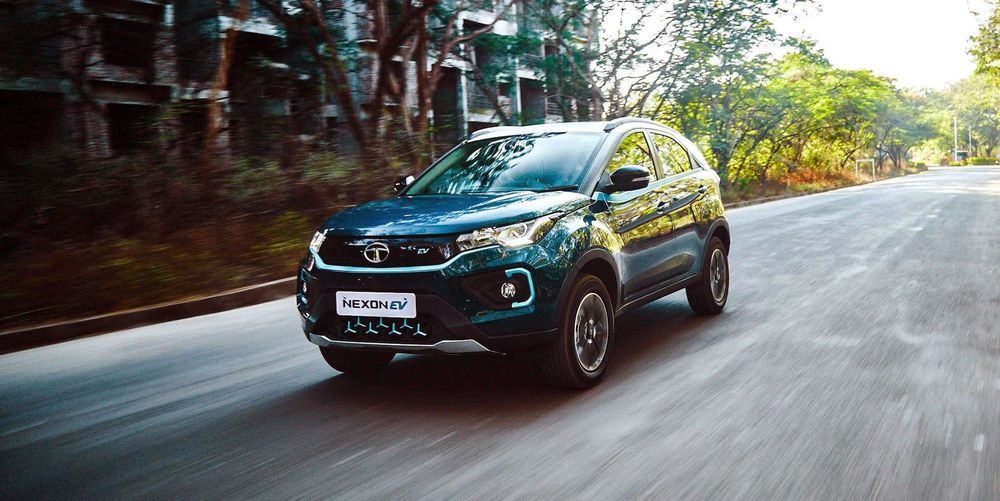
The Tata Nexon EV’s approach – reduced range, less power, and basic amenities – could bring the price down to $14,000 after incentives.



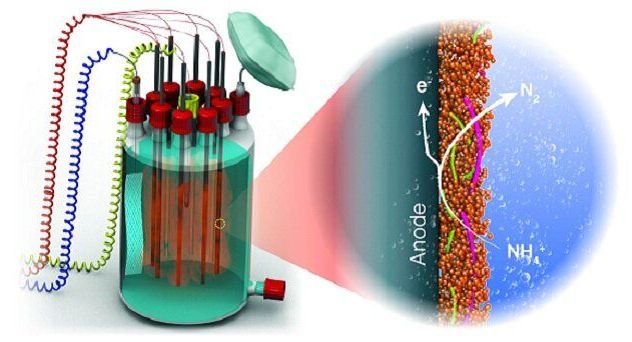
A type of anaerobic bacteria responsible for more than 50 percent of nitrogen loss from marine environments has been shown to use solid-state matter present outside their cells for respiration. The finding by KAUST researchers adds to knowledge of the global nitrogen cycle and has important energy-saving potential for wastewater treatment.
Living organisms use oxidation/reduction reactions to harvest the energy they need for survival. This involves the transfer of electrons from an electron donor to an electron acceptor with energy generation. In humans, electrons are released from the food we digest and accepted by soluble oxygen inside our cells. But in many bacteria, other strategies are used for oxidation/reduction, with different types of electron donors and acceptors.
Anammox are anaerobic bacteria found in oxygen-lacking marine and freshwater environments, such as sediments. They derive energy by using ammonium as their electron donor and intracellular soluble nitrite as the acceptor, with the release of nitrogen gas—or so scientists thought.
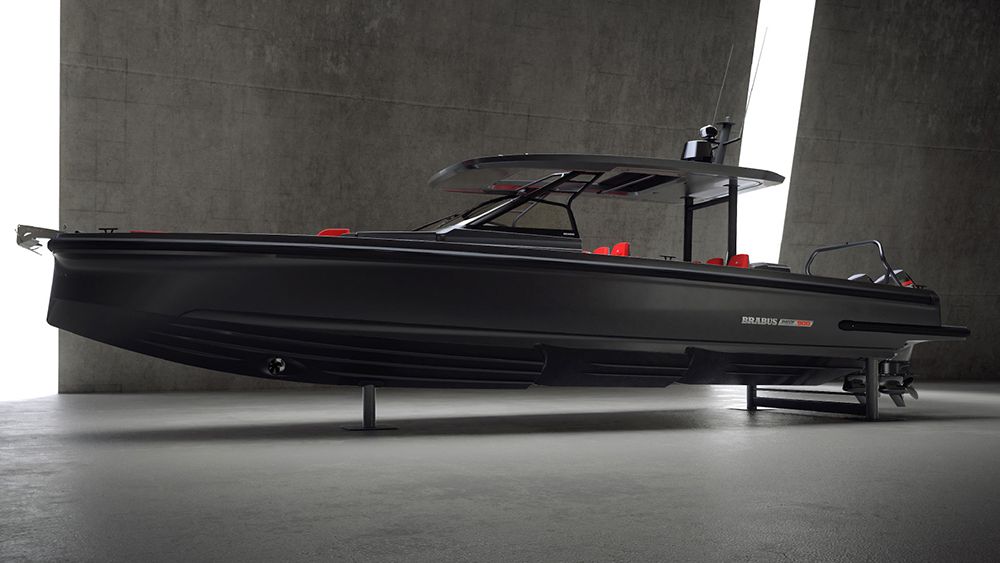

