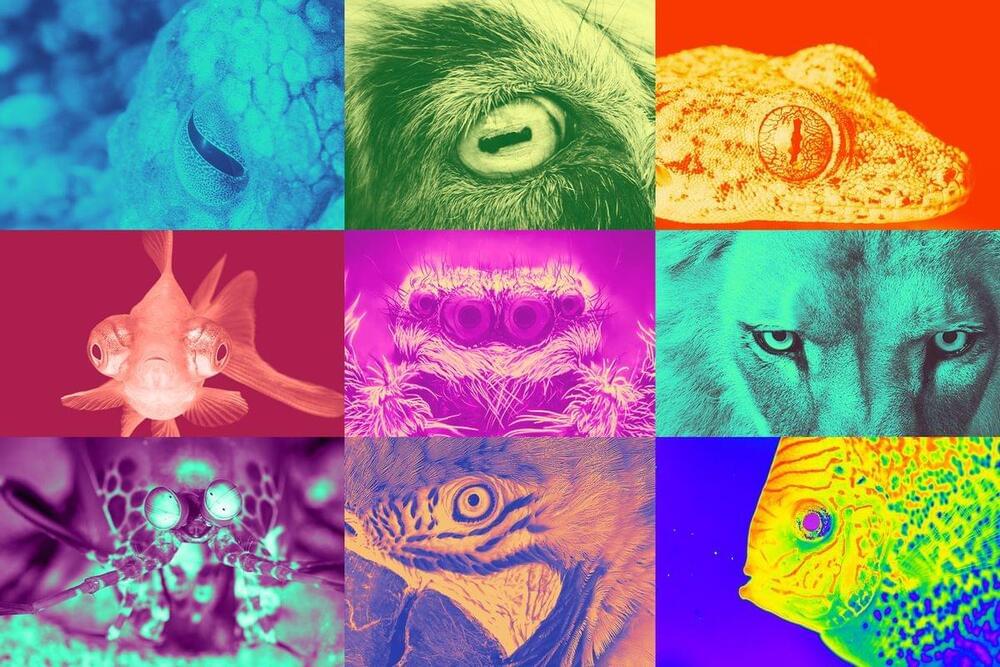
Evolution has produced many different eyes relatively quickly. Here’s how, and why, nature keeps evolving eyes.




The GPT phenomenon and the future of humanity in the face of advances in Artificial Intelligence.
The Age of Artificial Intelligence is an increasingly present reality in our daily lives. With the rise of technologies such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), the possibility of creating machines capable of performing tasks that were previously exclusive to humans has emerged.
One of these technologies is the Generative Pre-trained Transformer, better known as GPT. It’s the Large Language Model (LLM) developed by OpenAI.
OpenAI was founded in San Francisco, California in 2015 by Sam Altman, Reid Hoffman, Jessica Livingston, Elon Musk, Ilya Sutskever, Peter Thiel, among others, who collectively pledged $1 billion. Musk resigned from the board in 2018, but continued to be a donor to the project.
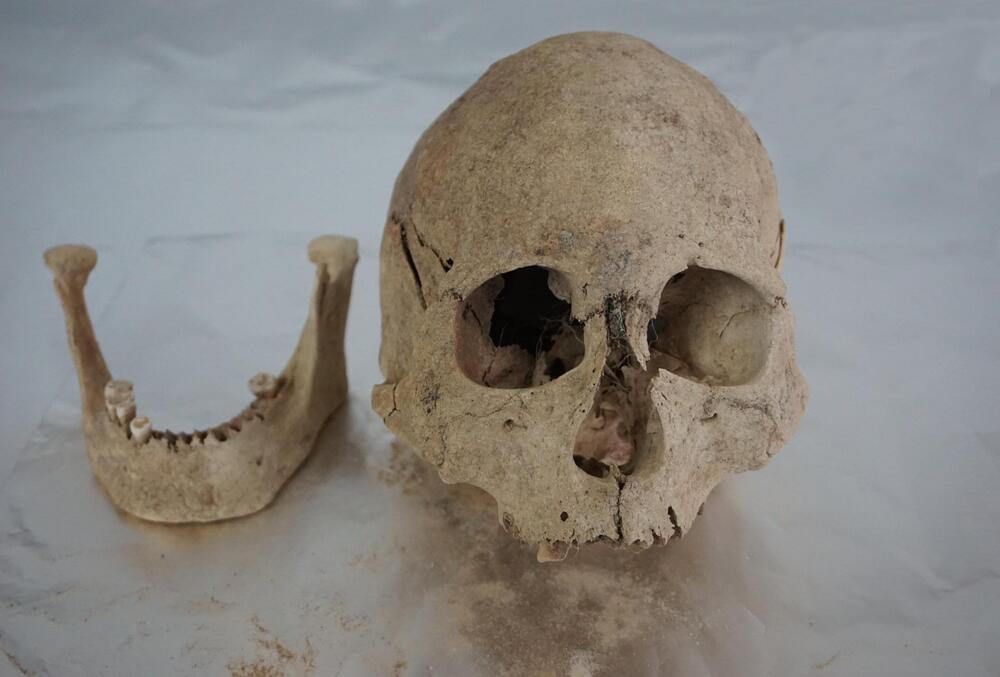
The Tibetan Plateau, the highest and largest plateau above sea level, is one of the harshest environments settled by humans. It has a cold and arid environment and its elevation often surpasses 4,000 meters above sea level (masl). The plateau covers a wide expanse of Asia—approximately 2.5 million square kilometers—and is home to over 7 million people, primarily belonging to the Tibetan and Sherpa ethnic groups.
