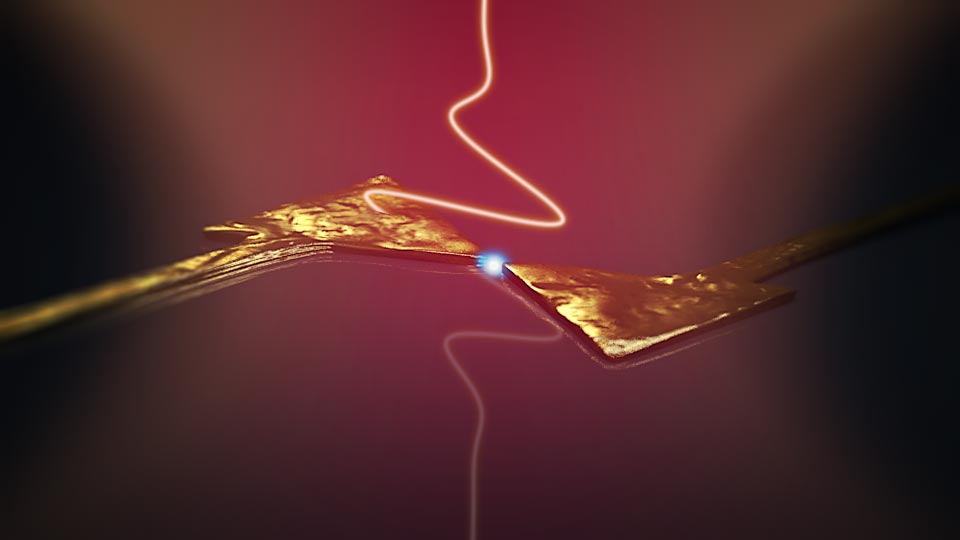
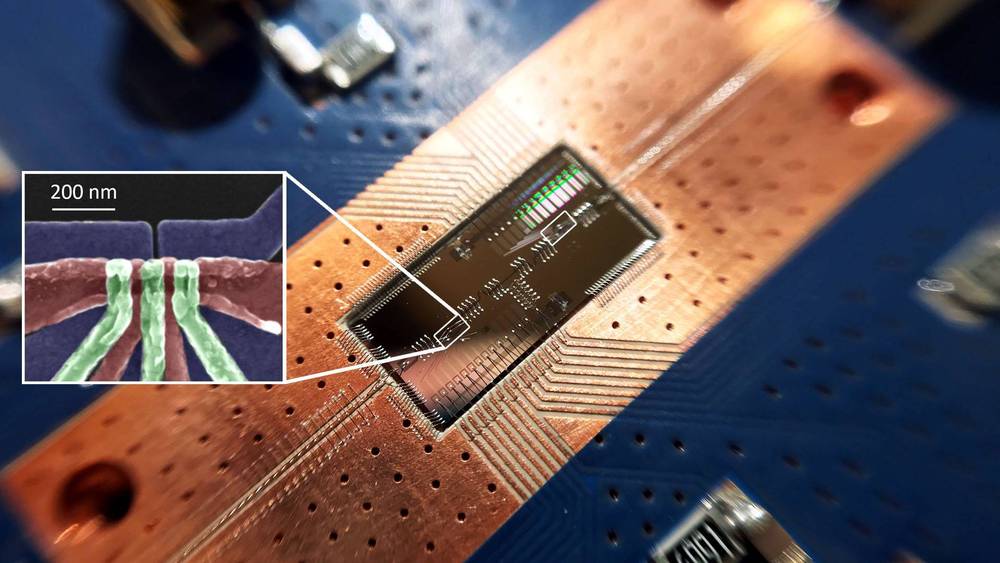
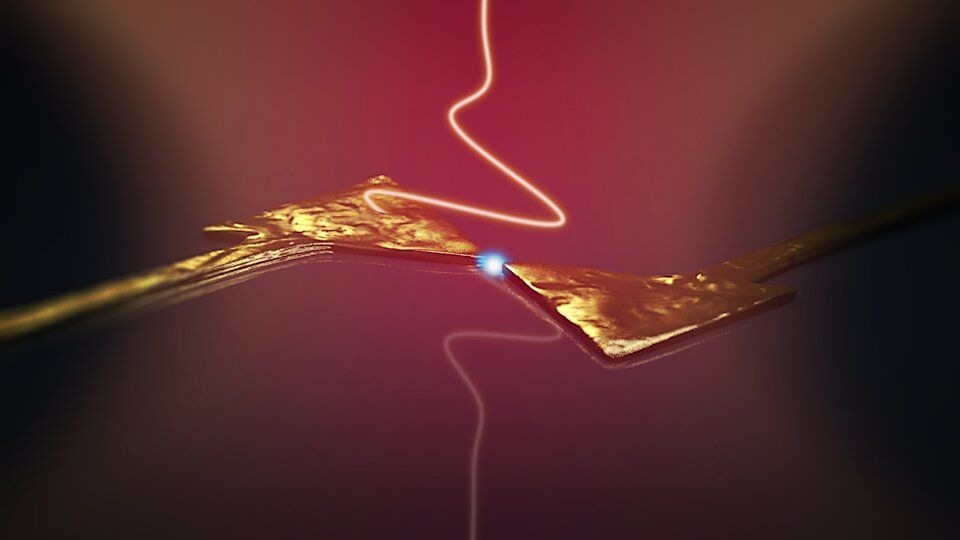
Scientists at the University of Bristol and the Technical University of Denmark have achieved quantum teleportation between two computer chips for the first time. The team managed to send information from one chip to another instantly without them being physically or electronically connected, in a feat that opens the door for quantum computers and quantum internet.
This kind of teleportation is made possible by a phenomenon called quantum entanglement, where two particles become so entwined with each other that they can “communicate” over long distances. Changing the properties of one particle will cause the other to instantly change too, no matter how much space separates the two of them. In essence, information is being teleported between them.
Hypothetically, there’s no limit to the distance over which quantum teleportation can operate – and that raises some strange implications that puzzled even Einstein himself. Our current understanding of physics says that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light, and yet, with quantum teleportation, information appears to break that speed limit. Einstein dubbed it “spooky action at a distance.”