Excitations in solids can also be represented mathematically as quasiparticles; for example, lattice vibrations that increase with temperature can be well described as phonons. Mathematically, also quasiparticles can be described that have never been observed in a material before. If such “theoretical” quasiparticles have interesting talents, then it is worth taking a closer look. Take fractons, for example.
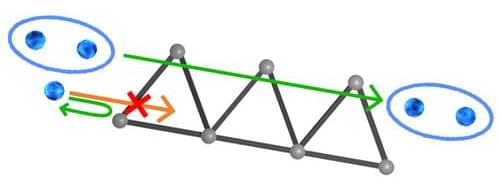
Fractons are fractions of spin excitations and are not allowed to possess kinetic energy. As a consequence, they are completely stationary and immobile. This makes fractons new candidates for perfectly secure information storage. Especially since they can be moved under special conditions, namely piggyback on another quasiparticle.
“Fractons have emerged from a mathematical extension of quantum electrodynamics, in which electric fields are treated not as vectors but as tensors—completely detached from real materials,” explains Prof. Dr. Johannes Reuther, theoretical physicist at the Freie Universität Berlin and at HZB.