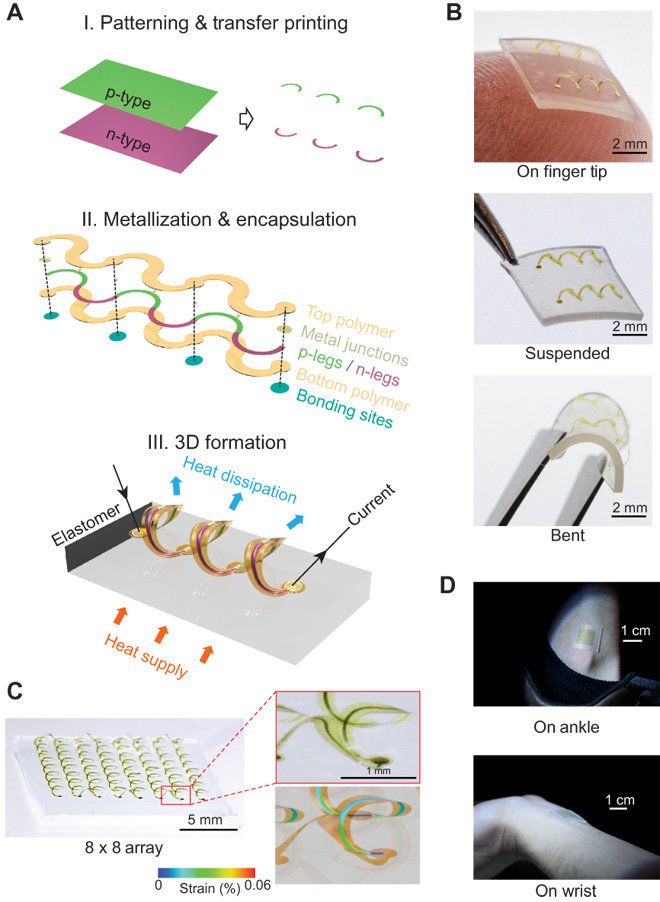
Miniaturized semiconductor devices with energy harvesting features have paved the way to wearable technologies and sensors. Although thermoelectric systems have attractive features in this context, the ability to maintain large temperature differences across device terminals remains increasingly difficult to achieve with accelerated trends in device miniaturization. As a result, a group of scientists in applied sciences and engineering has developed and demonstrated a proposal on an architectural solution to the problem in which engineered thin-film active materials are integrated into flexible three-dimensional (3D) forms.
The approach enabled efficient thermal impedance matching, and multiplied heat flow through the harvester to increase efficient power conversion. In the study conducted by Kewang Nan and colleagues, interconnected arrays of 3D thermoelectric coils were built with microscale ribbons of the active material monocrystalline silicon to demonstrate the proposed concepts. Quantitative measurements and simulations were conducted thereafter to establish the basic operating principles and key design features of the strategy. The results, now published on Science Advances, suggested a scalable strategy to deploy hard thermoelectric thin-films within energy harvesters that can efficiently integrate with soft material systems including human tissue to develop wearable sensors in the future.
Thermoelectric devices provide a platform to incorporate ubiquitous thermal gradients that generate electrical power. To operate wearable sensors or the “Internet of Things” devices, the temperature gradient between the surrounding environment and the human body/inanimate objects should provide small-scale power supplies. Continued advances in the field focus on aggressive downscaling of power requirements for miniaturized systems to enhance their potential in thermoelectric and energy harvesting applications. Integrated processors and radio transmitters for example can operate with power in the range of subnanowatts, some recent examples are driven via ambient light-based energy harvesting and endocochlear potential. Such platforms can be paired with sensors with similar power to enable distributed, continuous and remote environmental/biochemical monitoring.