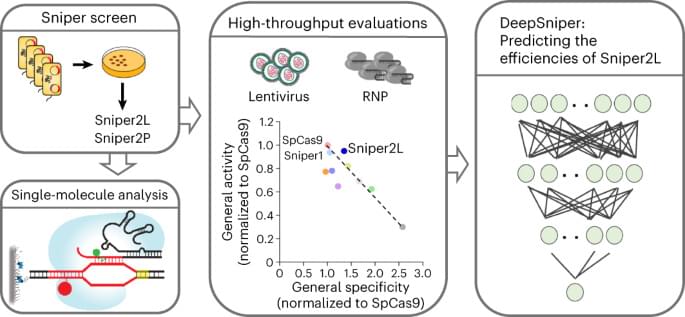
A trio of evolutionary biologists, two with Carleton University, the other with Seoul National University, has apparently solved the paradox of aposematism—how animals managed to evolve with bright colors to warn predators of their toxic nature. In their paper study, published in the journal Science, Karl Loeffler-Henry, Changku Kang and Thomas Sherratt, conducted an analysis of the family tree of over 1,000 frog, salamander and newt species.
For many years, evolutionary biologists have puzzled over the seeming paradox of aposematism, in which animals such as frogs develop bright colors to warn potential predators that eating them will make them sick or even kill them. How could such colors have evolved? Animals that stand out tend to be the first caught and eaten, preventing the evolution of even brighter colors from occurring. In this new effort, the research team set out to solve this riddle.
The work involved analyzing the family tree of 1,100 species of frogs, salamanders and newts, looking for evidence of evolution of aposematism in a new way—by breaking them down into more categories than previous efforts—five instead of two: conspicuous, cryptic, partially conspicuous, fully conspicuous and polymorphic.