The Philippines’ traditional three-hulled boat is being redesigned, to draw its power not from fossil fuels, but from the energy of the waves.




As levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide continue to climb, scientists are looking for new ways of breaking down CO2 molecules to make useful carbon-based fuels, chemicals and other products. Now, a team of Brown University researchers has found a way to fine-tune a copper catalyst to produce complex hydrocarbons—known as C2-plus products—from CO2 with remarkable efficiency.
In a study published in Nature Communications, the researchers report a catalyst that can produce C2-plus compounds with up to 72% faradaic efficiency (a measure of how efficiently electrical energy is used to convert carbon dioxide into chemical reaction products). That’s far better than the reported efficiencies of other catalysts for C2-plus reactions, the researchers say. And the preparation process can be scaled up to an industrial level fairly easily, which gives the new catalyst potential for use in large-scale CO2 recycling efforts.
“There had been reports in the literature of all kinds of different treatments for copper that could produce these C2-plus with a range of different efficiencies,” said Tayhas Palmore, the a professor of engineering at Brown who co-authored the paper with Ph.D. student Taehee Kim. “What Taehee did was a set of experiments to unravel what each of these treatment steps was actually doing to the catalyst in terms of reactivity, which pointed the way to optimizing a catalyst for these multi-carbon compounds.”
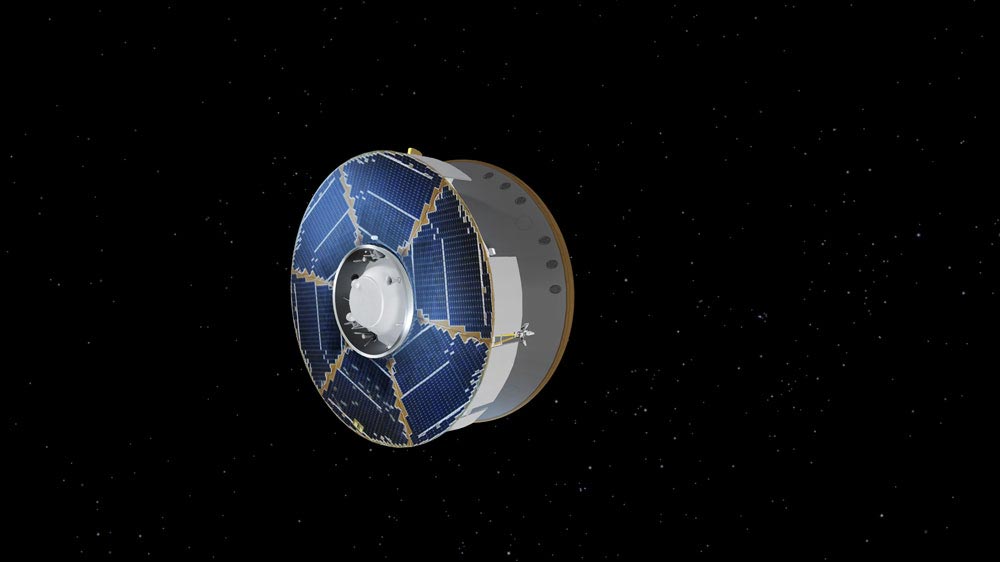

Headed to the Red Planet with the Perseverance rover, the pioneering helicopter is powered up for the first time in interplanetary space as part of a systems check.
NASAs Ingenuity Mars Helicopter received a checkout and recharge of its power system on Friday, August 7, one week into its near seven-month journey to Mars with the Perseverance rover. This marks the first time the helicopter has been powered up and its batteries have been charged in the space environment.
During the eight-hour operation, the performance of the rotorcraft’s six lithium-ion batteries was analyzed as the team brought their charge level up to 35%. The project has determined a low charge state is optimal for battery health during the cruise to Mars.

