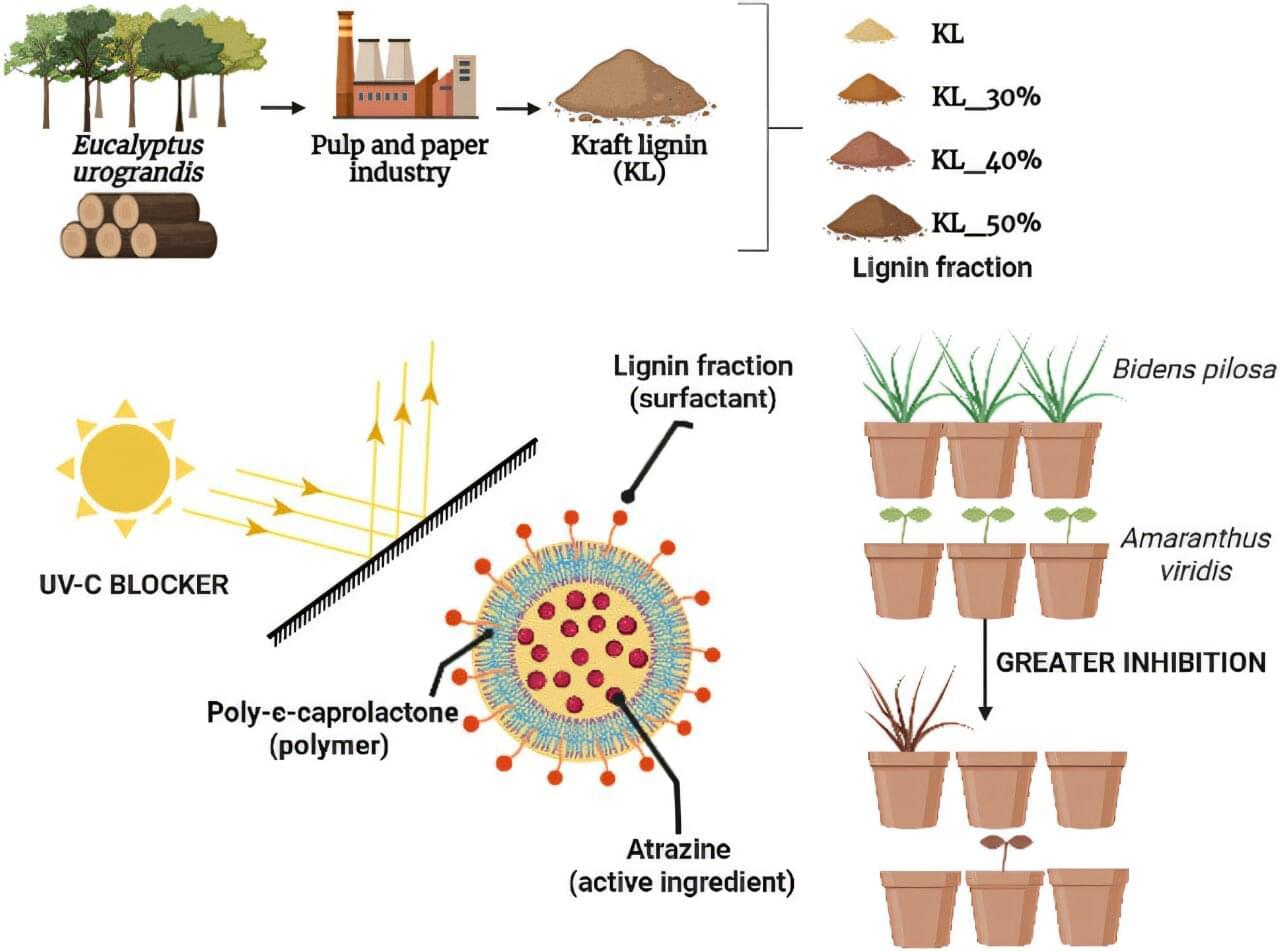
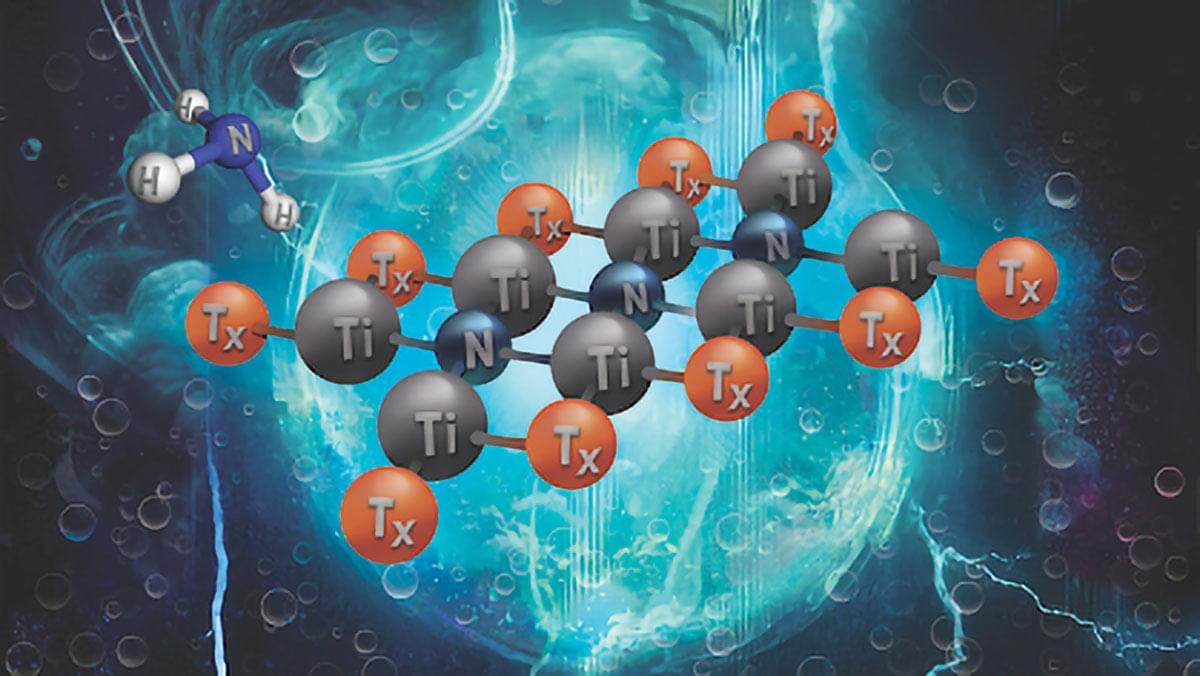
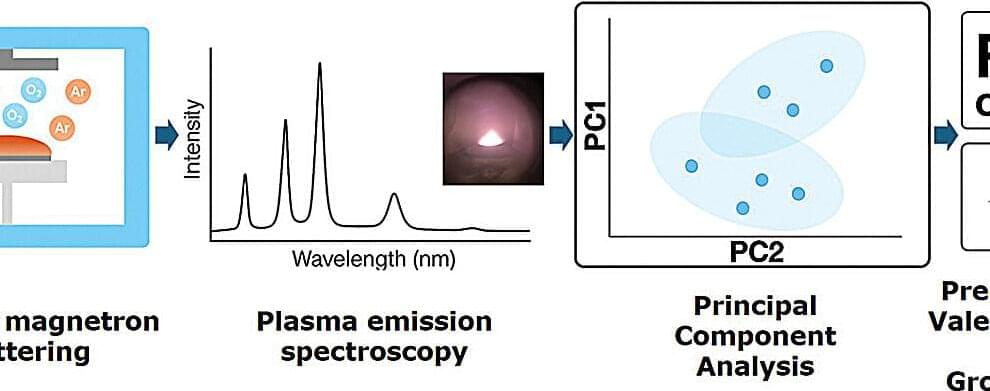
