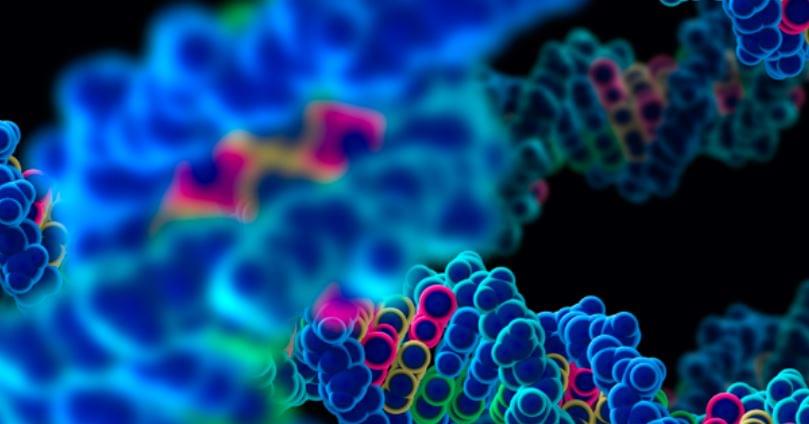
Significantly improved electric vehicle (EV) batteries could be a step closer thanks to a new study led by University of Oxford researchers, published today in Nature. Using advanced imaging techniques, this revealed mechanisms which cause lithium metal solid-state batteries (Li-SSBs) to fail. If these can be overcome, solid-state batteries using lithium metal anodes could deliver a step-change improvement in EV battery range, safety and performance, and help advance electrically powered aviation.
One of the co-lead authors of the study Dominic Melvin, a PhD student in the University of Oxford’s Department of Materials, said: ‘Progressing solid-state batteries with lithium metal anodes is one of the most important challenges facing the advancement of battery technologies. While lithium-ion batteries of today will continue to improve, research into solid-state batteries has the potential to be high-reward and a gamechanger technology.’
Li-SSBs are distinct from other batteries because they replace the flammable liquid electrolyte in conventional batteries with a solid electrolyte and use lithium metal as the anode (negative electrode). The use of the solid electrolyte improves the safety, and the use of lithium metal means more energy can be stored. A critical challenge with Li-SSBs, however, is that they are prone to short circuit when charging due to the growth of ‘dendrites’: filaments of lithium metal that crack through the ceramic electrolyte. As part of the Faraday Institution’s SOLBAT project, researchers from the University of Oxford’s Departments of Materials, Chemistry and Engineering Science, have led a series of in-depth investigations to understand more about how this short-circuiting happens.