Packed with twin 450 hp outboard engines, the speedster is capable of cutting through the seas at a blistering 60 knots and its engine’s power-to-weight ratio represents the best in class. In fact, these motors tip the scale at just 705 lbs—some 300 lbs less than competing models—which gives the svelte vessel 40 percent more torque than its competitors.
Hydrogen’s impressive energy density offers some compelling advantages that could see it make a huge difference in the electric aviation and eVTOL sectors, as well as in renewable energy, where it’s a lightweight and transportable, if not particularly efficient, way to store clean energy that’s not necessarily generated where or when you need it. It’s also being pushed as a means of exporting green energy, and Japan and Korea in particular are investing heavily in the idea of a hydrogen energy economy powering everything from vehicles to homes and industry.
For this to come about in a globally positive way, it’s imperative that clean, green hydrogen production becomes cheaper, because right now, the easiest and cheapest ways to get yourself a tank full of hydrogen are things like steam reforming, which produces up to 12 times as much carbon dioxide as it does hydrogen by weight.
Green, renewable production methods are thus hot topics for researchers and industry, and a new breakthrough from scientists at the Australian National University (ANU) could make a significant contribution.
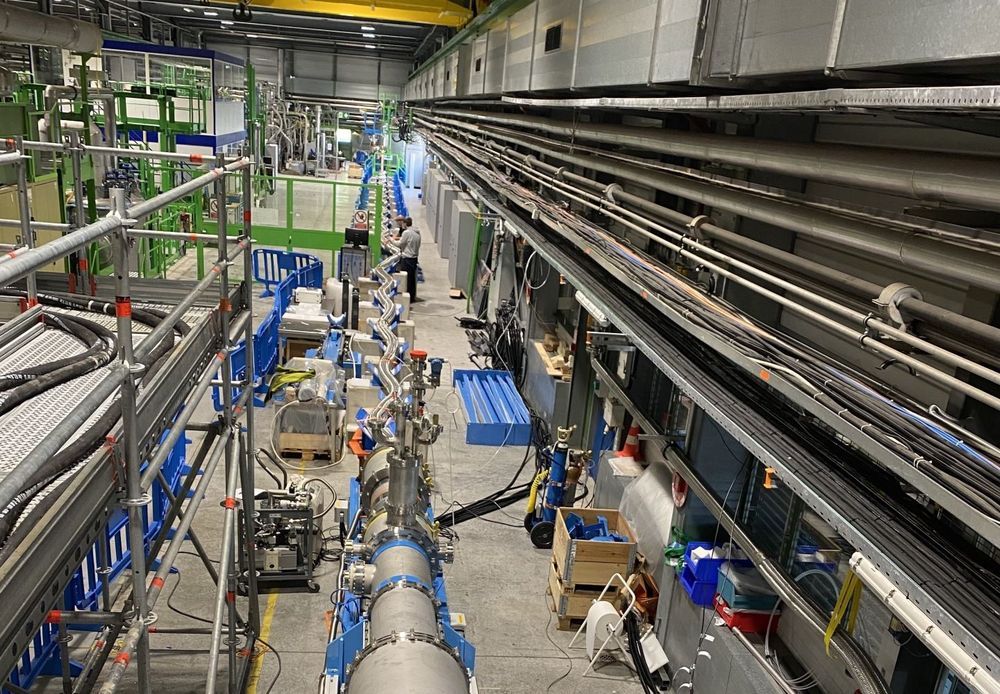

Intensity is rising at CERN. In the superconducting equipment testing hall, an innovative transmission line has set a new record for the transport of electricity. The link, which is 60 metres long, has transported a total of 54 000 amperes (54 kA, or 27 kA in either direction). “It is the most powerful electrical transmission line built and operated to date!” says Amalia Ballarino, the designer and project leader.
The line has been developed for the High-Luminosity LHC (HL-LHC), the accelerator that will succeed the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) and is scheduled to start up at the end of 2027. Links like this one will connect the HL-LHC’s magnets to the power converters that supply them.
The secret to the new line’s power can be summarised in one word: superconductivity.



