Academic study finds 25 attack methods in major cloud password managers exposing vault, recovery, and encryption design risks.



#Quantum #CyberSecurity
Quantum computing is not merely a frontier of innovation; it is a countdown. Q-Day is the pivotal moment when scalable quantum computers undermine the cryptographic underpinnings of our digital realm. It is approaching more rapidly than many comprehend.
For corporations and governmental entities reliant on outdated encryption methods, Q-Day will not herald a smooth transition; it may signify a digital catastrophe.
Comprehending Q-Day: The Quantum Reckoning
Q-Day arrives when quantum machines using Shor’s algorithm can dismantle public-key encryption within minutes—a task that classical supercomputers would require billions of years to accomplish.
Elon Musk Announces MAJOR Company Changes as XAI/SpaceX ## Elon Musk is announcing significant changes and advancements across his companies, primarily focused on developing and integrating artificial intelligence (AI) to drive innovation, productivity, and growth ## ## Questions to inspire discussion.
Product Development & Market Position.
🚀 Q: How fast did xAI achieve market leadership compared to competitors?
A: xAI reached number one in voice, image, video generation, and forecasting with the Grok 4.20 model in just 2.5 years, outpacing competitors who are 5–20 years old with larger teams and more resources.
📱 Q: What scale did xAI’s everything app reach in one year?
A: In one year, xAI went from nothing to 2M Teslas using Grok, deployed a Grok voice agent API, and built an everything app handling legal questions, slide decks, and puzzles.

A Chinese research team has reported a pair of advances that could remove two of the biggest technical barriers to building large-scale quantum communication networks, including the generation of ultra-secure encryption keys over 11 kilometers of optical fiber and the validation of the approach at distances up to 100 kilometers, according to China Daily, a state-associated news service.
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China said they have demonstrated, for the first time, a scalable core component of a quantum repeater — a long-sought technology needed to extend quantum communication across long distances — while also setting new records for ultra-secure quantum key distribution over fiber networks.
The findings were published in Nature and Science, underscoring their significance within the international research community. Noted Chinese physicist Pan Jianwei led the work.
As quantum computers continue to advance, many of today’s encryption systems face the risk of becoming obsolete. A powerful alternative—quantum cryptography—offers security based on the laws of physics instead of computational difficulty. But to turn quantum communication into a practical technology, researchers need compact and reliable devices that can decode fragile quantum states carried by light.
A new study from teams at the University of Padua, Politecnico di Milano, and the CNR Institute for Photonics and Nanotechnologies shows how this goal can be approached using a simple material: borosilicate glass. As reported in Advanced Photonics, their work demonstrates a high-performance quantum coherent receiver fabricated directly inside glass using femtosecond laser writing. The approach provides low optical loss, stable operation, and broad compatibility with existing fiber-optic infrastructure—key factors for scaling quantum technologies beyond the laboratory.

Even supercomputers can stall out on problems where nature refuses to play by everyday rules. Predicting how complex molecules behave or testing the strength of modern encryption can demand calculations that grow too quickly for classical hardware to keep up. Quantum computers are designed to tackle that kind of complexity, but only if engineers can build systems that run with extremely low error rates.
One of the most promising routes to that reliability involves a rare class of materials called topological superconductors. In plain terms, these are superconductors that also have built-in “protected” quantum behavior, which researchers hope could help shield delicate quantum information from noise. The catch is that making materials with these properties is famously difficult.
