To meet ambitious targets, policymakers should overhaul regulation to incentivize creating transmission infrastructure that supports renewables. Continuing with the status quo could scupper the transition to Net Zero.


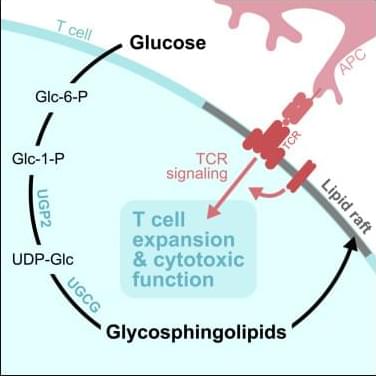
Glucose controls CD8+ T cell function.
The researchers demonstrate that in CD8+ effector T cells, glucose metabolism extends beyond energy production by fueling glycosphingolipid (GSL) biosynthesis, a pathway critical for T cell expansion and cytotoxic function.
The authors show that CD8+ effector T cells use glucose to synthesize uridine diphosphate-glucose (UDP-Glc), a precursor for glycogen, glycan, and GSL biosynthesis. Inhibiting GSL production impairs CD8+ T cell expansion upon pathogen challenge.
Mechanistically, we show that glucose-dependent GSL biosynthesis is required for plasma membrane lipid raft integrity and optimal T cell receptor (TCR) signaling. https://sciencemission.com/Glucose-dependent-glycosphingolipid-biosynthesis
Glucose is required for T cell proliferation and function, but its key metabolic fates in vivo are not well defined. Longo et al. demonstrate that in CD8+ effector T cells, glucose metabolism extends beyond energy production by fueling glycosphingolipid biosynthesis, a pathway critical for T cell expansion and cytotoxic function.
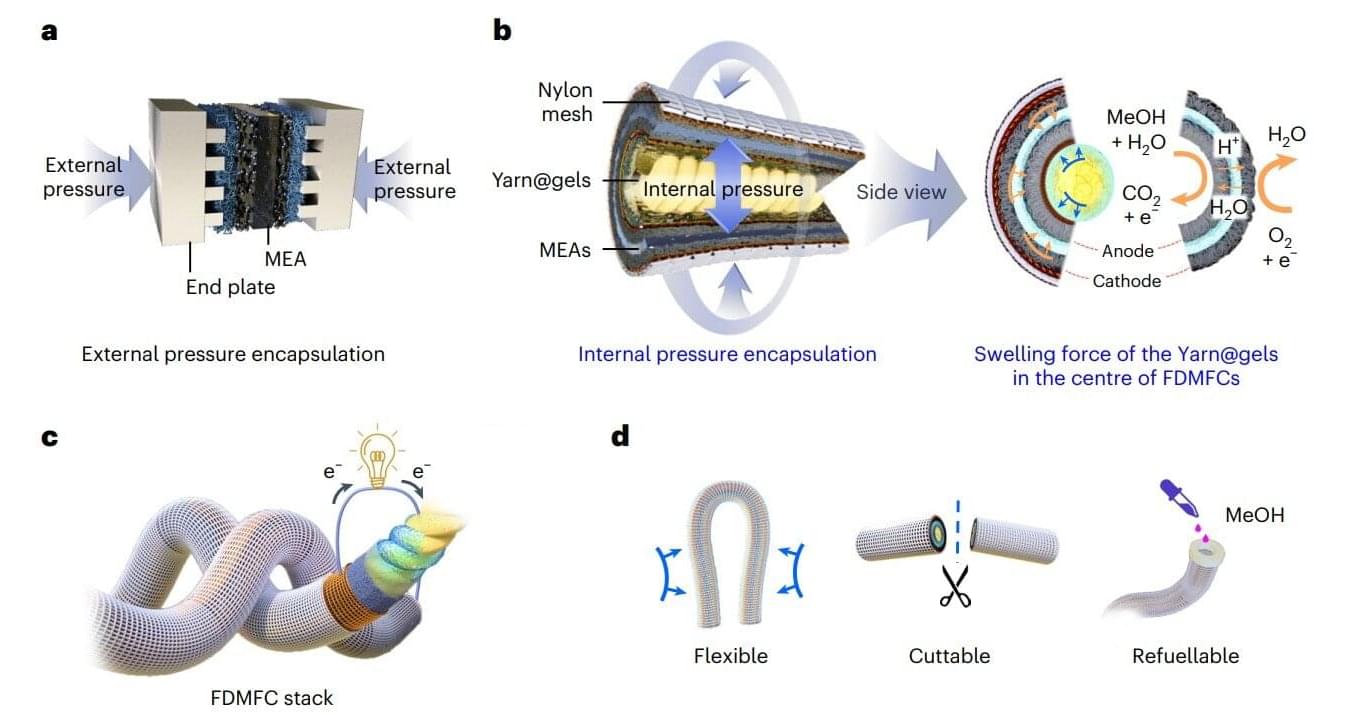
Cotton-based fiber fuel cells can now convert methanol into electricity while sustaining peak power density through 2,000 continuous flex cycles. This breakthrough paves the way for safe, high-performance power sources for flexible electronics and wearable devices.
