FBI flags $262M in account-takeover losses while researchers track AI-boosted phishing, fake stores, and holiday scam domains.


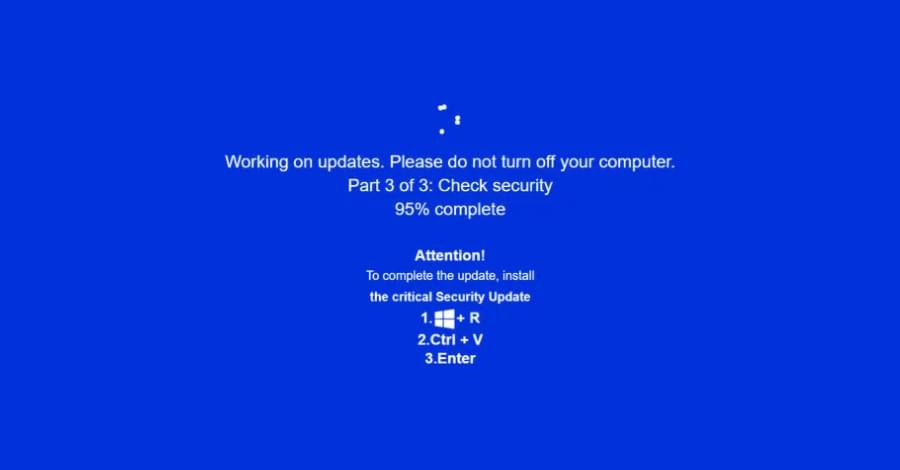
“Campaign leverages fake adult websites (xHamster, PornHub clones) as its phishing mechanism, likely distributed via malvertising,” Acronis said in a new report shared with The Hacker News. “The adult theme, and possible connection to shady websites, adds to the victim’s psychological pressure to comply with sudden ‘security update’ installation.”
ClickFix-style attacks have surged over the past year, typically tricking users into running malicious commands on their own machines using prompts for technical fixes or completing CAPTCHA verification checks. According to data from Microsoft, ClickFix has become the most common initial access method, accounting for 47% of attacks.
The latest campaign displays highly convincing fake Windows update screens in an attempt to get the victim to run malicious code, indicating that attackers are moving away from the traditional robot-check lures. The activity has been codenamed JackFix by the Singapore-based cybersecurity company.
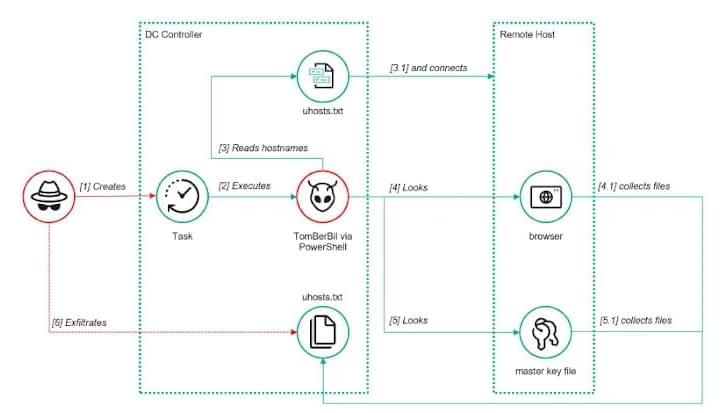


Risk management company Crisis24 has confirmed its OnSolve CodeRED platform suffered a cyberattack that disrupted emergency notification systems used by state and local governments, police departments, and fire agencies across the United States.
The CodeRED platform enables these agencies to send alerts to residents during emergencies.
The cyberattack forced Crisis24 to decommission the legacy CodeRED environment, causing widespread disruption for organizations that use the platform for emergency notifications, weather alerts, and other sensitive warnings.
#homelandsecurity #innovation
Having been involved in the creation of the Department of Homeland Security’s Science & Technology Directorate, and with decades of experience working at the intersection of government, industry, and academia, I have come to a simple but important observation: innovation in homeland security doesn’t happen in one area. Instead, it thrives where mission, research, and engineering come together.
Convergence is the catalyst. Cyber defense, autonomous systems, identity management, quantum computing, and photonics are all examples of technological advancements that didn’t develop in isolation. Their progress was the result of different sectors working together on shared goals, risk management, and practical use. Homeland security enterprise is constituted by a multi-sectoral nature: government sets mission needs, industry creates scalable solutions, and academia provides the necessary research. Real innovation happens when these areas come together.
Statistical data highlights the significance of this alignment. Research on cyber-behavior, for instance, demonstrates that organizational culture, national context, and employee backgrounds significantly impact risk outcomes. Practically speaking, this implies that secure systems cannot be developed in isolation. The human and institutional context is as crucial as technical advancements.

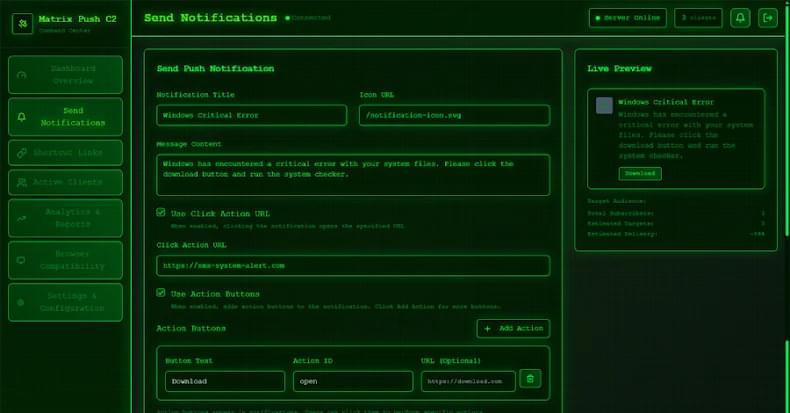
That’s not all. Since the attack plays out via the web browser, it’s also a cross-platform threat. This essentially turns any browser application on any platform that subscribes to the malicious notifications to be enlisted to the pool of clients, giving adversaries a persistent communication channel.
Matrix Push C2 is offered as a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) kit to other threat actors. It’s sold directly through crimeware channels, typically via Telegram and cybercrime forums, under a tiered subscription model: about $150 for one month, $405 for three months, $765 for six months, and $1,500 for a full year.
“Payments are accepted in cryptocurrency, and buyers communicate directly with the operator for access,” Dr. Darren Williams, founder and CEO of BlackFog, told The Hacker News. “Matrix Push was first observed at the beginning of October and has been active since then. There’s no evidence of older versions, earlier branding, or long-standing infrastructure. Everything indicates this is a newly launched kit.”

Once installed, the malware is designed to launch a core module that’s responsible for loading other plugins embedded in the shellcode into memory. It also comes fitted with a variety of anti-detection and persistence techniques. The activity has not been attributed to any known threat actor or group.
“After the proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code for the vulnerability was publicly released, attackers quickly weaponized it to distribute ShadowPad malware via WSUS servers,” AhnLab said. “This vulnerability is critical because it allows remote code execution with system-level permission, significantly increasing the potential impact.”
Found this article interesting? Follow us on Google News, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.

A Russian-linked campaign delivers the StealC V2 information stealer malware through malicious Blender files uploaded to 3D model marketplaces like CGTrader.
Blender is a powerful open-source 3D creation suite that can execute Python scripts for automation, custom user interface panels, add-ons, rendering processes, rigging tools, and pipeline integration.
If the Auto Run feature is enabled, when a user opens a character rig, a Python script can automatically load the facial controls and custom UI panels with the required buttons and sliders.