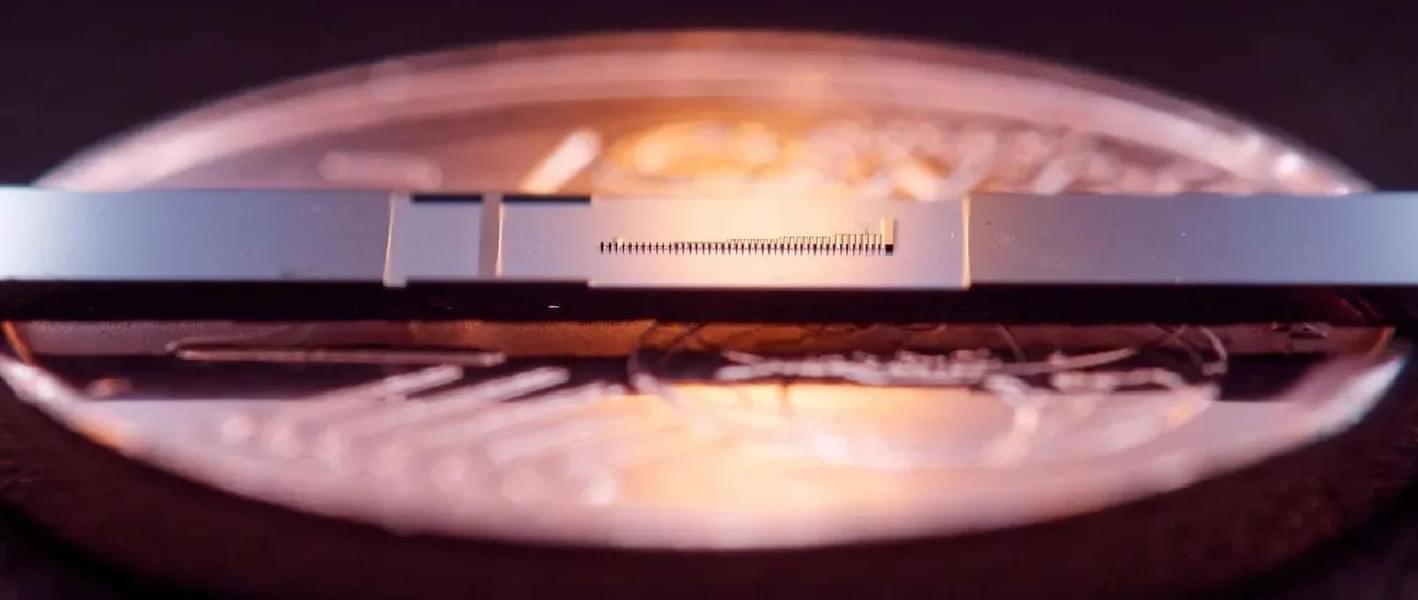
A research team from the University of Science and Technology of China has demonstrated the ability to electrically manipulate the spin filling sequence in a bilayer graphene (BLG) quantum dot (QD). This achievement, published in Physical Review Letters, showcases the potential to control the spin degree of freedom in BLG, a material with promising applications in quantum computing and advanced electronics.
BLG has drawn extensive attention in recent years due to its unique properties. When an out-of-plane electric field is applied, it can generate a tunable band gap. Moreover, the trigonal warping effect, caused by the skew interlayer coupling, gives rise to additional minivalley degeneracy, greatly influencing the behavior of charge carriers. Quantum dot devices, which can precisely control the number of charge carriers, have become a crucial tool for studying these phenomena at the single-particle level.
