The FDA issued the emergency authorization to use blood purification devices to treat coronavirus patients on Friday.



Around a year ago…
Pretty cool.
In the past several months, China has offered several remote surgery demonstrations using 5G. The technologies promise better care over a wider area.

Within a week, many world leaders went from downplaying the seriousness of coronavirus to declaring a state of emergency. Even the most efficacious of nations seem to be simultaneously confused and exasperated, with delayed responses revealing incompetence and inefficiency the world over.
So this begs the question: why is it so difficult for us to comprehend the scale of what an unmitigated global pandemic could do? The answer likely relates to how we process abstract concepts like exponential growth. Part of the reason we’ve struggled so much applying basic math to our practical environment is because humans think linearly. But like much of technology, biological systems such as viruses can grow exponentially.
As we scramble to contain and fight the pandemic, we’ve turned to technology as our saving grace. In doing so, we’ve effectively hit a “fast-forward” button on many tech trends that were already in place. From remote work and virtual events to virus-monitoring big data, technologies that were perhaps only familiar to a fringe tech community are now entering center stage—and as tends to be the case with wartime responses, these changes are likely here to stay.
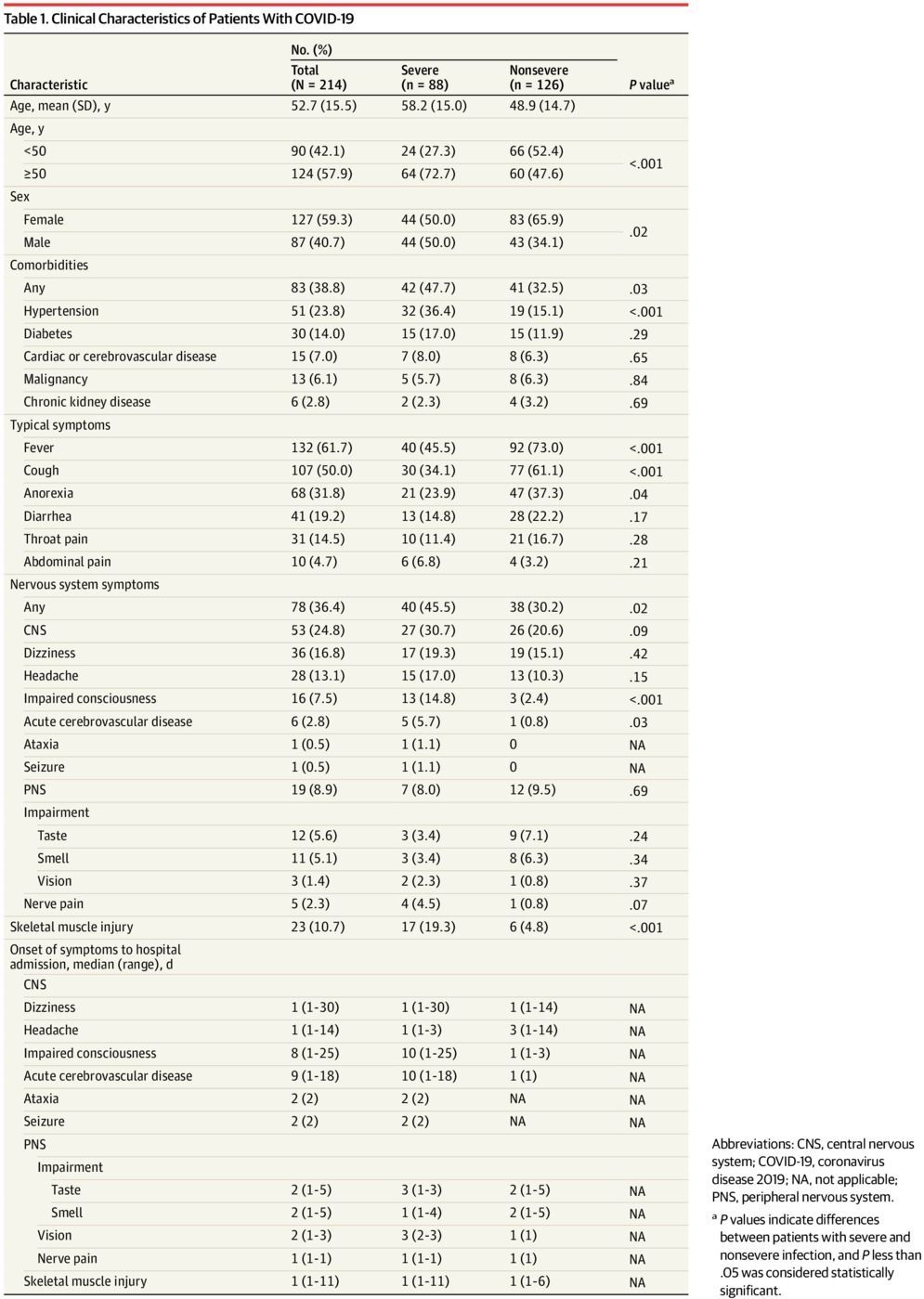
Findings In a case series of 214 patients with coronavirus disease 2019, neurologic symptoms were seen in 36.4% of patients and were more common in patients with severe infection (45.5%) according to their respiratory status, which included acute cerebrovascular events, impaired consciousness, and muscle injury.
Published Online: April 10, 2020. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127
Author Contributions: Dr B. Hu had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Drs Mao, Jin, M. Wang, Y. Hu, Chen, He, and Chang contributed equally and share first authorship.
Concept and design: Mao, Jin, Y. Hu, He, Miao, B. Hu.

