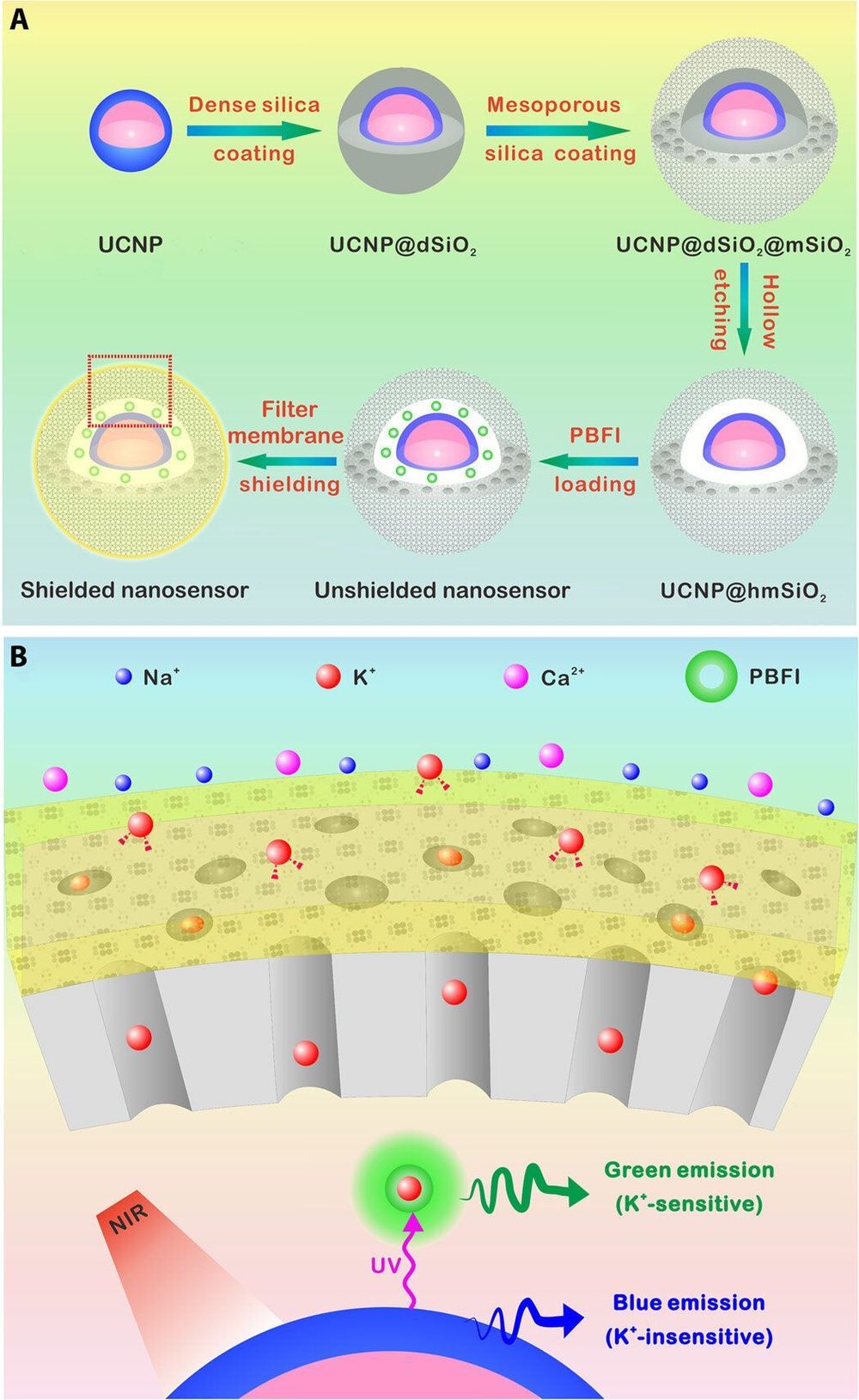
Researchers have developed a number of potassium ion (K+) probes to detect fluctuating K+ concentrations during a variety of biological processes. However, such probes are not sensitive enough to detect physiological fluctuations in living animals and it is not easy to monitor deep tissues with short-wavelength excitations that are in use so far. In a new report, Jianan Liu and a team of researchers in neuroscience, chemistry, and molecular engineering in China, describe a highly sensitive and selective nanosensor for near infrared (NIR) K+ ion imaging in living cells and animals. The team constructed the nanosensor by encapsulating upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and a commercial potassium ion indicator in the hollow cavity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and coated them with a K+ selective filter membrane. The membrane adsorbed K+ from the medium and filtered away any interfering cations. In its mechanism of action, UCNPs converted NIR to ultraviolet (UV) light to excite the potassium ion indicator and detect fluctuating potassium ion concentrations in cultured cells and in animal models of disease including mice and zebrafish larvae. The results are now published on Science Advances.
The most abundant intracellular cation potassium (K+) is extremely crucial in a variety of biological processes including neural transmission, heartbeat, muscle contraction and kidney function. Variations in the intracellular or extracellular K+ concentration (referred herein as [K+]) suggest abnormal physiological functions including heart dysfunction, cancer, and diabetes. As a result, researchers are keen to develop effective strategies to monitor the dynamics of [K+] fluctuations, specifically with direct optical imaging.
Most existing probes are not sensitive to K+ detection under physiological conditions and cannot differentiate fluctuations between [K+] and the accompanying sodium ion ([Na+]) during transmembrane transport in the Na+/K+ pumps. While fluorescence lifetime imaging can distinguish K+ and Na+ in water solution, the method requires specialized instruments. Most K+ sensors are also activated with short wavelength light including ultraviolet (UV) or visible light—leading to significant scattering and limited penetration depth when examining living tissues. In contrast, the proposed near-infrared (NIR) imaging technique will offer unique advantages during deep tissue imaging as a plausible alternative.