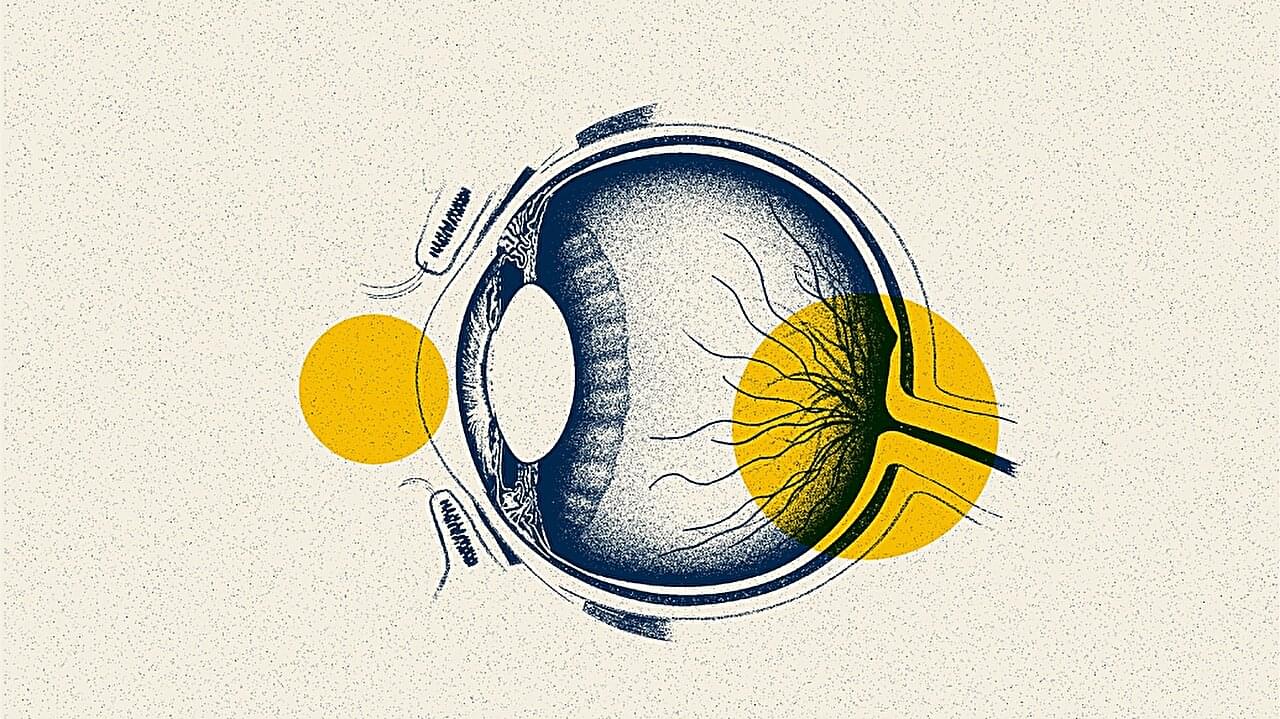
“We want to learn more about how our solar system formed moons. This means that we need to look at other systems that are still under construction. We’re trying to understand how it all works,” said Dr. Gabriela Cugno.