However, our understanding of their origins and history on the plateau is patchy. Despite a rich archaeological context spanning the plateau, sampling of DNA from ancient humans has been limited to a thin slice of the southwestern plateau in the Himalayas.
Now, a study published in Science Advances led by Prof. Fu Qiaomei from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has filled this gap by sequencing the genomes of 89 ancient humans dating back to 5,100 BP from 29 archaeological sites spanning the Tibetan Plateau.
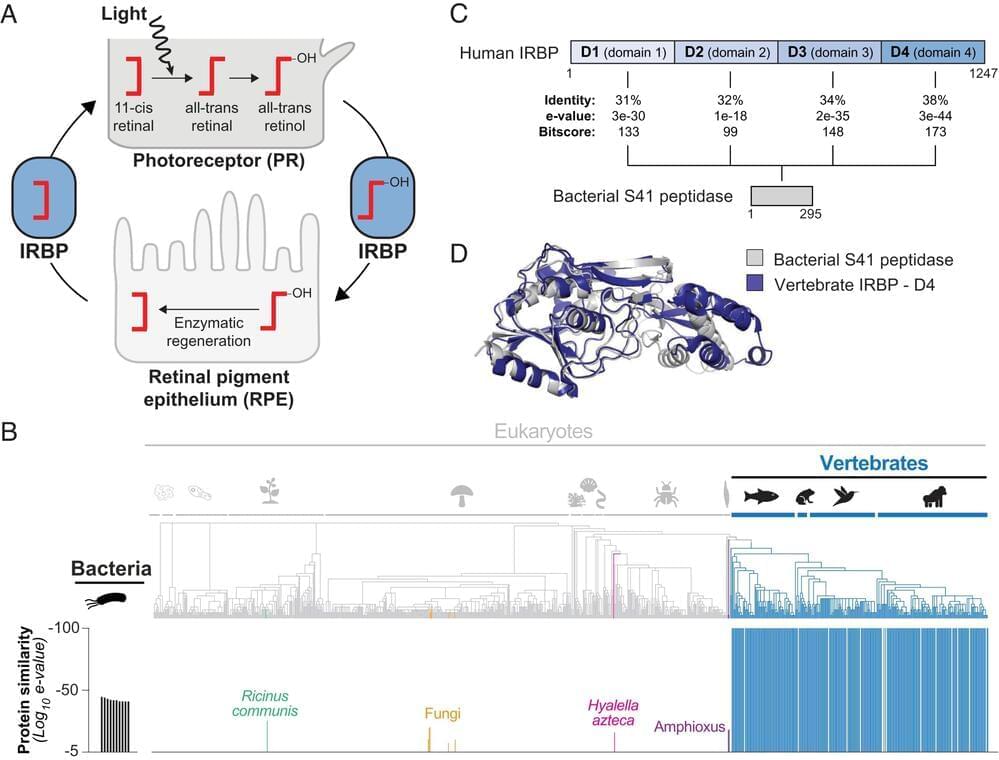
A group of molecular and chemical biologists at the University of California, San Diego, has found possible evidence of interdomain horizontal gene transfer leading to the development of the eye in vertebrates. In their study, reported in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Chinmay Kalluraya, Alexander Weitzel, Brian Tsu and Matthew Daugherty used the IQ-TREE software program to trace the evolutionary history of genes associated with vision.