Researchers at Soochow University developed fiber-shaped direct methanol fuel cells (FDMFCs) using gel-encapsulated woven yarns. These “Yarn@gels” employ an adaptive internal pressure strategy, where the natural swelling of cotton fibers within the gel matrix generates pressure to keep the cell components tightly bound, removing the need for bulky, rigid parts. The result is a fuel cell that is flexible, cuttable, water-resistant, and quick to refuel in just one minute.
The findings of this study are published in Nature Materials.
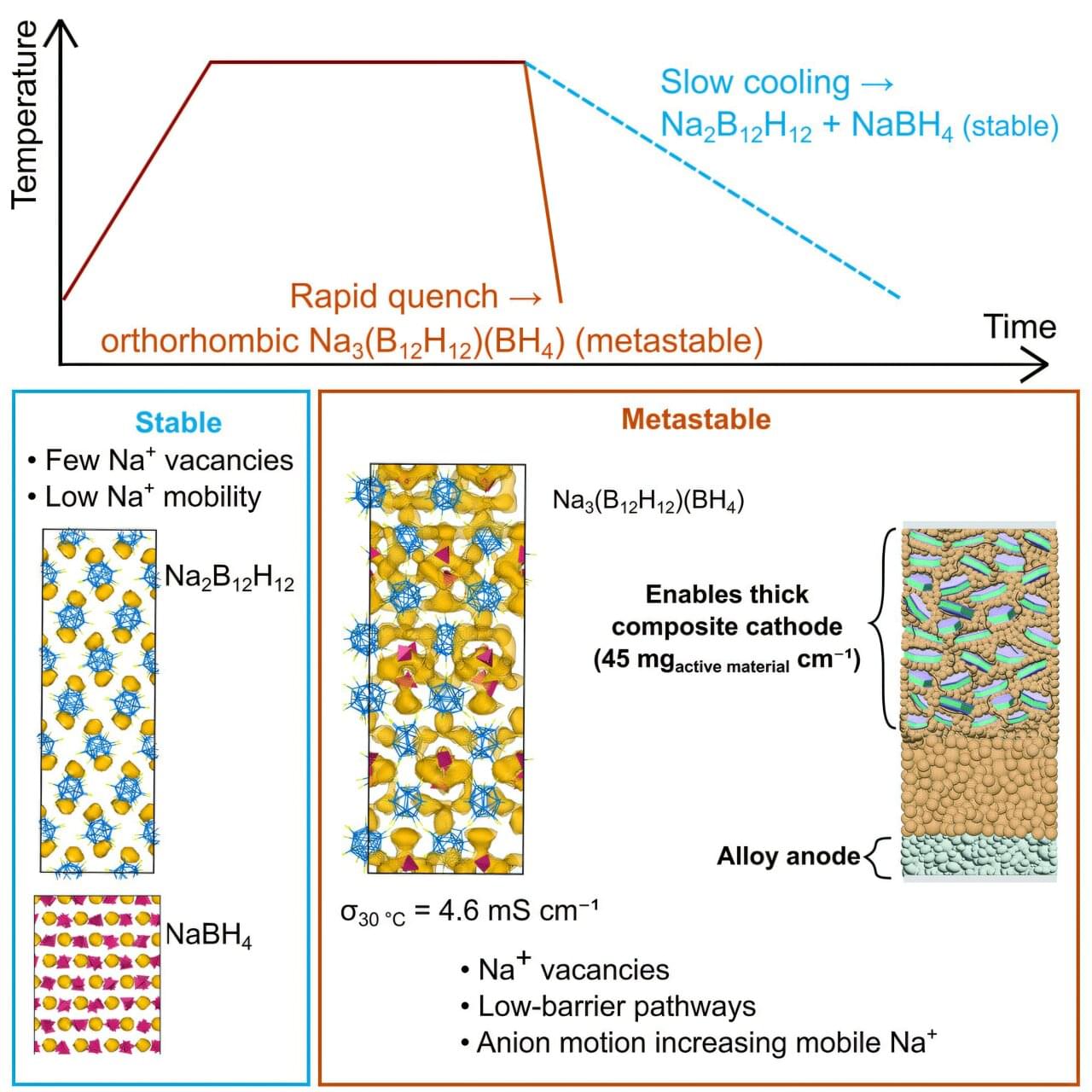
All-solid-state batteries are safe, powerful ways to power EVs and electronics and store electricity from the energy grid, but the lithium used to build them is rare, expensive and can be environmentally devastating to extract.
