Circa 2015
New system destructively scans objects transmits them through encrypted communications across any distance and rebuilds it the other side.
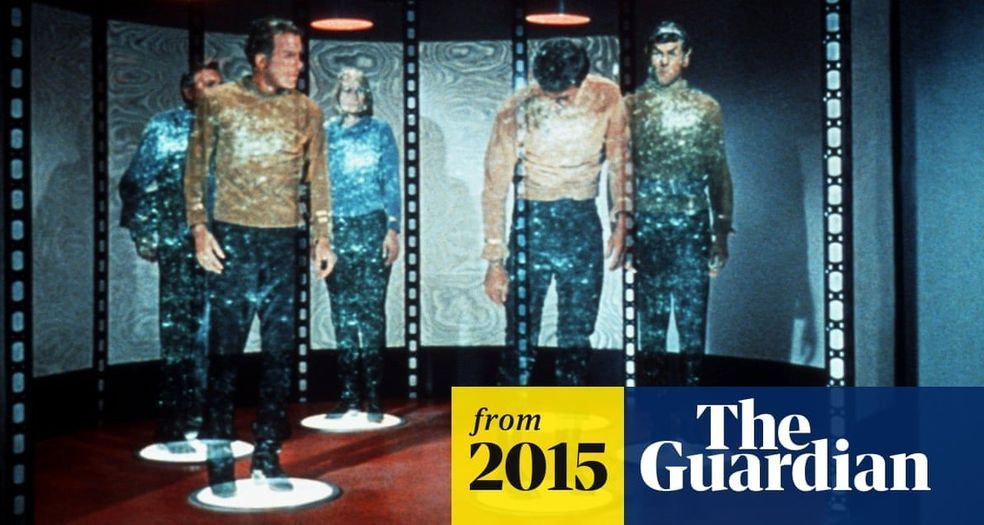


:oooo.
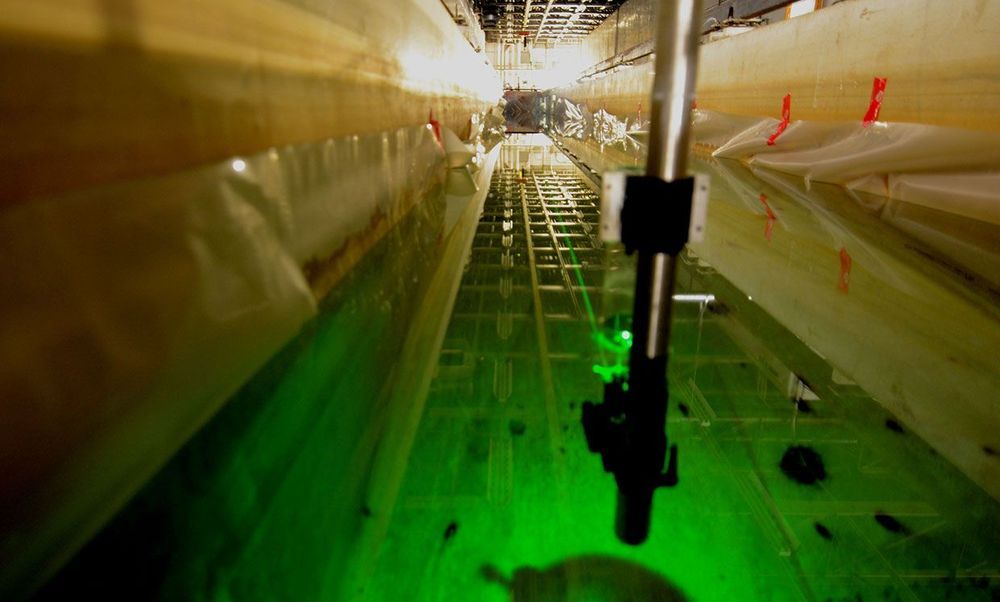
Underwater quantum links are possible across 30 meters (100 feet) of turbulent water, scientists have shown. Such findings could help to one day secure quantum communications for submarines.
