Steerable arm helps save energy while capturing panoramic views.
Category: energy – Page 212

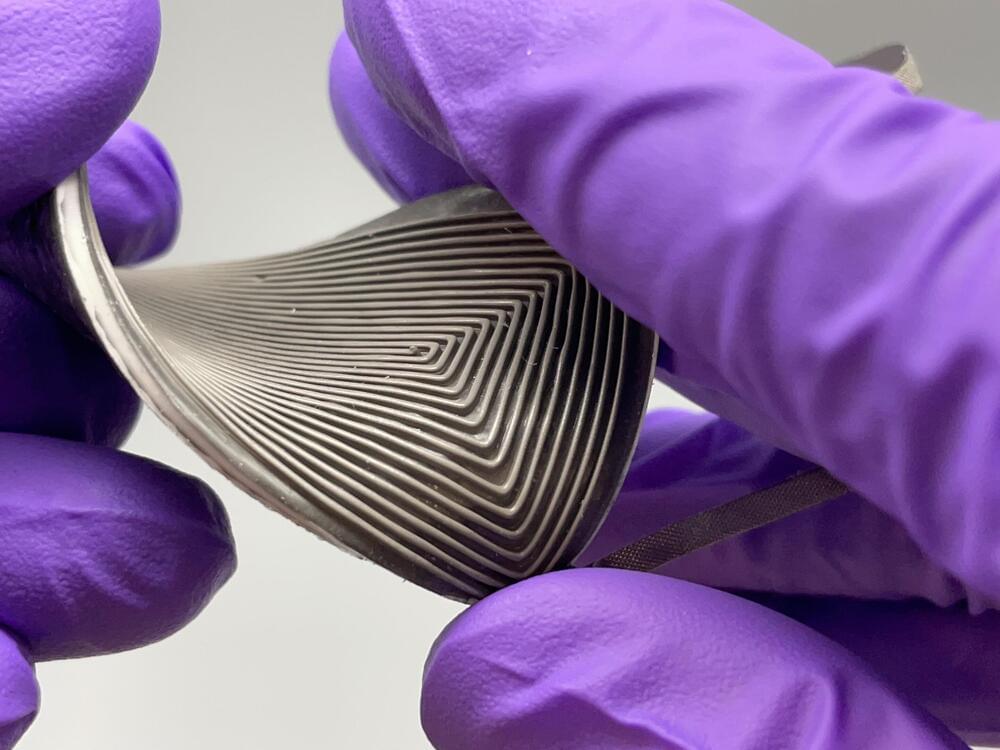
A flexible device that harvests thermal energy to power wearable electronics
Wearable electronics, from health and fitness trackers to virtual reality headsets, are part of our everyday lives. But finding ways to continuously power these devices is a challenge.
University of Washington researchers have developed an innovative solution: the first-of-its kind flexible, wearable thermoelectric device that converts body heat to electricity. This device is soft and stretchable, yet sturdy and efficient—properties that can be challenging to combine.
The team published these findings July 24 in Advanced Energy Materials.
Study finds nickelate superconductors are intrinsically magnetic
Electrons find each other repulsive. Nothing personal—it’s just that their negative charges repel each other. So getting them to pair up and travel together, like they do in superconducting materials, requires a little nudge.
In old-school superconductors, which were discovered in 1911 and conduct electric current with no resistance, but only at extremely cold temperatures, the nudge comes from vibrations in the material’s atomic lattice.
But in newer, “unconventional” superconductors—which are especially exciting because of their potential to operate at close to room temperature for things like zero-loss power transmission—no one knows for sure what the nudge is, although researchers think it might involve stripes of electric charge, waves of flip-flopping electron spins that create magnetic excitations, or some combination of things.

