Carnegie Mellon University computer scientists have taken a deep learning method that has revolutionized face recognition and other image-based applications in recent years and redirected its power to explore the relationship between genes.
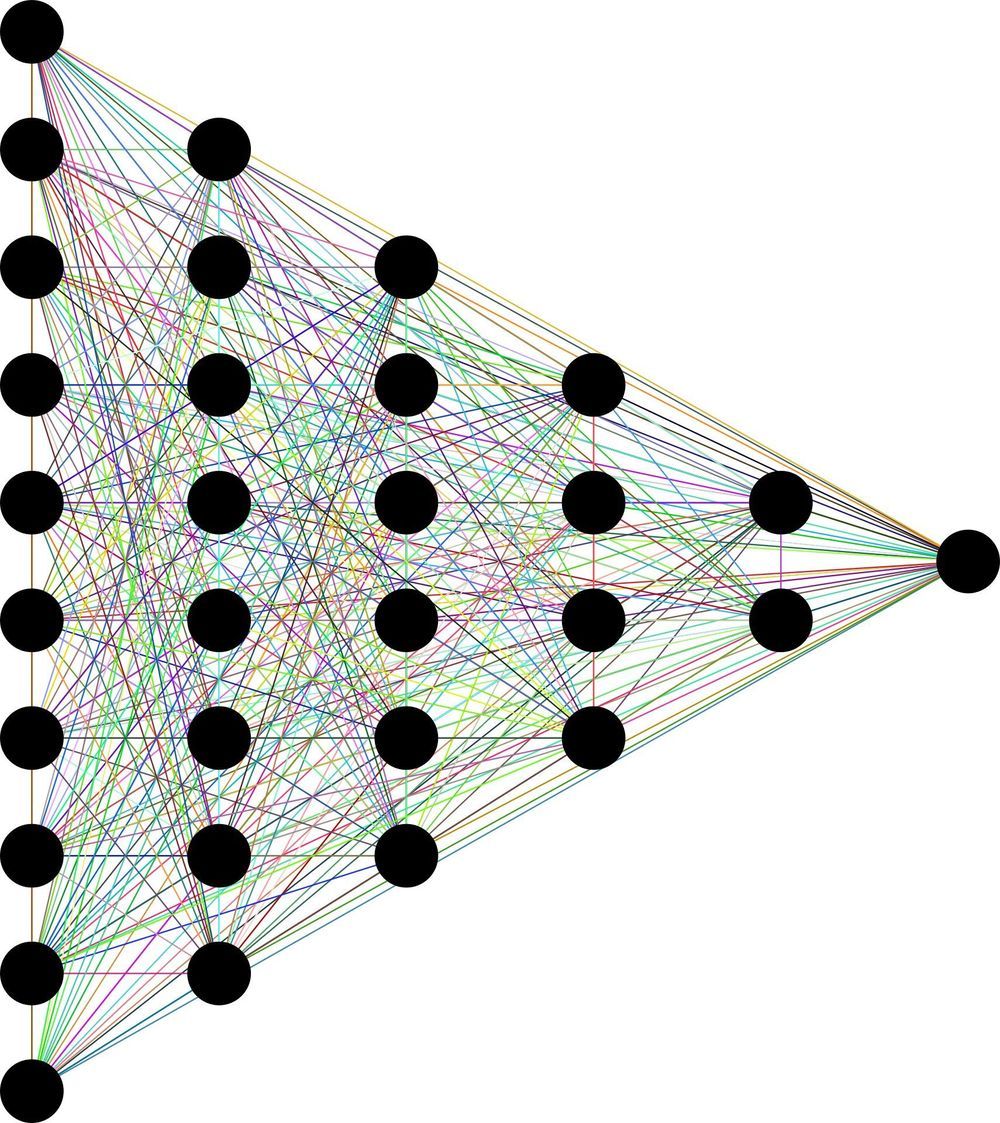
The trick, they say, is to transform massive amounts of gene expression data into something more image-like. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which are adept at analyzing visual imagery, can then infer which genes are interacting with each other. The CNNs outperform existing methods at this task.
The researchers’ report on how CNNs can help identify disease-related genes and developmental and genetic pathways that might be targets for drugs is being published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. But Ziv Bar-Joseph, professor of computational biology and machine learning, said the applications for the new method, called CNNC, could go far beyond gene interactions.