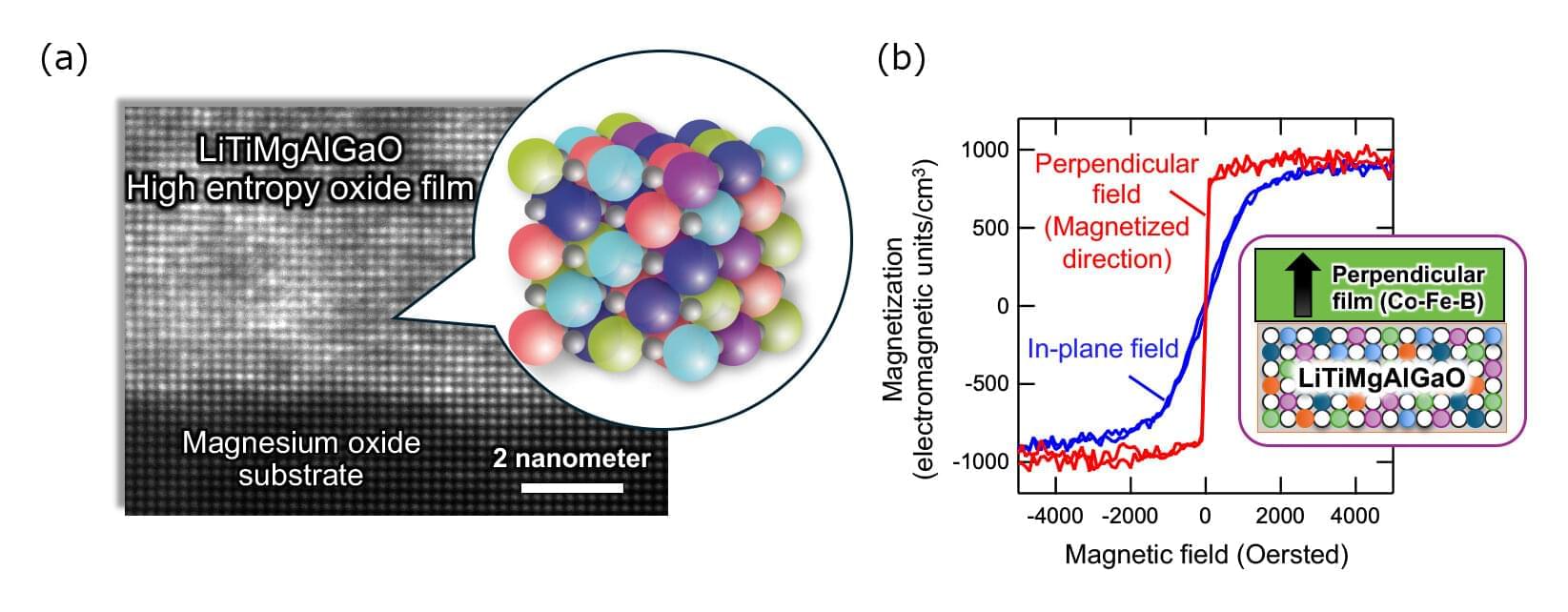
A NIMS research team has developed a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) featuring a tunnel barrier made of a high-entropy oxide composed of multiple metallic elements. This MTJ simultaneously demonstrated stronger perpendicular magnetization, a higher tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) ratio (i.e., the relative change in electrical resistance when the magnetization directions of the two ferromagnetic layers switch between parallel and antiparallel alignments) and lower electrical resistance.
These properties may contribute to the development of smaller, higher-capacity and higher-performance hard disk drives (HDDs) and magnetoresistive random access memory (MRAM).
This research is published in Materials Today.