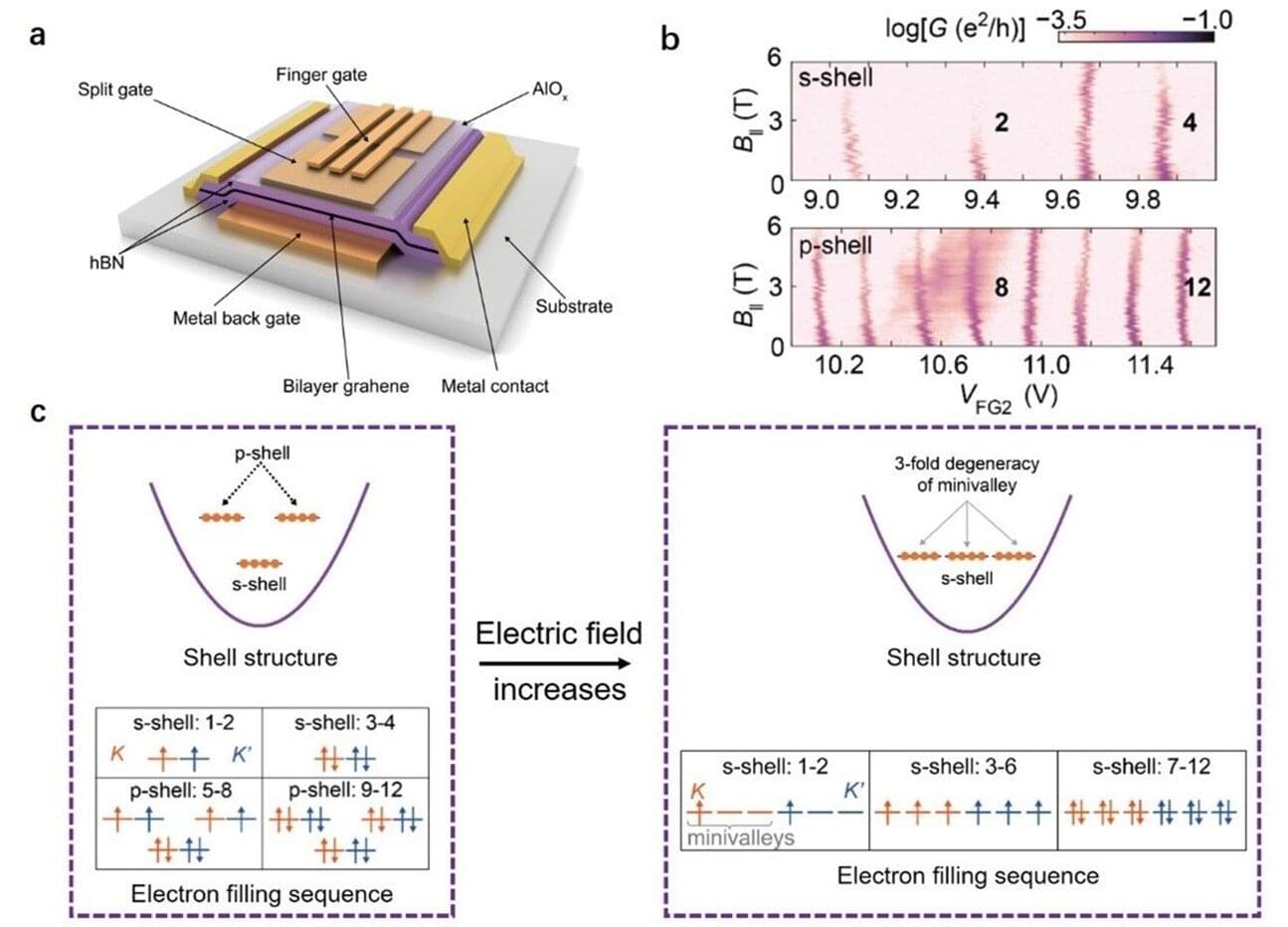
The research team delved into the intricate dynamics of electron shell structures within bilayer graphene quantum dot, focusing on how these structures can be manipulated through the trigonal warping effect, a unique feature of bilayer graphene. They employed a highly tunable quantum dot device, which provided the means to control the electron filling sequence. They began by applying a small perpendicular electric field, observing that the s-shell filled with four electrons, two with spin-up and two with spin-down, each from opposite valleys.