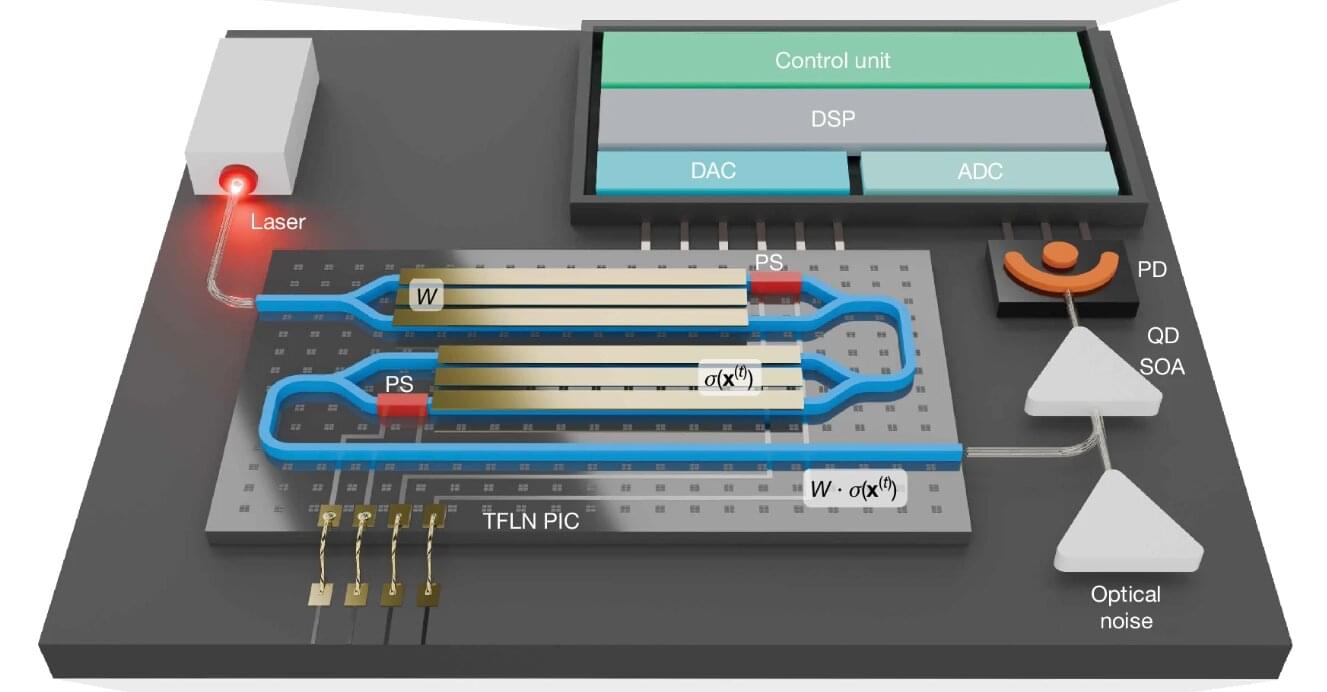
A team of researchers at Queen’s University has developed a powerful new kind of computing machine that uses light to take on complex problems such as protein folding (for drug discovery) and number partitioning (for cryptography). Built from off-the-shelf components, it also operates at room temperature and remains remarkably stable while performing billions of operations per second. The research was published in Nature.
The breakthrough shows that it is possible to build a practical and scalable machine that can tackle extremely difficult problems.
The project, led by Bhavin Shastri, Canada Research Chair in Neuromorphic Photonic Computing and professor in the Department of Physics, Engineering Physics, and Astronomy, with a team of his graduate students including Nayem Al Kayed and Hugh Morison, uses commercially available lasers, fiber optics, and modulators—the same technology that powers today’s internet infrastructure. The team partnered with McGill University researcher David Plant and his graduate student Charles St-Arnault.

Scientists achieved the ‘impossible’ in 2024, teleporting a quantum state through more than 30 kilometers amid a torrent of internet traffic.
In 2024, a quantum state of light was successfully teleported through more than 30 kilometers (around 18 miles) of fiber optic cable amid a torrent of internet traffic – a feat of engineering once considered impossible.
The impressive demonstration by researchers in the US may not help you beam to work to beat the morning traffic, or download your favorite cat videos faster.
However, the ability to teleport quantum states through existing infrastructure represents a monumental step towards achieving a quantum-connected computing network, enhanced encryption, or powerful new methods of sensing.
