Passwd is a Google Workspace–only password manager using zero-knowledge AES-256 encryption, Google SSO, audit logs, and scalable team pricing.
Category: encryption – Page 3
Microsoft rolls out hardware-accelerated BitLocker in Windows 11
Microsoft is rolling out hardware-accelerated BitLocker in Windows 11 to address growing performance and security concerns by leveraging the capabilities of system-on-a-chip and CPU.
BitLocker is the native full-disk encryption feature in Windows that protects data from being readable without proper authentication. During normal device boot, it relies on the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to securely manage encryption keys and automatically unlock the drive.
Microsoft states that as non-volatile memory express (NVMe) storage has become more performant, BitLocker’s cryptographic operations have a more noticeable performance impact for gaming and video editing activities.
Introducing TinyAleph: Revolutionizing How Computers Understand Meaning with Primes and Oscillators
Imagine if meaning — the elusive essence of language and thought — could be broken down into mathematical building blocks as fundamental as prime numbers. What if computers could “reason” by synchronizing oscillators, much like neurons firing in harmony in our brains?
That’s the bold idea behind TinyAleph, a new framework and library I’ve developed for semantic computing. Unlike today’s AI models that gobble up massive datasets to mimic understanding, TinyAleph grounds meaning in pure math: primes, hypercomplex algebra, and dynamic oscillators.
In this article, I’ll walk you through the core ideas of TinyAleph, stripping away the academic jargon to show why this could be a game-changer for AI, cryptography, and even quantum-inspired simulations. No PhD required — just an open mind.

The Hidden Risk in Virtualization: Why Hypervisors are a Ransomware Magnet
Ransomware groups are targeting hypervisors to maximize impact, allowing a single breach to encrypt dozens of virtual machines at once. Drawing on real-world incident data, Huntress explains how attackers exploit visibility gaps at the hypervisor layer and outlines steps orgs can take to harden virtualization infrastructure.
The mind-bending reality of quantum mechanics — with Jim Al Khalili
Jim Al-Khalili explores emerging technologies powering the future of quantum, and looks at how we got here.
This Discourse was recorded at the Ri on 7 November 2025, in partnership with the Institute of Physics.
Watch the Q&A session for this talk here (exclusively for our Science Supporter members):
Join this channel as a member to get access to perks:
/ @theroyalinstitution.
Physicist and renowned broadcaster Jim Al-Khalili takes a look back at a century of quantum mechanics, the strangest yet most successful theory in all of science, and how it has shaped our world. He also looks forward to the exciting new world of Quantum 2.0 and how a deeper understanding of such counterintuitive concepts as quantum superposition and quantum entanglement is leading to the development of entirely new technologies, from quantum computers and quantum sensors to quantum cryptography and the quantum internet.
The United Nations has proclaimed 2025 as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, to celebrate the centenary of quantum mechanics and the revolutionary work of the likes of Werner Heisenberg and Erwin Schrödinger. Together with the Institute of Physics, join us to celebrate the culmination of the International Year of Quantum at the penultimate Discourse of our Discover200 year.
