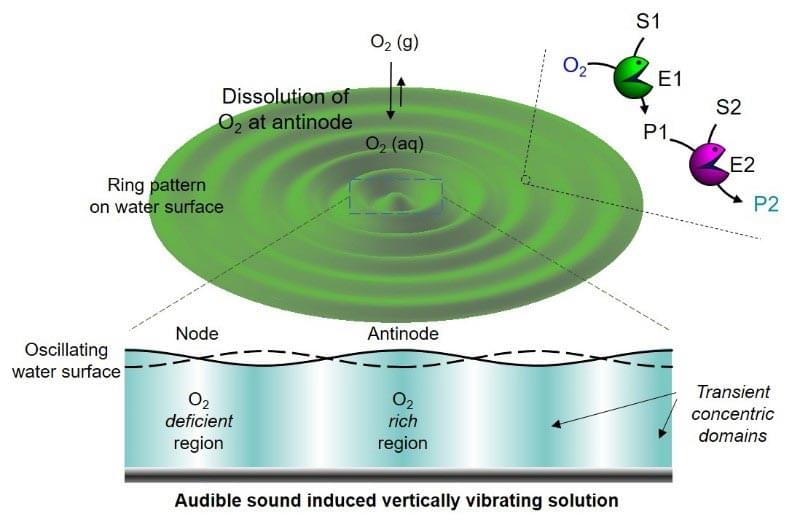
Unhackneyed compartmentalization generated by audible sound allows the enzyme reactions to be controlled spatiotemporally.
Spatiotemporal regulation of multistep enzyme reactions through compartmentalization is essential in studies that mimic natural systems such as cells and organelles. Until now, scientists have used liposomes, vesicles, or polymersomes to physically separate the different enzymes in compartments, which function as ‘artificial organelles’. But now, a team of researchers led by Director KIM Kimoon at the Center for Self-assembly and Complexity within the Institute for Basic Science in Pohang, South Korea successfully demonstrated the same spatiotemporal regulation of chemical reactions by only using audible sound, which is completely different from the previous methods mentioned above.
Although sound has been widely used in physics, materials science, and other fields, it has rarely been used in chemistry. In particular, audible sound (in the range of 20–20,000 Hz) has not been used in chemical reactions so far because of its low energy. However, for the first time, the same group from the IBS had previously successfully demonstrated the spatiotemporal regulation of chemical reactions through a selective dissolution of atmospheric gases via standing waves generated by audible sound back in 2020.