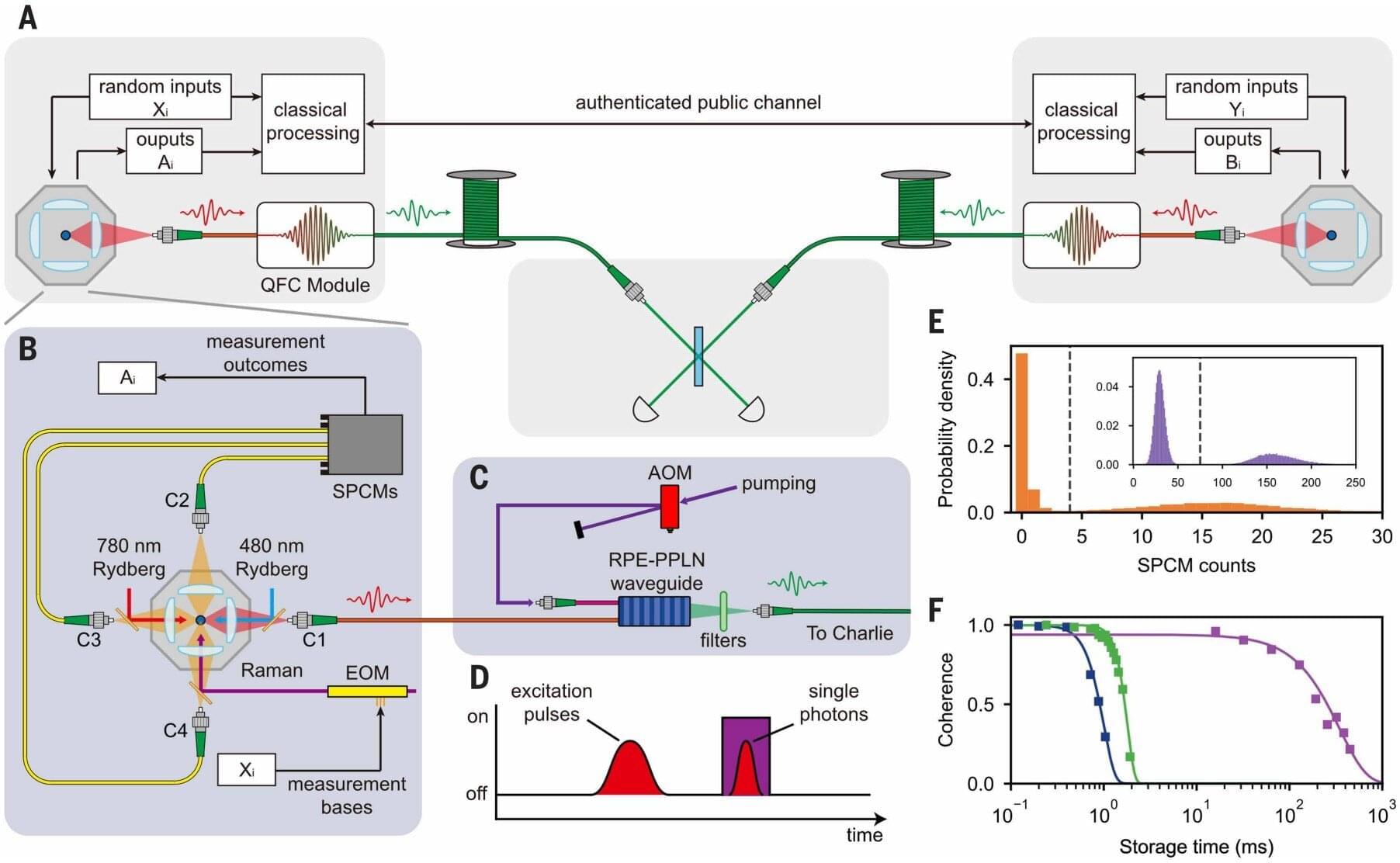
Concerns that quantum computers may start easily hacking into previously secure communications has motivated researchers to work on innovative new ways to encrypt information. One such method is quantum key distribution (QKD), a secure, quantum-based method in which eavesdropping attempts disrupt the quantum state, making unauthorized interception immediately detectable.
Previous attempts at this solution were limited by short distances and reliance on special devices, but a research team in China recently demonstrated the ability to maintain quantum encryption over longer distances. The research, published in Science, describes device-independent QKD (DI-QKD) between two single-atom nodes over up to 100 km of optical fiber.
Today’s most powerful computers hit a wall when tackling certain problems, from designing new drugs to cracking encryption codes. Error-free quantum computers promise to overcome those challenges, but building them requires materials with exotic properties of topological superconductors that are incredibly difficult to produce. Now, researchers at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) and West Virginia University have found a way to tune these materials into existence by simply tweaking a chemical recipe, resulting in a change in many-electron interactions.
The team adjusted the ratio of two elements— tellurium and selenium —that are grown in ultra-thin films. By doing so, they found they could switch the material between different quantum phases, including a highly desirable state called a topological superconductor.
The findings, published in Nature Communications, reveal that as the ratio of tellurium and selenium changes, so too do the correlations between different electrons in the material—how strongly each electron is influenced by those around it. This can serve as a sensitive control knob for engineering exotic quantum phases.