Quantum cryptography exploits the quantum properties of particles such as photons to help encrypt and decrypt messages in a theoretically unhackable way. Scientists worldwide are now endeavoring to develop satellite-based quantum communications networks for a global real-time quantum Internet.
In addition to beaming quantum communications signals across the air, through a vacuum, and within fiber optic cables, researchers have investigated establishing quantum communications links through water. Such work could lead to secure quantum communications between submarines and surface vessels, and with other subs, aircraft, or even satellites.

NASA, one of SpaceX’s biggest customers, also prohibits its employees from using Zoom, said Stephanie Schierholz, a spokeswoman for the U.S. space agency.
The Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Boston office on Monday issued a warning about Zoom, telling users not to make meetings on the site public or share links widely after it received two reports of unidentified individuals invading school sessions, a phenomenon known as “zoombombing.”
Investigative news site The Intercept on Tuesday reported that Zoom video is not end-to-end encrypted between meeting participants, and that the company could view sessions.
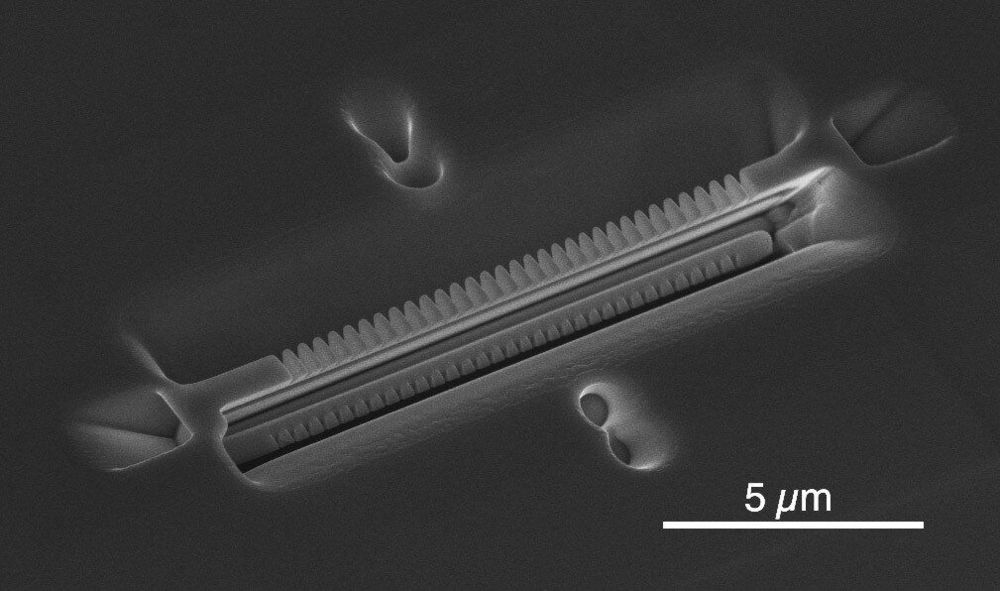
Engineers at Caltech have shown that atoms in optical cavities—tiny boxes for light—could be foundational to the creation of a quantum internet. Their work was published on March 30 by the journal Nature.
Quantum networks would connect quantum computers through a system that also operates at a quantum, rather than classical, level. In theory, quantum computers will one day be able to perform certain functions faster than classical computers by taking advantage of the special properties of quantum mechanics, including superposition, which allows quantum bits to store information as a 1 and a 0 simultaneously.
As they can with classical computers, engineers would like to be able to connect multiple quantum computers to share data and work together—creating a “quantum internet.” This would open the door to several applications, including solving computations that are too large to be handled by a single quantum computer and establishing unbreakably secure communications using quantum cryptography.
