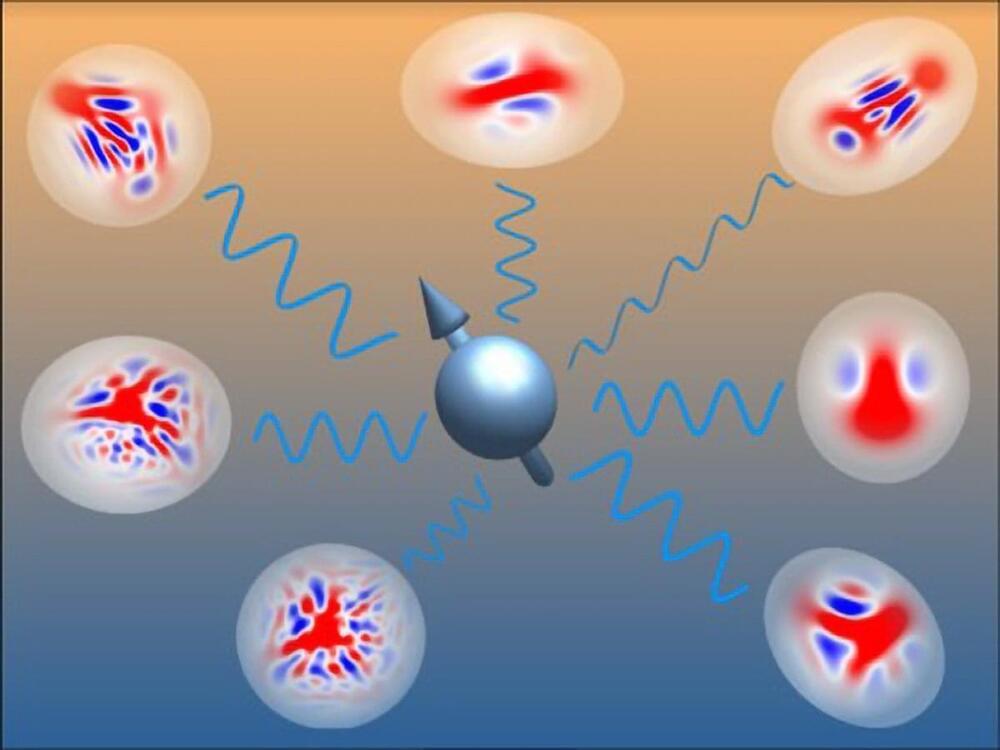
A new method developed by Amsterdam researchers uses non-Gaussian states to efficiently describe and configure quantum spin-boson systems, promising advancements in quantum computing and sensing.
Many modern quantum devices operate using groups of qubits, or spins, which have just two energy states: ‘0’ and ‘1’. However, in actual devices, these spins also interact with photons and phonons, collectively known as bosons, making the calculations much more complex. In a recent study published in Physical Review Letters, researchers from Amsterdam have developed a method to effectively describe these spin-boson systems. This breakthrough could help in efficiently setting up quantum devices to achieve specific desired states.
Quantum devices use the quirky behavior of quantum particles to perform tasks that go beyond what ‘classical’ machines can do, including quantum computing, simulation, sensing, communication, and metrology. These devices can take many forms, such as a collection of superconducting circuits, or a lattice of atoms or ions held in place by lasers or electric fields.