New technology could mean passengers would no longer need to remove items from hand luggage for screening.


New technology could mean passengers would no longer need to remove items from hand luggage for screening.
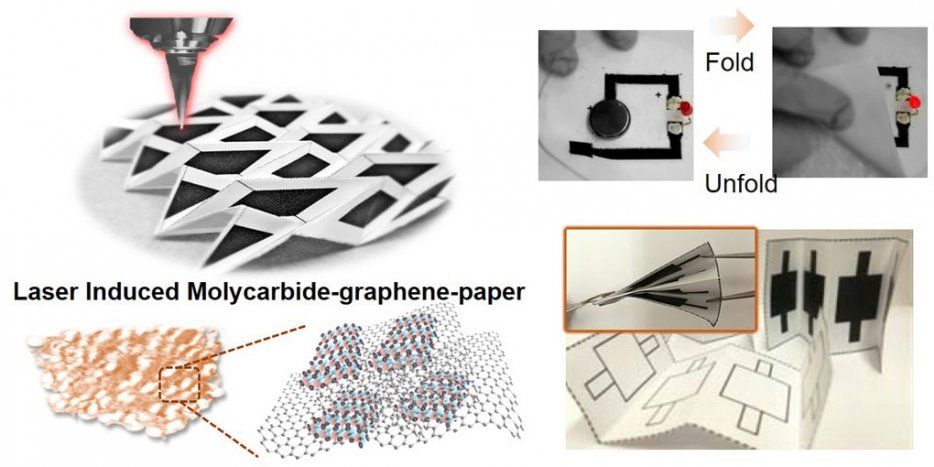
UC Berkeley engineers have given new meaning to the term “working paper.” Using inexpensive materials, they have fabricated foldable electronic switches and sensors directly onto paper, along with prototype generators, supercapacitors and other electronic devices for a range of applications.
Research to develop paper electronics has accelerated in the last 10 years. Besides its availability and low cost, paper offers an intriguing potential: simply folding it could switch circuits on and off or otherwise change their activity—a kind of electronic origami.
But most efforts to fabricate electrodes onto paper with sufficient conductivity for practical use have employed expensive metals such as gold or silver as the conducting material, swamping the potential savings of paper as a substrate.

Life on Mars will continue after all. After three seasons on cable television, the Syfy space war drama The Expanse was given the axe on May 10. Since then, support from the show’s fans has helped it find new life: The series has officially been renewed by Amazon for Season 4, which will be streamable. That’s right — not only will the sci-fi favorite return, but it is now marathon material. So, when is The Expanse Season 4? A premiere date has not yet been announced, but one thing is for sure — fans and The Expanse cast members alike can’t get enough of the show’s revival.
The Expanse, based on the New York Times bestselling eight-part book series co-written by Daniel Abraham and Ty Franck under the pen name James S. A. Corey, is set in a fully colonized solar system on the brink of war. There are three main parties that make up this narrative — Earth, Mars, and the asteroid belt — and their biggest mission is universal peace. Just like Rome wasn’t built in a day, though, universal peace wasn’t achieved in three seasons, so it only makes sense that Amazon picked up the story for continuation on a new platform.
It helps that Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos is a big fan of the books on which the show is based, according to the Hollywood Reporter, and he wasn’t ready to see the TV series go. He made the public announcement on May 25 at a National Space Society panel where the show’s cast and crew were in attendance.
Would you? www.disclose.tv
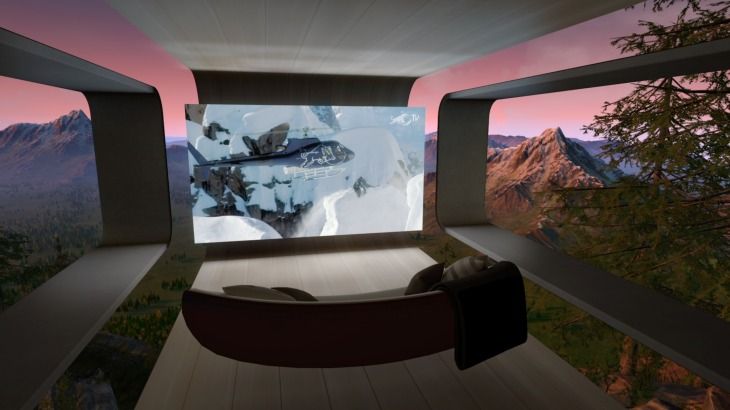

Oculus is launching a TV app for users to check out streaming video content on a big virtual screen on the Oculus Go headset.
The company highlighted Oculus TV at Facebook’s F8 developer conference as one of four new Oculus-built apps that would allow users to get the most out of the inexpensive headset. The app was supposed to launch by the end of May, but we’re finally getting to take a look at it.
Facebook wants a big selling point of the $199 Oculus Go to be that it’s the cheapest home theater you can buy. Oculus TV is a sizable step toward making all of the features related to conventional video viewing available easily. The app will be a free download for existing users of the headset and will come pre-installed on the device moving forward.
This flying camera drone will put your selfie skills to shame. Buy it here: https://amzn.to/2xvPgDp