The precious metal has been torn between its potential as a haven investment and a mad scramble to sell the tangible asset in a bid for cash to cover losses in the stock market.
“The Covid-19 outbreak has had a major impact on the gold market, bringing massive price swings as investors react to new developments related to the pandemic,” says Steven Dunn, head of exchange-traded funds at Aberdeen Standard Investments.
“Because of Covid-19, refiners were knocked offline…and the ability to move gold became a challenge as normal means of transport became almost impossible,” he says.
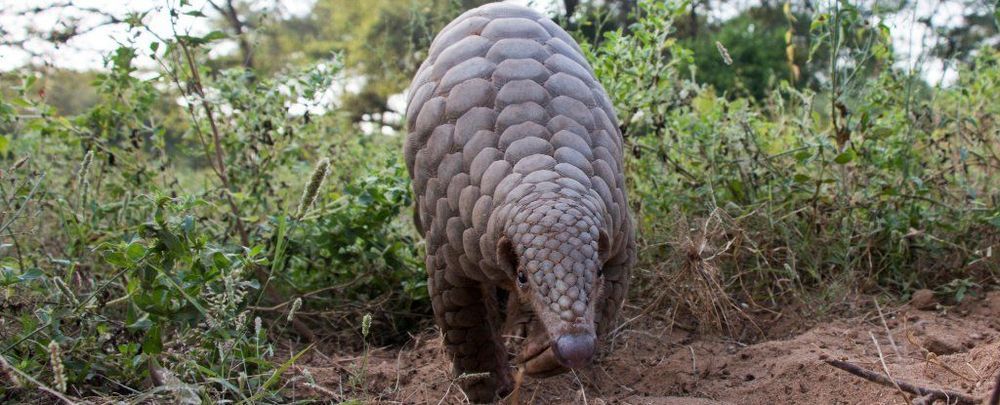

Pangolins, not snakes, may be the missing link for transmission of the new coronavirus from bats to humans.
Since its initial outbreak at Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, China, in late 2019, COVID-19 has since infected more than a million people across the globe. To understand and control the transmission of COVID-19, scientists are racing to study the coronavirus causing the disease: SARS-CoV-2, previously named 2019-nCoV.
SARS-CoV-2 is zoonotic, which means that the virus originated in animals and jumped to humans. A critical challenge is to determine which animal transmitted the virus to humans.


NEW DELHI: For the last four years, it was used for crop dusting. But now, it has a new name and purpose. Chennai-based startup Garuda Aerospace’s drone is spraying disinfectant all over locked down cities in its new avatar of Corona Killer-100.
Garuda has deployed 300 drones across 26 Indian cities, including Varanasi, Raipur and many in Tamil Nadu, at the behest of state governments and municipal bodies that are looking for ways to disinfect their areas with as little human intervention as possible. “We spray in public areas, hospitals, bus stations — anywhere Covid-19 can spread,” says Agnishwar Jayaprakash, the founder and president of the startup. Commercial pilot volunteers are steering these drones.
Across the country, startups are utilising the lockdown period to innovate and add to the state’s arsenal to fight the coronavirus pandemic. Their work has resulted in disinfectant-spraying drones, drones that make public announcements or shoo away crowds during a lockdown, disinfectant trucks, new kinds of sanitisers and even robotic dispensers.