Arup unveils world’s first algae-powered building
Circa 2013 😃
News: the world’s first building to be powered entirely by algae is being piloted in Hamburg, Germany, by engineering firm Arup.
The “bio-adaptive facade”, which Arup says is the first of its kind, uses live microalgae growing in glass louvres to generate renewable energy and provide shade at the same time.
Installed in the BIQ building as part of the International Building Exhibition, the algae are continuously supplied with liquid nutrients and carbon dioxide via a water circuit running through the facade.
Innovative Wave Energy Ocean Power Plant Energy From The Waves
Eco Wave Power developed an innovative technology for production of clean electricity from ocean and sea waves. EWP’s innovative technology has been recognized as a “Pioneering Technology” by the Chief Scientist of the Energy Ministry of Israel and received an Efficient Solution label from Solar Impulse Foundation.
source/image(PrtSc): EcoWavePower.

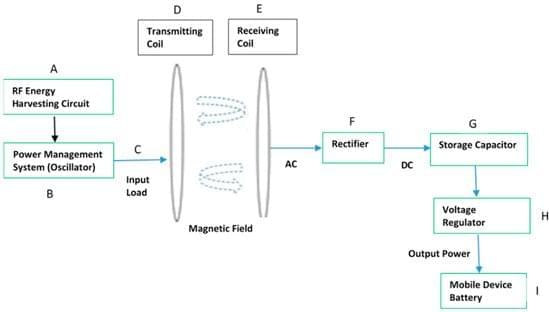
Wireless Power Transfer Using Harvested Radio Frequency Energy with Magnetic Resonance Coupling to Charge Mobile Device Batteries
This research paper presents the design of a wireless power transfer (WPT) circuit integrated with magnetic resonance coupling (MRC) and harvested radio frequency (RF) energy to wirelessly charge the battery of a mobile device. A capacitor (100 µF, 16 V) in the RF energy harvesting circuit stored the converted power, and the accumulated voltage stored in the capacitor was 9.46 V. The foundation of the proposed WPT prototype circuit included two coils (28 AWG)—a transmitter coil, and a receiver coil. The transmitter coil was energized by the alternating current (AC), which produced a magnetic field, which in turn induced a current in the receiver coil. The harvested RF energy (9.46 V) was converted into AC, which energized the transmitter coil and generated a magnetic field. The electronics in the receiver coil then converted the AC into direct current (DC), which became usable power to charge the battery of a mobile device. The experimental setup based on mathematical modeling and simulation displayed successful charging capabilities of MRC, with the alternate power source being the harvested RF energy. Mathematical formulae were applied to calculate the amount of power generated from the prototype circuit. LTSpice simulation software was applied to demonstrate the behavior of the different components in the circuit layout for effective WPT transfer.

DARPA’S Hypersonic Air-breathing Weapon Concept achieves successful flight
DARPA, in partnership with the U.S. Air Force, completed a free flight test of its Hypersonic Air-breathing Weapon Concept (HAWC) last week. The missile, built by Raytheon Technologies, was released from an aircraft seconds before its Northrop Grumman scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) engine kicked on. The engine compressed incoming air mixed with its hydrocarbon fuel and began igniting that fast-moving airflow mixture, propelling the cruiser at a speed greater than Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound).
The HAWC vehicle operates best in oxygen-rich atmosphere, where speed and maneuverability make it difficult to detect in a timely way. It could strike targets much more quickly than subsonic missiles and has significant kinetic energy even without high explosives.
“The HAWC free flight test was a successful demonstration of the capabilities that will make hypersonic cruise missiles a highly effective tool for our warfighters,” said Andrew “Tippy” Knoedler, HAWC program manager in DARPA’s Tactical Technology Office. “This brings us one step closer to transitioning HAWC to a program of record that offers next generation capability to the U.S military.”
Boosting Michigan’s Energy Future with Regional Transmission Upgrades
The regional entity overseeing much of the electric power grid in the Midwest — the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) — approved a set of major new transmission system upgrades that will bring billions of dollars in benefits to the region while better enabling states and utilities to pursue transitions to clean energy.
See here for my colleague Sam Gomberg’s excellent post explaining the background and details on what is known as “Tranche 1” of MISO’s long range transmission planning process. This much-needed set of 18 projects will improve electricity reliability, address overloaded wires, and help unlock more lower-cost wind and solar power to replace costly, polluting fossil fuel plants in Michigan and many other states in the Midwest (including Illinois and Minnesota).