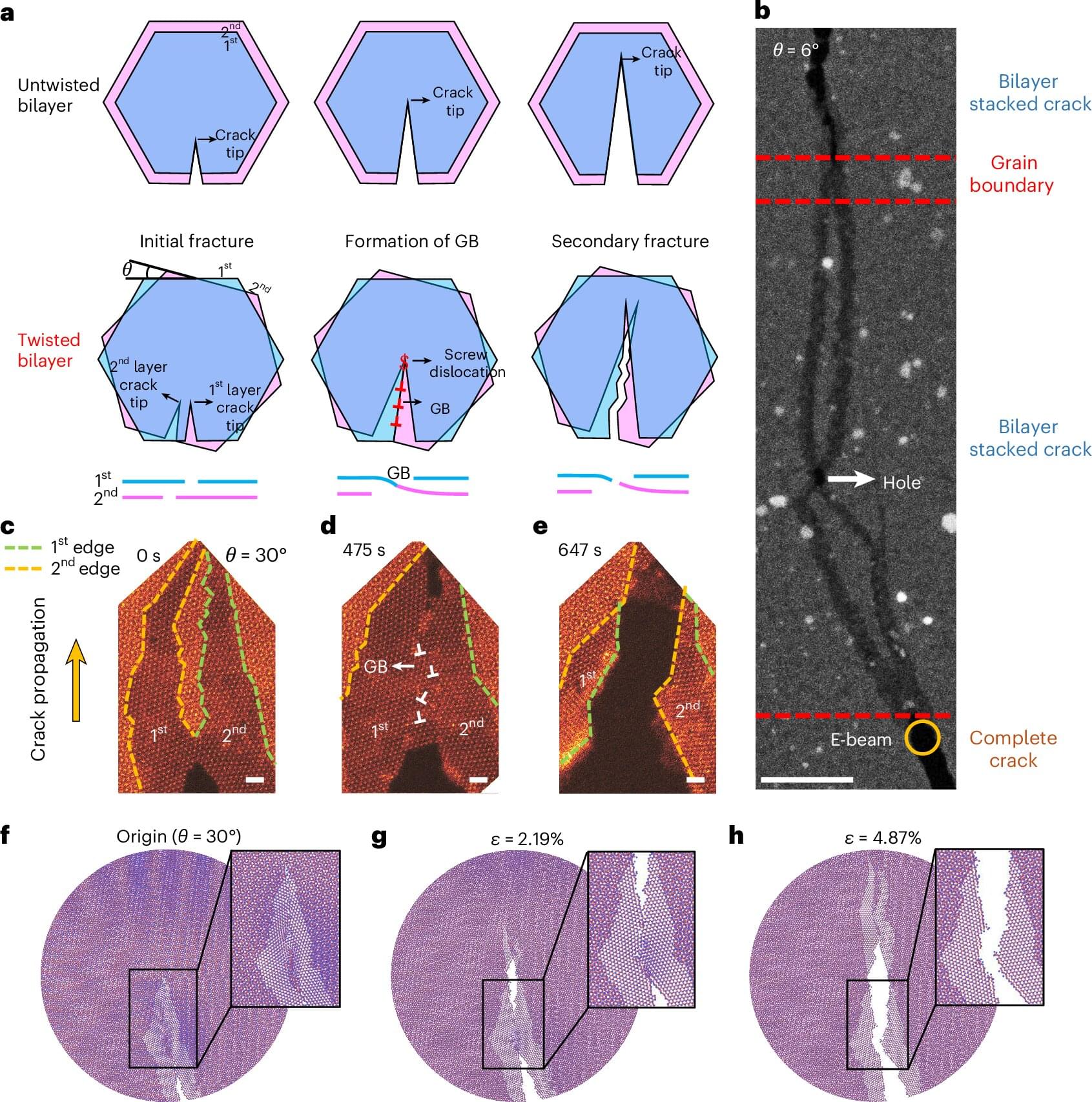
The mechanical strength and toughness of engineering materials are often mutually exclusive, posing challenges for material design and selection. To address this, a research team from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) has uncovered an innovative strategy: by simply twisting the layers of 2D materials, they can enhance toughness without compromising material’s strength.
This breakthrough facilitates the design of strong and tough new 2D materials, promoting their broader applications in photonic and electronic devices. The findings have been published in Nature Materials.
While 2D materials often exhibit exceptional strength, they are extremely brittle. Fractures in materials are also typically irreversible. These attributes limit the use of 2D materials in devices that require repeated deformation, such as high-power devices, flexible electronics and wearables.