-
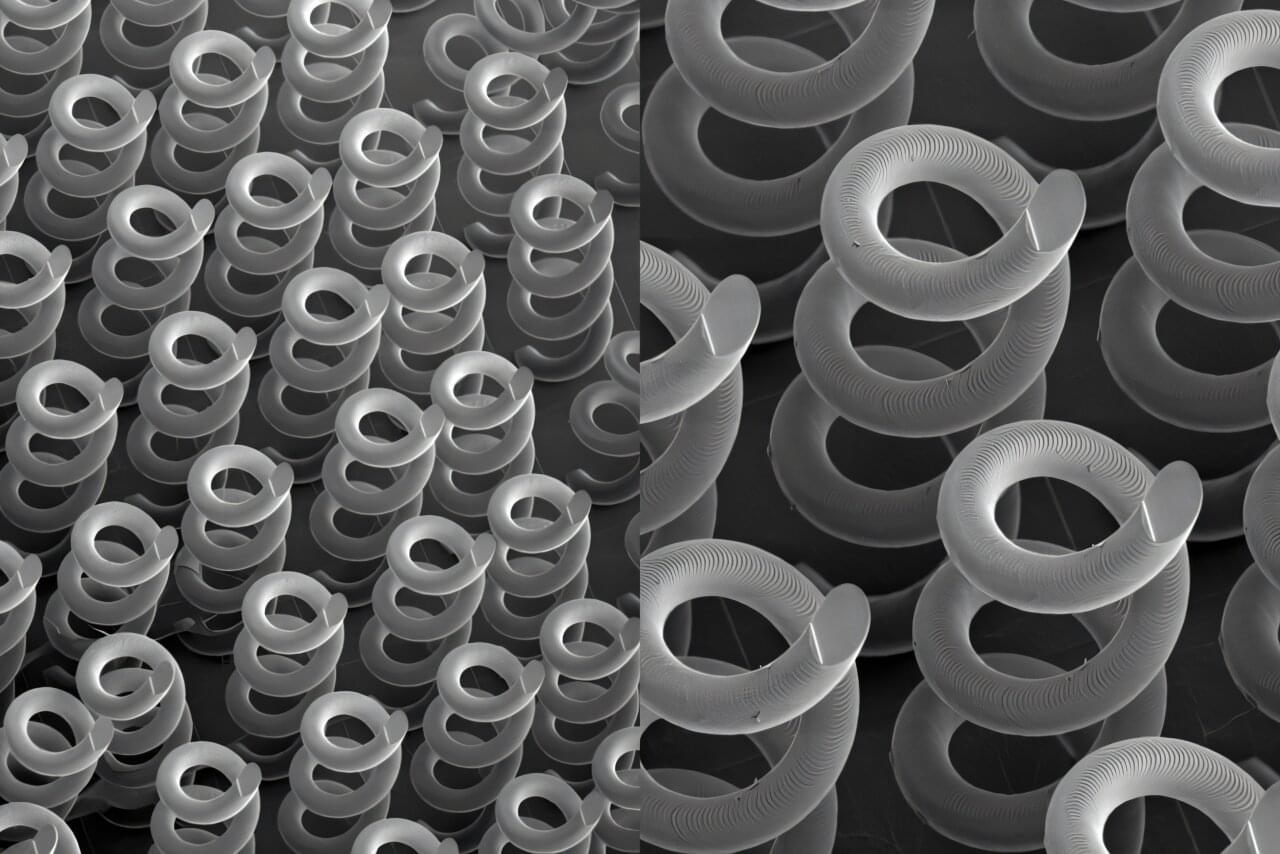
3D-printed helixes show promise as THz optical materials
Researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have optimized and 3D-printed helix structures as optical materials for terahertz (THz) frequencies, a potential way to address a technology gap for next-generation telecommunications, non-destructive evaluation, chemical/biological sensing and more.
The printed microscale helices reliably create circularly polarized beams in the THz range and, when arranged in patterned arrays, can function as a new type of Quick Response (QR) for advanced encryption/decryption. Their results, published in Advanced Science, represent the first full parametric analysis of helical structures for THz frequencies and show the potential of 3D printing for fabricating THz devices.
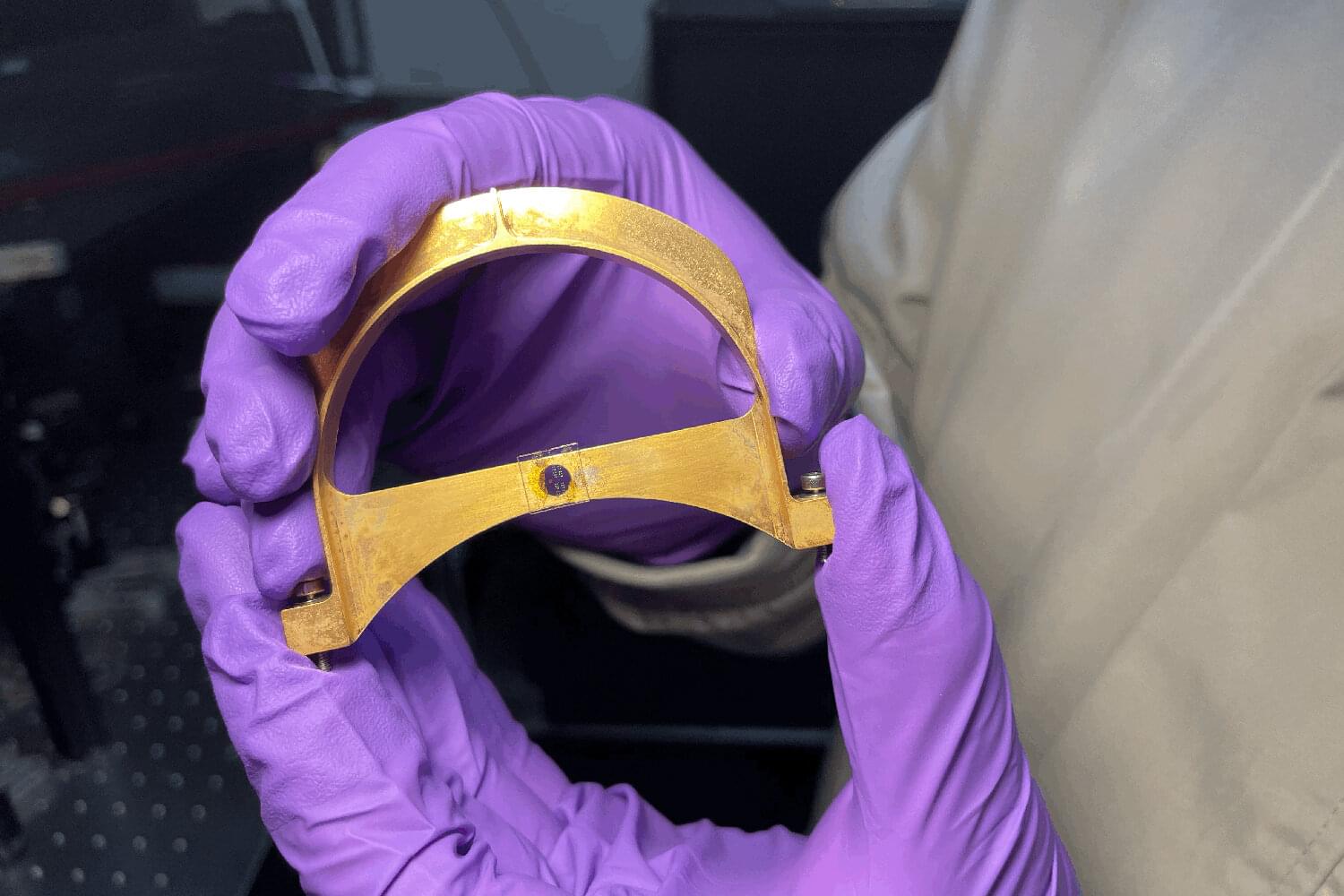



Scientists advance quantum signaling with twisted light technology
A tiny device that entangles light and electrons without super-cooling could revolutionize quantum tech in cryptography, computing, and AI.
Present-day quantum computers are big, expensive, and impractical, operating at temperatures near-459 degrees Fahrenheit, or “absolute zero.” In a new paper, however, materials scientists at Stanford University introduce a new nanoscale optical device that works at room temperature to entangle the spin of photons (particles of light) and electrons to achieve quantum communication—an approach that uses the laws of quantum physics to transmit and process data. The technology could usher in a new era of low-cost, low-energy quantum components able to communicate over great distances.
“The material in question is not really new, but the way we use it is,” says Jennifer Dionne, a professor of materials science and engineering and senior author of the paper just published in Nature Communications describing the novel device. “It provides a very versatile, stable spin connection between electrons and photons that is the theoretical basis of quantum communication. Typically, however, the electrons lose their spin too quickly to be useful.”

Popular Forge library gets fix for signature verification bypass flaw
A vulnerability in the ‘node-forge’ package, a popular JavaScript cryptography library, could be exploited to bypass signature verifications by crafting data that appears valid.
The flaw is tracked as CVE-2025–12816 and received a high severity rating. It arises from the library’s ASN.1 validation mechanism, which allows malformed data to pass checks even when it is cryptographically invalid.
“An interpretation-conflict vulnerability in node-forge versions 1.3.1 and earlier enables unauthenticated attackers to craft ASN.1 structures to desynchronize schema validations, yielding a semantic divergence that may bypass downstream cryptographic verifications and security decisions,” reads the flaw’s description in the National Vulnerabilities Database (NVD).