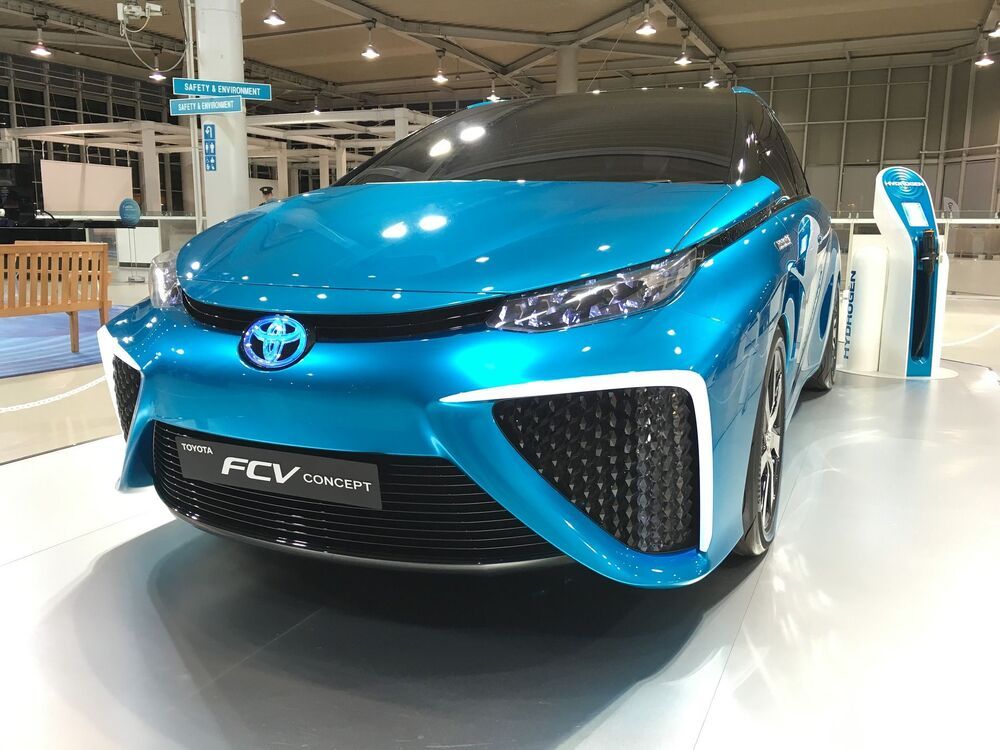
People are continually interested in creative ways to get rid of waste. The world has too much of it, so how could technology solve that problem by addressing another need? Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are an emerging possibility.
The processes used by many forward-thinking companies center on converting waste into hydrogen energy. Here’s a look at what the future may hold.
Waste-to-Energy Projects Are Happening