Sodium is an inexpensive, plentiful, less-destructive alternative, but the all-solid-state batteries they create currently don’t work as well at room temperature.
“It’s not a matter of sodium versus lithium. We need both. When we think about tomorrow’s energy storage solutions, we should imagine the same gigafactory can produce products based on both lithium and sodium chemistries,” said Y. Shirley Meng, Liew Family Professor in Molecular Engineering at the UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME). “This new research gets us closer to that ultimate goal while advancing basic science along the way.”

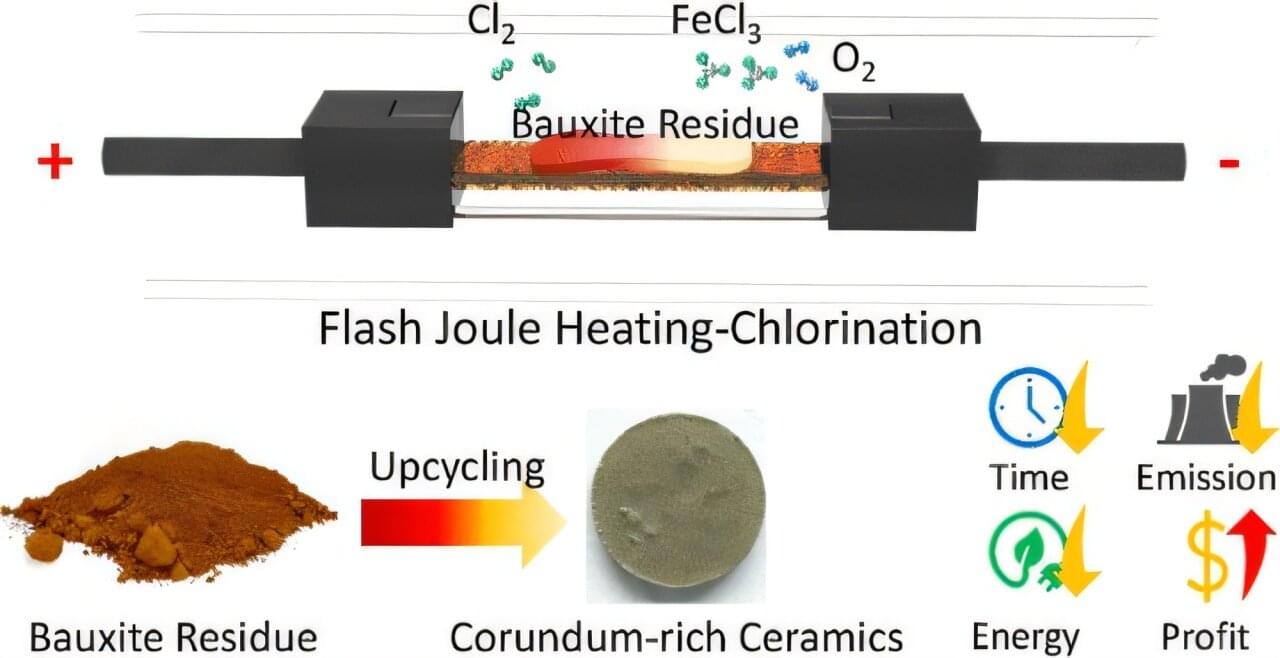
A team of researchers at Rice University has developed a faster and cleaner method for recovering aluminum and removing toxic metals from bauxite residue, or red mud, which is a hazardous by-product of aluminum production.
This new technique, published in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, involves a brief electrical pulse lasting under one minute, along with a small amount of chlorine gas. If implemented on a larger scale, it could revolutionize global waste management and materials recovery.
