Wish he & a couple of others would join this ranks that others are on which makes way more sense plus benefits the masses tremendously. Musk needs to join others in their work to enhance humans via Quantum Biosystems as this work is already showing signs of success across multiple areas such as anti-aging, disease elimination, intelligence & communications, security, reduction in costs of healthcare & social programs, advancements in new creative innovations in technology & medicine, new industry new growth/ economic expansion, elimination of starvation, etc.
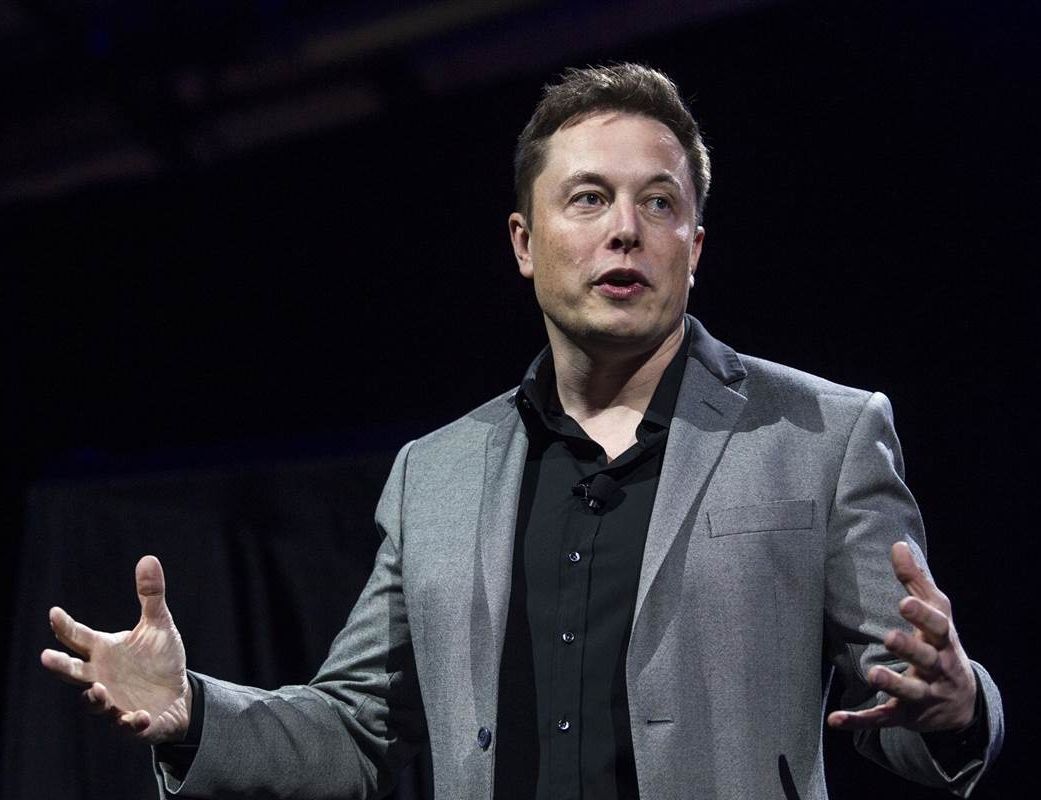
How can humans stay relevant in an age of artificial intelligence? Elon Musk thinks cyborgs are the answer.
The Tesla and SpaceX CEO discussed the need for a “merger of biological intelligence and digital intelligence” during a talk on Monday at the World Government Summit in Dubai, CNBC reported.
One of the main advantages computers have over humans is the speed at which they can send out information, Musk said. While humans are limited by the speed of their typing, a computer can send out information at “a trillion bits per second,” Musk said. As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more advanced, humans will also need to evolve to remain relevant, he added.