“The most striking thing was the high dust levels,” said Dr. Eva Dock.
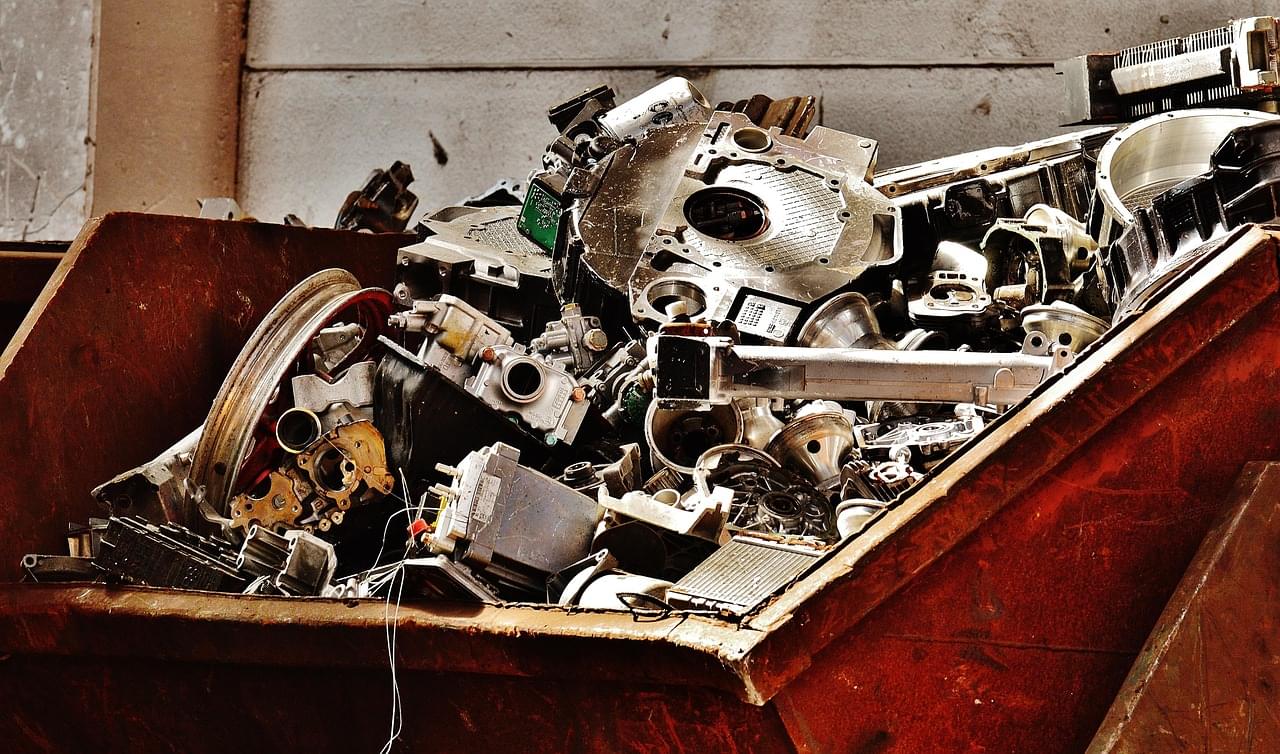
What risks can metal recycling pose to workers? This is what a recent study published in the International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health hopes to address as a collaborative team of researchers from Sweden investigated metal and dust exposure to recycling workers. This study holds the potential to help scientists, legislators, and the public better understand the risks of metal recycling as a means for enhancing green technologies.
For the study, the researchers analyzed observation and questionnaire data obtained from 139 recycling workers across 13 Swedish metal recycling companies. Additionally, the team obtained dust and metal samples to ascertain employee exposure and biological samples, including blood and urine, to ascertain individual metal and dust exposure. The goal of the study was to ascertain the efficacy of safety protocols and the severity of exposure to employees.
In the end, the researchers discovered alarming results, including 19 percent of the employees discovered to have heightened levels of more than 10 metals within their body and 94 having heightened levels of six metals. Of the 139 employees, 32 percent were involved in e-waste recycling, while safety protocols to mitigate dust exposure were discovered to be less than satisfactory, specifically regarding the use of respiratory equipment or hygiene protocols.