The process uses flash joule heating (FJH), which rapidly heats materials with a short, high-power electrical pulse to vaporize harmful metals, leaving behind a residue rich in aluminum. This aluminum-rich material can then be repurposed into durable ceramic tiles or bricks or resubjected to the normal aluminum production process. The method offers a practical and scalable solution to address a significant pollution problem by transforming it into valuable materials, marking an advancement in industrial waste recovery.

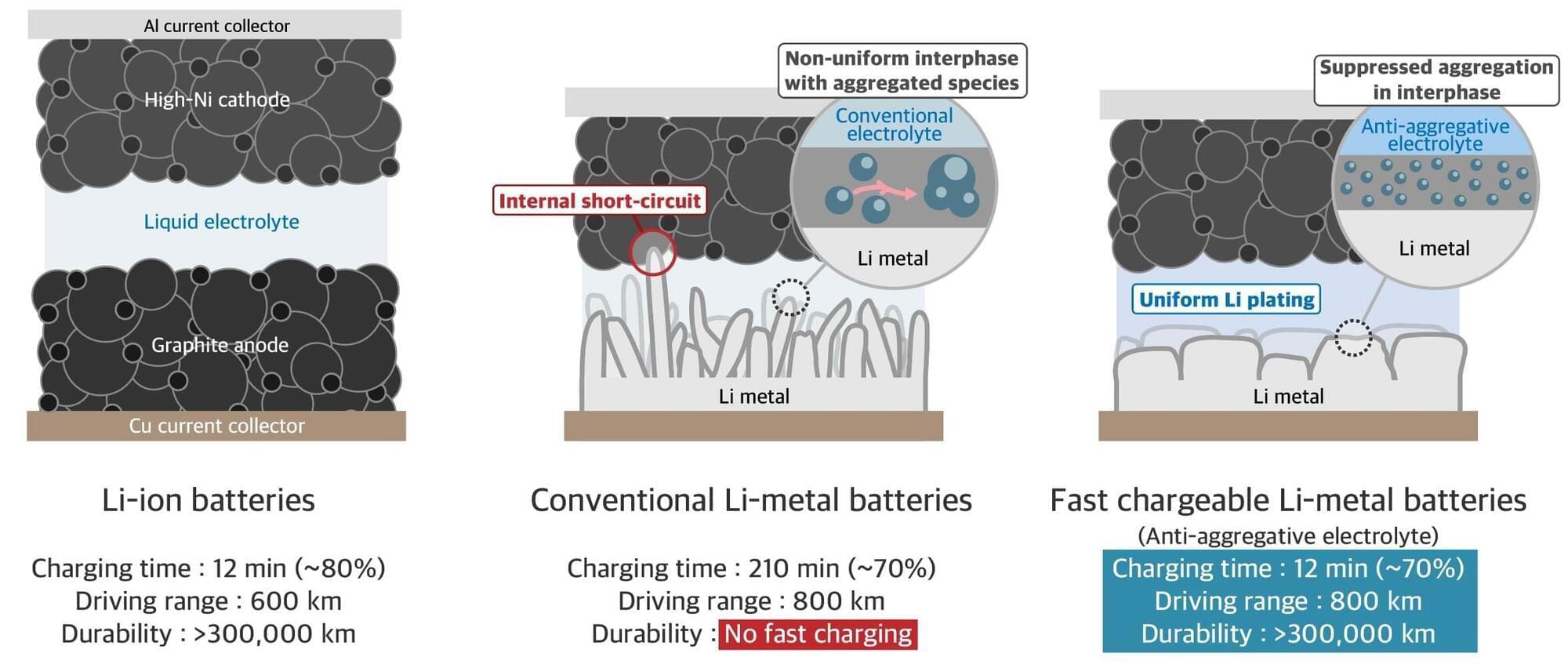
Korean researchers have ushered in a new era for electric vehicle (EV) battery technology by solving the long-standing dendrite problem in lithium-metal batteries. While conventional lithium-ion batteries are limited to a maximum range of 600 km, the new battery can achieve a range of 800 km on a single charge, a lifespan of over 300,000 km, and a super-fast charging time of just 12 minutes.
A research team from the Frontier Research Laboratory (FRL), a joint project between Professor Hee Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and LG Energy Solution, has developed a “cohesion-inhibiting new liquid electrolyte” original technology that can dramatically increase the performance of lithium-metal batteries. Their paper is published in Nature Energy.
