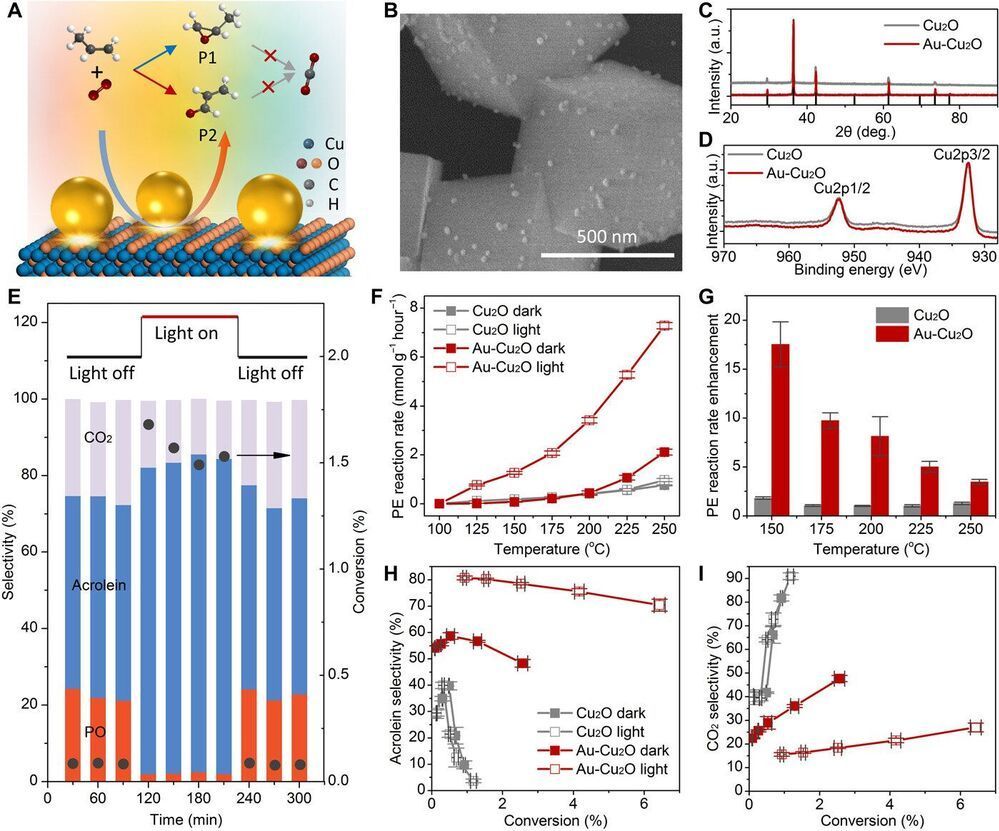
When optimizing catalysis in the lab, product selectivity and conversion efficiency are primary goals for materials scientists. Efficiency and selectivity are often mutually antagonistic, where high selectivity is accompanied by low efficiency and vice versa. Increasing the temperature can also change the reaction pathway. In a new report, Chao Zhan and a team of scientists in chemistry and chemical engineering at the Xiamen University in China and the University of California, Santa Barbara, U.S., constructed hierarchical plasmonic nanoreactors to show nonconfined thermal fields and electrons. The combined attributes uniquely coexisted in plasmonic nanostructures. The team regulated parallel reaction pathways for propylene partial oxidation and selectively produced acrolein during the experiments to form products that are different from thermal catalysis. The work described a strategy to optimize chemical processes and achieve high yields with high selectivity at lower temperature under visible light illumination. The work is now published on Science Advances.
Catalysts
Ideal catalytic processes can produce desired target products without undesirable side effects under cost-effective conditions, although such conditions are rarely achieved in practice. For instance, high efficiency and high selectivity are antagonistic goals, where a relatively high temperature is often necessary to overcome the large barrier of oxygen activation to achieve high reactant conversion. Increasing the functional temperature can also lead to overoxidized and therefore additional byproducts. As a result, researchers must compromise between selectivity and efficiency. For instance, a given molecule typically requires diverse catalysts to generate different products, where each catalyst has different efficiency and selectivity. To circumvent any limitations, they can use surface plasmons (SPs) to redistribute photons, electrons and heat energy in space and time.