This is concerning in what is being proposed in the US for doctor report errors and it’s whole timing. Why now? I mean why wait to report on this when this has been known about for many decades plus mistakes today are actually a lot less than they were 2 decades ago thanks to medical records, and the self-monitor/ medicated drip devices, etc. My guess is this is part of a huge push by some to replace doctors and medical teams with more AI which in the US patients have been blocking AI to treat them due to their own distrust of AI.
Now, if US Laws are in place requiring doctors to publish, report, etc. their errors for the 1st time in the US it does help build case to the public and conditions the public to rethink their position on AI.
I am just not buying “the experts’” report stats given that he has no official records to back up his report especially detail records for the past 40 years showing doctors openly reporting any mistakes they made in the 70s, 80s or 90s when the equipment was poorer plus medical records in many situations were not always digital and could be easily lost in the 70s and 80s.
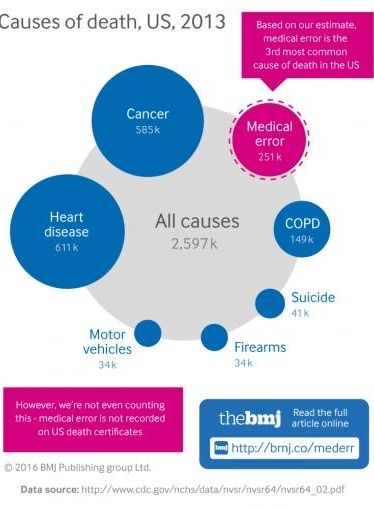
Medical error is the third leading cause of death in the US after heart disease and cancer, say experts in The BMJ today.
Martin Makary and Michael Daniel at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine in Baltimore say death certificates in the US have no facility for acknowledging medical error, and they call for better reporting to help understand the scale of the problem and how to tackle it.
Currently, death certification in the US relies on assigning an International Classification of Disease (ICD) code to the cause of death — so causes of death not associated with an ICD code, such as human and system factors, are not captured.