US scientists tap seaweed for rare earths and metals used in EVs, electronics.
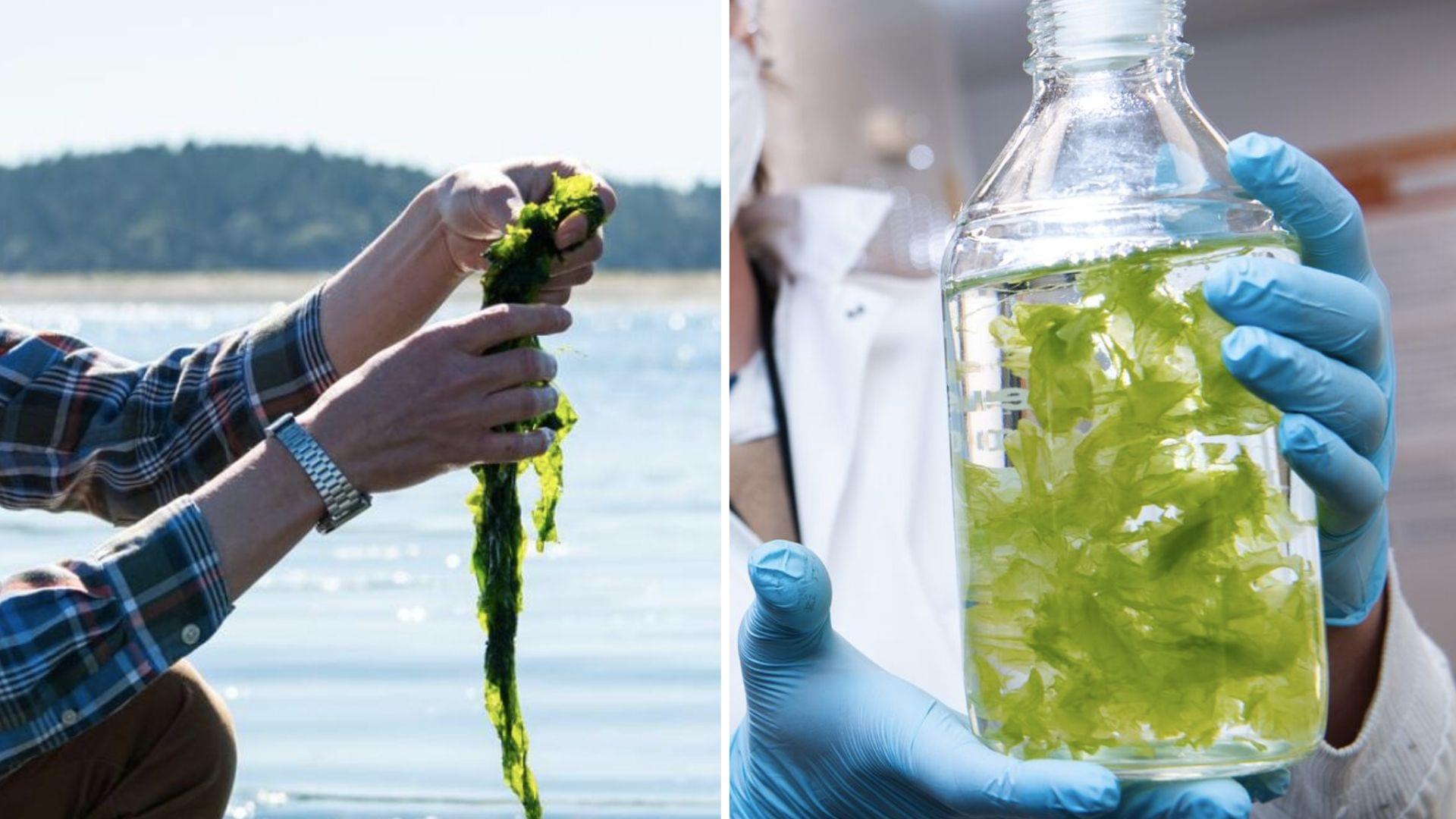
Researchers in the United States discovered a new way to extract rare earth minerals. They focused on seaweed, which hosts rare earth minerals in their leaf-like tissues. After multiple efforts, the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) research team successfully extracted critical mineral content from the seaweed biomass.
They have been growing several species in the Sequim campus and investigating different methods of extracting minerals from seaweed.