Everyone knows that the great and power omnipresent mushroom that lives across the universe able to survive even in space.
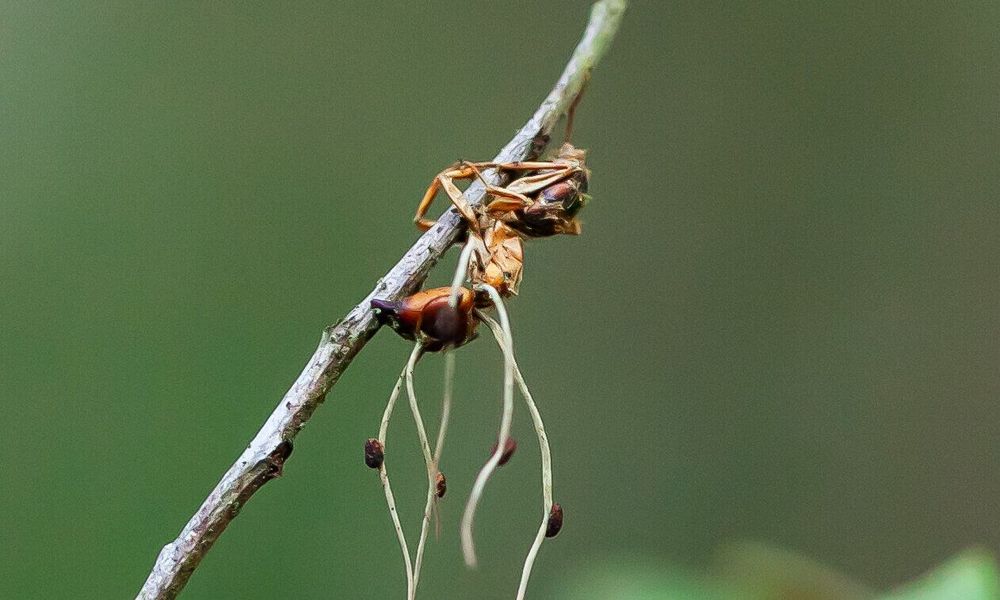
Researchers have elucidated the molecular mechanism of the fungus that turns ants into living zombies. The fungus specifically affects the ants’ neurobiology, odor perception and biological clock. The Utrecht microbiologist Robin Ohm publishes this, together with American and German colleagues, in G3.
The fungus Ophiocordyceps camponoti-floridani can infect ants and manipulate their behavior in a way that is beneficial for fungus growth and transmission. These infected ants are called “zombie ants.” Influenced by the fungus, the ants climb to a high point and bite into a branch, attaching themselves until death. The fungus then digests the ant and forms a fruitbody with which the fungus spreads its spores. The molecular mechanisms behind this behavioral modification are still largely unknown, as in similar parasitic interactions in which the behavior of a host is manipulated.
“We can realistically recreate this interaction between the fungus and the ant in the lab. We have sequenced the genome of the fungus and determined all its genes. This gives us an important tool with which we can examine this system in detail,” says fungal researcher Robin Ohm of Utrecht University. “We then looked at the expression of all genes in the fungus and the ant during the behavioral modification. In this way, you get a good picture of the genes of both the fungus and the ant that may be involved in the behavioral modification.”