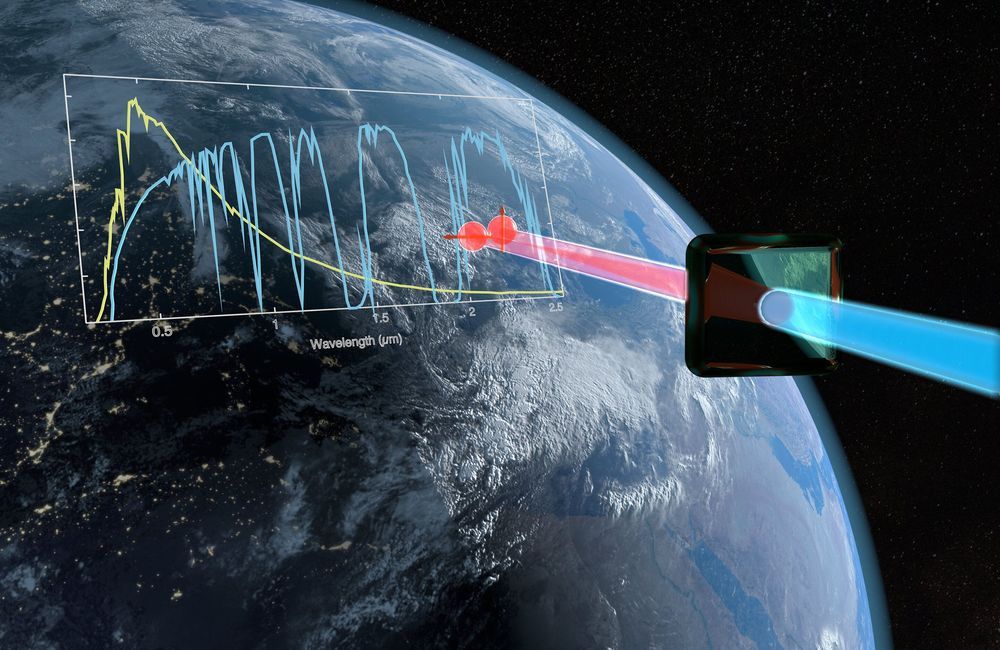
An international team with the participation of Prof. Dr. Michael Kues from the Cluster of Excellence PhoenixD at Leibniz University Hannover has developed a new method for generating quantum-entangled photons in a spectral range of light that was previously inaccessible. The discovery can make the encryption of satellite-based communications much more secure in the future.
A 15-member research team from the U.K., Germany and Japan has developed a new method for generating and detecting quantum-entangled photons at a wavelength of 2.1 micrometers. In practice, entangled photons are used in encryption methods such as quantum key distribution to completely secure telecommunications between two partners against eavesdropping attempts. The research results are presented to the public for the first time in the current issue of Science Advances.
It has been regarded as technically possible to implement encryption mechanisms with entangled photons in the near-infrared range of 700 to 1550 nanometers. However, these shorter wavelengths have disadvantages, especially in satellite-based communication. They are disturbed by light-absorbing gases in the atmosphere as well as the background radiation of the sun. With existing technology, end-to-end encryption of transmitted data can only be guaranteed at night, but not on sunny and cloudy days.

Circa 2019
Makers of Titanic claimed that it is ‘unsinkable’ and we know how it went down in history. Now, researchers from the University of St Andrews have claimed to have developed an ‘unhackable’ encryption system that stores data in the form of light.
The chip designed by the researchers generates one-time-only key when data is sent through it. The data is stored as light and passed through a specially designed chip that bends and refracts the light to scramble the information.
The trick behind the tech is that the bending and refracting of light is unique every time as it depends upon the data being sent through the chip. It would be safe to say that the chip is a physical realization of the OTP mechanism which is popularly used today to authenticate several services.




Quantum computing might initially sound like a far-fetched futuristic idea, but companies such as Amazon, Google, and IBM are putting their weight behind it and preparations have begun. With quantum computing potentially within our reach, what will happen to our current security models and modern-day encryption? See what security experts are doing to prepare for quantum threats.
The future is here. Or just about. After a number of discoveries, researchers have proven that quantum computing is possible and on its way. The wider world did not pause long on this discovery: Goldman Sachs, Amazon, Google, and IBM have just announced their own intentions to embark on their own quantum developments.
Now that it’s within our reach we have to start seriously considering what that means in the real world. Certainly, we all stand to gain from the massive benefits that quantum capabilities can bring, but so do cybercriminals.