Lithium-metal batteries replace the graphite anode, a key component of lithium-ion batteries, with lithium metal. However, lithium metal has a technical challenge known as dendrite, which makes it difficult to secure the battery’s lifespan and stability. Dendrites are tree-like lithium crystals that form on the anode surface during battery charging, negatively affecting battery performance and stability.

Engineers in Australia have created a new carbon-based material which allows supercapacitors to store as much energy as traditional lead-acid batteries and deliver charge much faster.
The new graphene materials are now being made in commercial quantities, says Dr Phillip Aitchison, chief technical officer of Monash University spinout Ionic Industries.
“We’re working with energy storage partners to bring this breakthrough to market-led applications – where both high energy and fast power delivery are essential.”
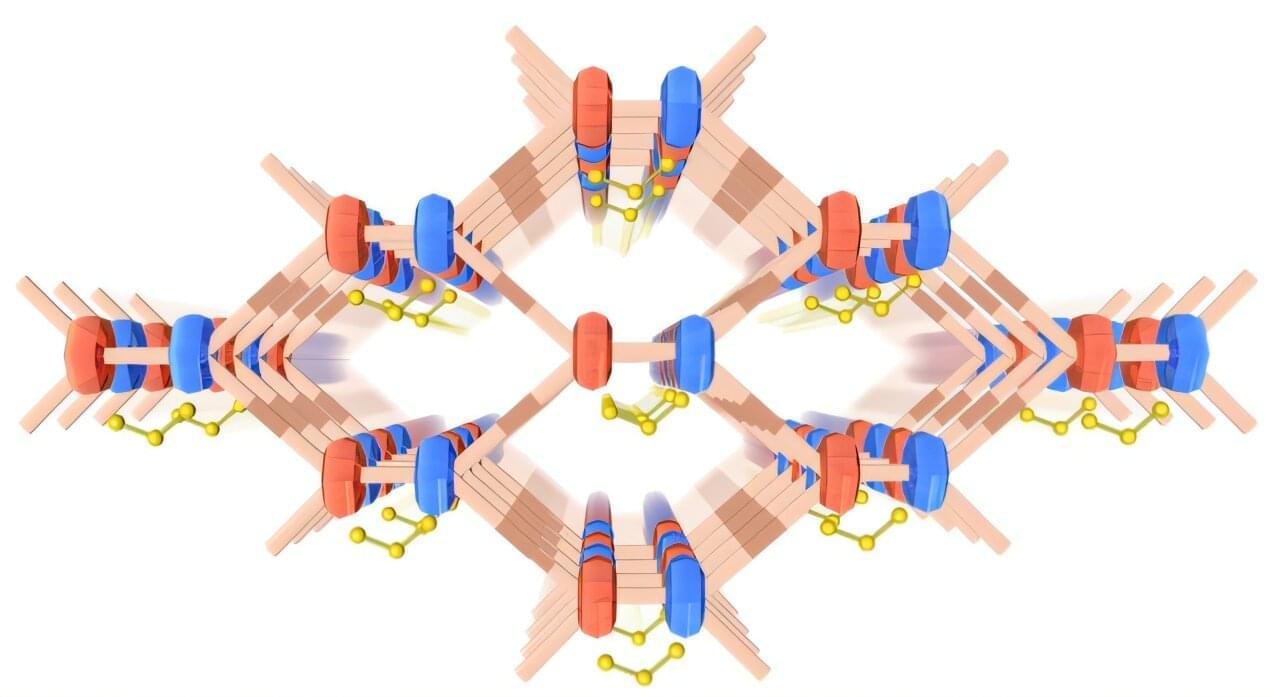
A team led by Prof. Yan Lu, HZB, and Prof. Arne Thomas, Technical University of Berlin, has developed a material that enhances the capacity and stability of lithium-sulfur batteries. The material is based on polymers that form a framework with open pores (known as radical-cationic covalent organic frameworks or COFs). Catalytically accelerated reactions take place in these pores, firmly trapping polysulfides, which would shorten the battery life.
Some of the experimental analyses were conducted at the BAMline at BESSY II. The research is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Crystalline framework structures made of organic polymers are a particularly interesting class of materials. They are characterized by their high porosity, comparable to a sponge, but with pores measuring only a few micrometers at most. These materials can exhibit special functionalities, which make them interesting for certain applications in electrochemical energy storage devices.