Ever since scientists proved that humans, along with other animals, developed due to evolutionary processes, one problem has stood out—how could evolution possibly account for the development of something as complicated as the eyeball? Even Charles Darwin was said to be stumped by the question. In recent times, this seeming conundrum has been used by some groups as a means to discredit evolutionary theory altogether. In this new effort, the team in California sought to answer the question once and for all.
Their work began with the idea that vision in vertebrates may have got its start by using light-sensitive genes transferred from microbes. To find out if that might be the case, the team submitted likely human gene candidates to the IQ-TREE program to look for similar genetic sequences in other creatures, most specifically, microbes.
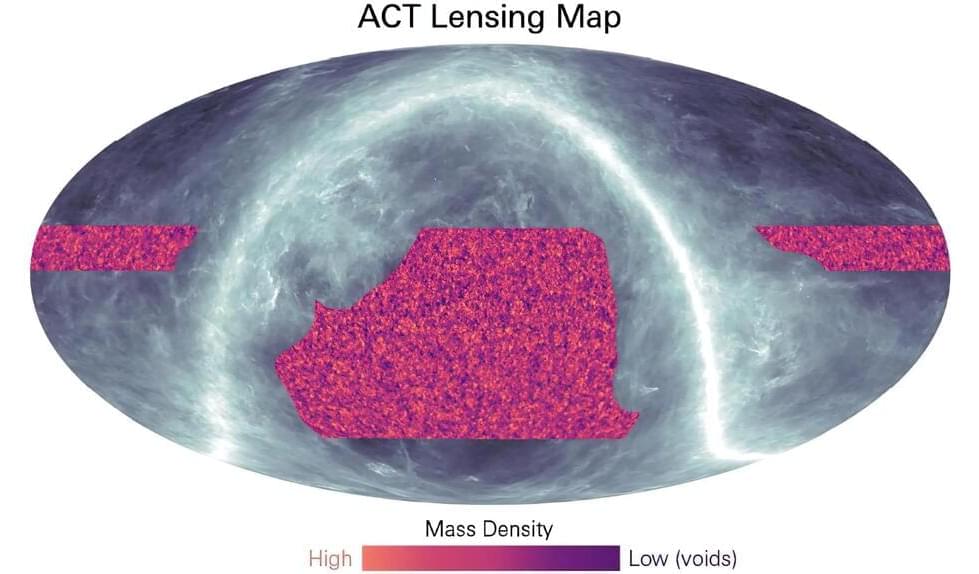
Research by the Atacama Cosmology Telescope collaboration has culminated in a significant breakthrough in understanding the evolution of the universe.
For millennia, humans have been fascinated by the mysteries of the cosmos.
Unlike ancient philosophers imagining the universe’s origins, modern cosmologists use quantitative tools to gain insights into its evolution and structure. Modern cosmology dates back to the early 20th century, with the development of Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
(Visit: http://www.uctv.tv/) Animal development is directed by a genetic toolkit shared by all animals — from fruit flies to frogs to human beings — rather than different animals having different genetic toolkits. UCLA Professor of Biological Chemistry Edward De Robertis explains that the field of evolutionary development (or Evo-Devo) seeks to understand how so many beautiful animal forms evolved through the use of the original genetic toolkit of the last common ancestor of all animals, urbilateria, which existed at least 560 million years ago. Recorded on 10.25.2016. Series: “UCLA Faculty Research Lectures” [12/2016] [Science] [Show ID: 31409].

The remarkable physicochemical properties of the natural nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, define modern biology at the molecular level and are widely believed to have been central to life’s origins. However, their ability to form repositories of information as well as functional structures such as ligands (aptamers) and catalysts (ribozymes/DNAzymes) is not unique. A range of nonnatural alternatives, collectively termed xeno nucleic acids (XNAs), are also capable of supporting genetic information storage and propagation as well as evolution. This gives rise to a new field of “synthetic genetics,” which seeks to expand the nucleic acid chemical toolbox for applications in both biotechnology and molecular medicine. In this review, we outline XNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase engineering as a key enabling technology and summarize the application of “synthetic genetics” to the development of aptamers, enzymes, and nanostructures.
Copyright © 2019 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.