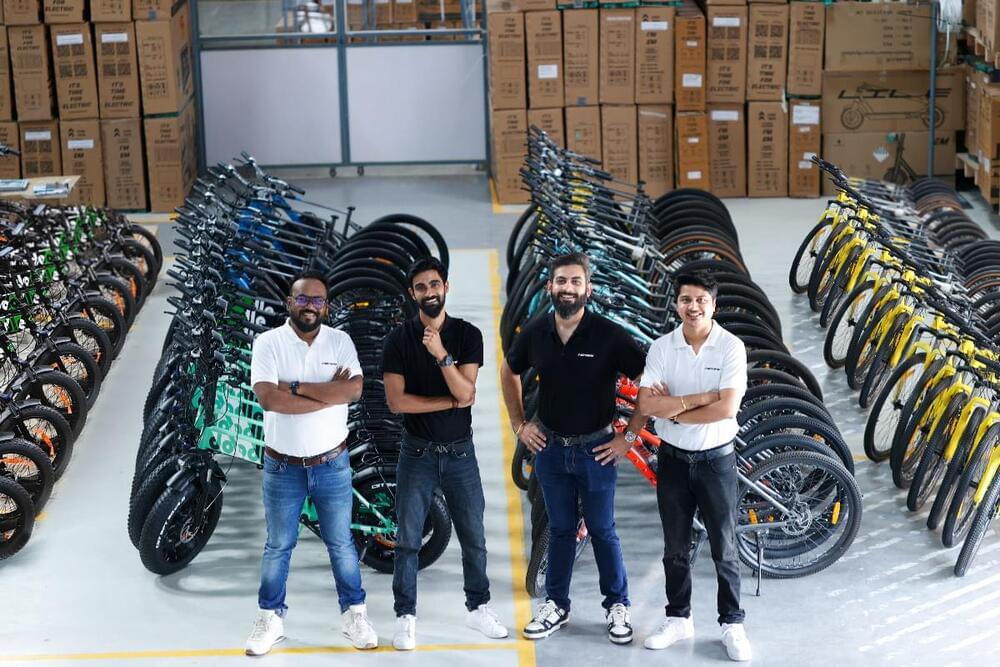
EMotorad, an Indian startup manufacturing electric bikes, raised $20 million in a Series B round as it aims to disrupt China’s market domination and expand its presence in global markets.
The three-year-old startup has raised more than $22.5 million in total funding, with Singapore’s Panthera Growth Partners leading the latest round, along with participation from Alteria Capital, xto10x Technologies, and Green Frontier Capital — the startup’s existing investor. Additionally, the fresh funding round includes a debt of $2.5 million.
The demand for e-bikes is growing in markets beyond China and India as people seek to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, ease traffic congestion on the roads and find alternative transportation options that do not require rigorous physical activity throughout their daily commute. In 2021, the World Bank predicted (PDF) that as many as 300 million e-bikes will circulate in cities across the globe by 2023. However, despite growing demand worldwide, e-bike supplies rely heavily on Chinese manufacturers. EMotorad is striving to overturn this trend by establishing its manufacturing operations in India.