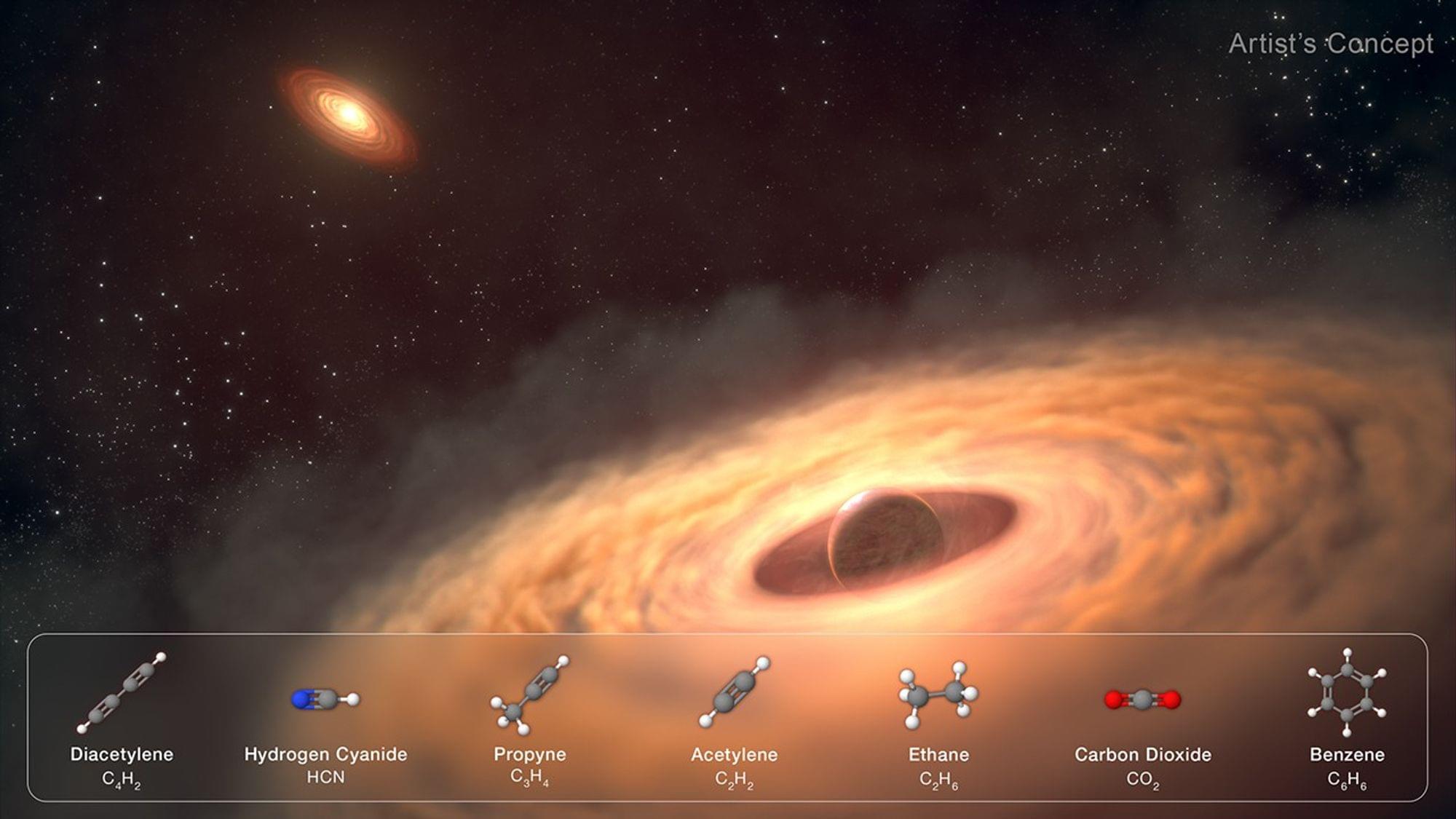
How do moons form around gas giant planets? This is what a recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated how circumplanetary disks (CPDs) comprised of the gas and dust leftover from planetary formation evolve into moons. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand the conditions for exomoon formation and evolution and where scientists could potentially search for life beyond Earth.
For the study, the researchers used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to observe the CPD orbiting CT Cha b, which is located approximately 620 light-years from Earth and is approximately 17 times as massive as Jupiter. The goal of the study was to ascertain the composition of the CPD and compare it to CT Cha b and the surrounding disk of the host star, CT Cha A.
In the end, the researchers found that the CPD around CT Cha b was composed of carbon-rich chemistry that contrasted compositions of gas giant exoplanet atmospheres. Additionally, the researchers found the CPD’s carbon-rich chemistry composition also contrasted with the disk surrounding CT Cha A. The team concluded that this is the first evidence of moon formation around a gas giant exoplanet and compared this to the potential formation mechanism for Jupiter’s Galilean moons.