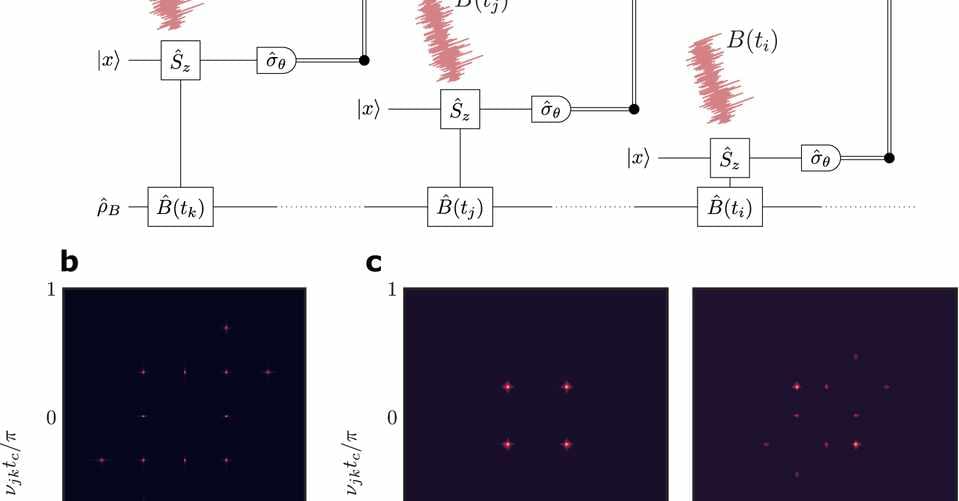
Circa 2021 face_with_colon_three
Metallic non-metals
In theory, most materials are capable of becoming metallic if put under enough pressure. Atoms or molecules can be squeezed together so tightly that they begin to share their outer electrons, which can then travel and conduct electricity as they do in a chunk of copper or iron. Geophysicists think that the centres of massive planets such as Neptune or Uranus host water in such a metallic state, and that high-pressure metallic hydrogen can even become a superconductor, able to conduct electricity without any resistance.
Turning water into a metal in this way would require an expected 15 million atmospheres of pressure, which is out of reach for current lab techniques, says Jungwirth. But he suspected that water could become conductive in an alternative way: by borrowing electrons from alkali metals. These reactive elements in group 1 of the periodic table, which includes sodium and potassium, tend to donate their outermost electron. Last year, Jungwirth and his colleague Phil Mason — a chemist who is also known for making science videos on YouTube — led a team that demonstrated a similar effect in ammonia2. The fact that ammonia can turn shiny in such conditions was known to the British chemist Humphry Davy in the early nineteenth century, Edwards points out.