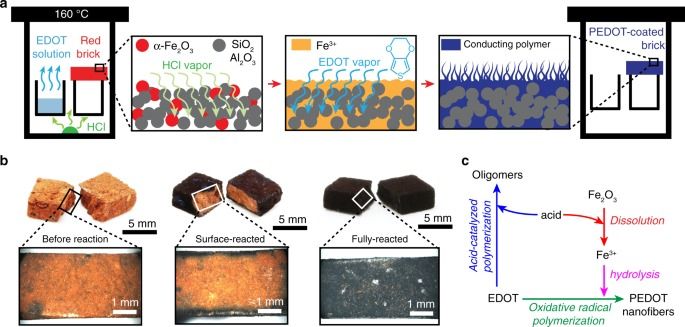
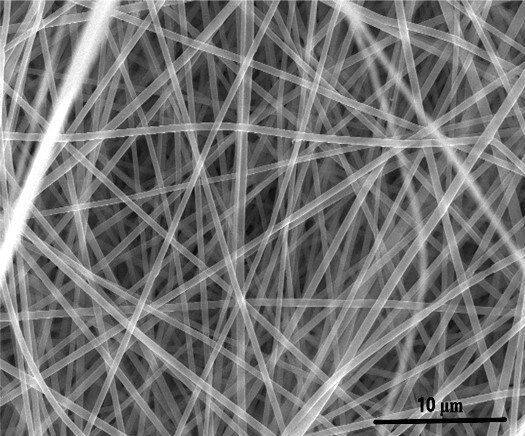
Fired brick is a universal building material, produced by thousand-year-old technology, that throughout history has seldom served any other purpose. Here, we develop a scalable, cost-effective and versatile chemical synthesis using a fired brick to control oxidative radical polymerization and deposition of a nanofibrillar coating of the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT). A fired brick’s open microstructure, mechanical robustness and ~8 wt% α-Fe2O3 content afford an ideal substrate for developing electrochemical PEDOT electrodes and stationary supercapacitors that readily stack into modules. Five-minute epoxy serves as a waterproof case enabling the operation of our supercapacitors while submerged underwater and a gel electrolyte extends cycling stability to 10,000 cycles with ~90% capacitance retention.

Energy solutions company Hanwha Energy has completed its $212m hydrogen fuel cell power plant, located at the Daesan Industrial Complex in Seosan, South Korea.
Built by Hanwha Engineering & Construction, the plant is thought to be the largest industrial hydrogen fuel cell power plant globally, and the first to only use hydrogen recycled from petrochemical manufacturing.
The recycled hydrogen is supplied by the Hanwha Total Petrochemical plant located within the same Daesan Industrial Complex. Hanwha Total Petrochemical pumps the recycled hydrogen into the new power plant via underground pipes and feeds it directly into the fuel cells.

What if you could solve two of Earth’s biggest problems in one stroke? UC Riverside engineers have developed a way to recycle plastic waste, such as soda or water bottles, into a nanomaterial useful for energy storage.
Mihri and Cengiz Ozkan and their students have been working for years on creating improved energy storage materials from sustainable sources, such as glass bottles, beach sand, Silly Putty, and portabella mushrooms. Their latest success could reduce plastic pollution and hasten the transition to 100% clean energy.
“Thirty percent of the global car fleet is expected to be electric by 2040, and high cost of raw battery materials is a challenge,” said Mihri Ozkan, a professor of electrical engineering in UCR’s Marlan and Rosemary Bourns College of Engineering. “Using waste from landfill and upcycling plastic bottles could lower the total cost of batteries while making the battery production sustainable on top of eliminating plastic pollution worldwide.”

Researchers at Argonne National Laboratory say they’ve found a breakthrough way to recycle carbon dioxide into energy-rich ethanol fuel. The secret is an electrified catalyst made from copper and carbon, which the researchers say can be powered using low-cost off-peak or renewable energy. What results is a process that’s more than 90 percent effective, which they say is far higher than any similar existing process.
Northern Illinois University professor and participating Argonne researcher Tao Xu says the new catalyst isn’t just a single stop that can produce ethanol—it’s the first step down a possible long list of ways to turn carbon dioxide into other useful chemicals. Despite the obvious plenitude of carbon dioxide, recycling it effectively into new things has been hard because of how stable and chemically stubborn the molecules are.