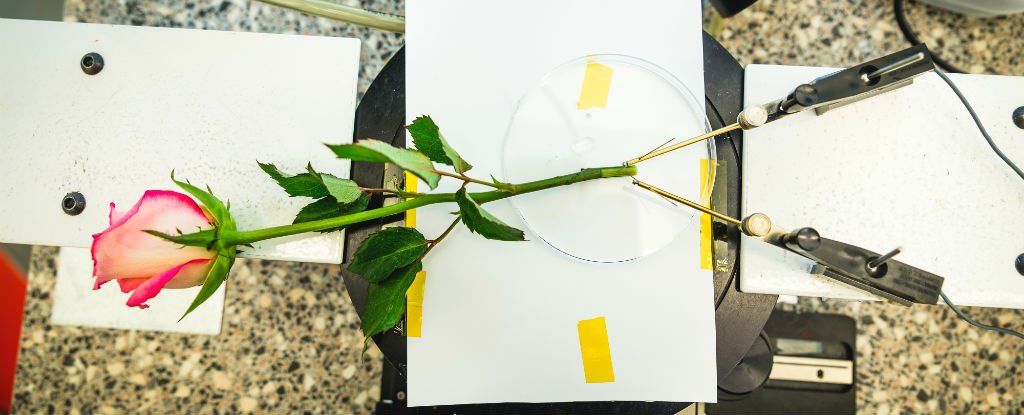
Scientists have figured out how to inject a conducting solution into a rose cutting, and have it spontaneously form wires throughout its stem, leaves, and petals to create fully functioning supercapacitors for energy storage.
The so-called e-Plant was able to be charged hundreds of times without any loss on the performance, and the team behind the invention says it could allow us to one day create fuel cells or autonomous energy systems inside living plants.
“A few years ago, we demonstrated that it is possible to create electronic plants, ‘power plants’, but we have now shown that the research has practical applications,” says one of the team, Magnus Berggren from Linköping University in Sweden.