A new laser-based field instrument developed by a collaborative team of researchers can quantify methane leaks as tiny as 1/4 of a human exhalation from nearly…a mile away. The system, constructed around a dual-frequency comb spectrometer, provides efficient, accurate data collection at a fraction of the cost of previous technologies. The research was partially funded by DARPA’s Spectral Combs from UV to THz (SCOUT) program.
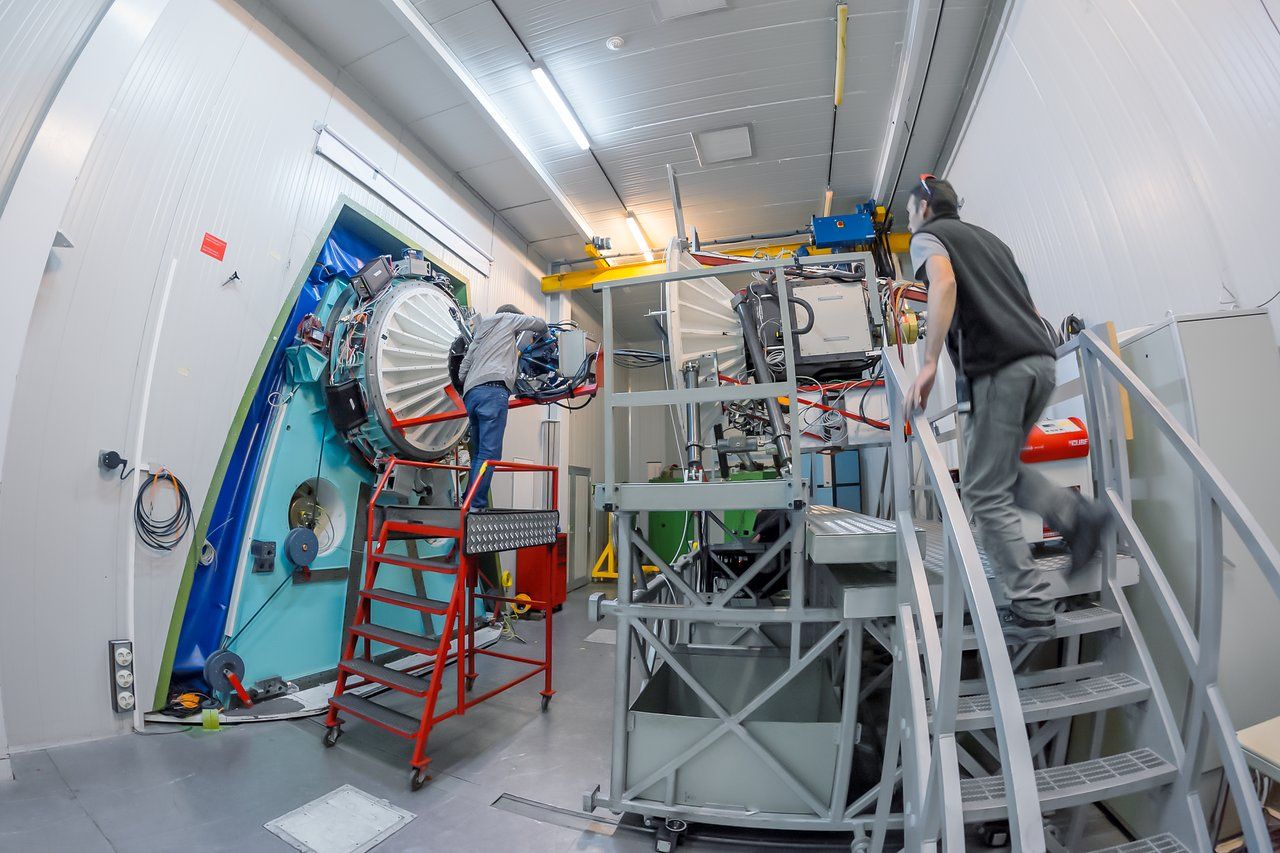

The ULTRACAM has been a staple in ESO for almost 16 years. This high-speed camera is able to do 500 photographs per second in three different wavelengths and, since 2002 has been operating at the William Herschel Telescope at La Palma (Canary Islands, Spain), the New Technology Telescope at La Silla (Chile) (where this picture was taken) and, most recently, at the Very Large Telescope at Paranal (Chile) and the Thai National Telescope at Chiang Mai (Thailand).
Some of its past targets have included: the study of black holes, “hot-Jupiters” or variable stars.
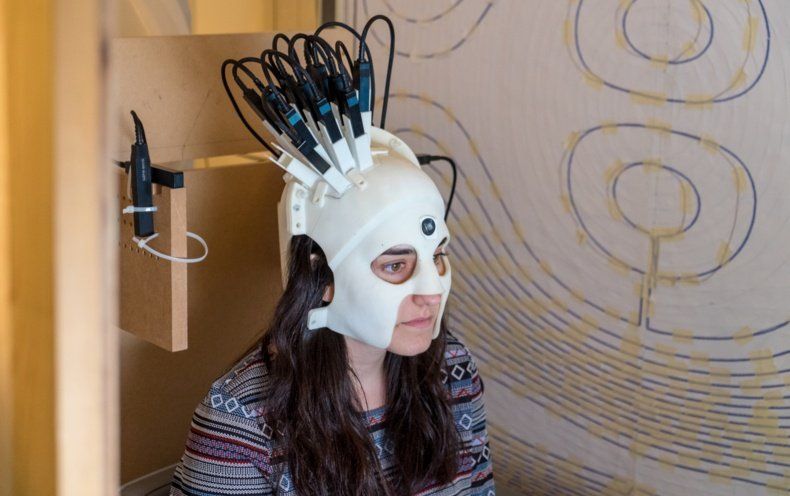

Lightweight equipment is not much larger than what a bicyclist would wear.