The power needed is so small, you could do this almost for free.’
Flying saucers are on their way to the Moon.
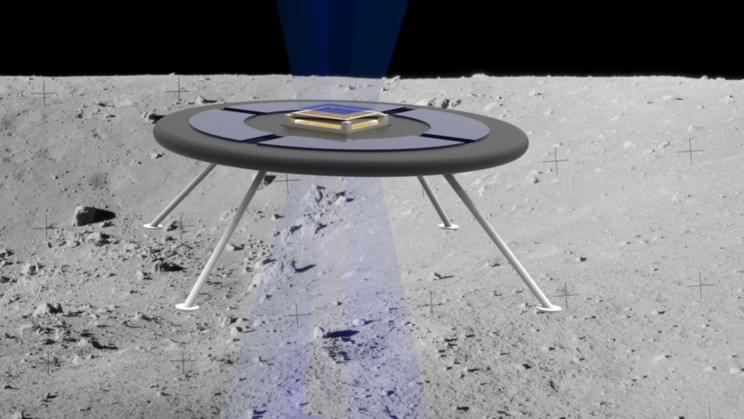
MIT scientists are developing a new concept for a circular hovering rover that levitates thanks to the moon’s natural electric field, a press statement reveals.
The new machines take advantage of the fact that airless bodies such as the moon and asteroids build up an electric field through direct exposure to the sun and their surrounding plasma. Such machines could be deployed on lucrative scouting missions on the surface of the moon as well as to nearby asteroids.
A new type of hovering spacecraft On a body as large as the moon, the surface charge is strong enough to power levitating machines — in fact, it has already been shown to levitate lunar dust up to a meter above the ground.
The MIT team’s levitating rover, which, in renders, looks remarkably like a flying saucer sending a beam down to the lunar surface, uses tiny ion beams to charge the vehicle and boost the surface’s natural surface charge. Small ion thrusters, called liquid ion sources, connect to a tank containing ionic liquid in the form of room-temperature molten salt. When the electric charge reaches the ionic liquid, its ions are charged and emitted downwards and out of the rover as a beam through the thrusters. The system’s disc shape maximizes the repulsive force between the rover and the ground, meaning that it needs very little power.
Full Story: