By studying the DNA of people who lived in East Asia thousands of years ago, scientists are starting to untangle how the region was populated.
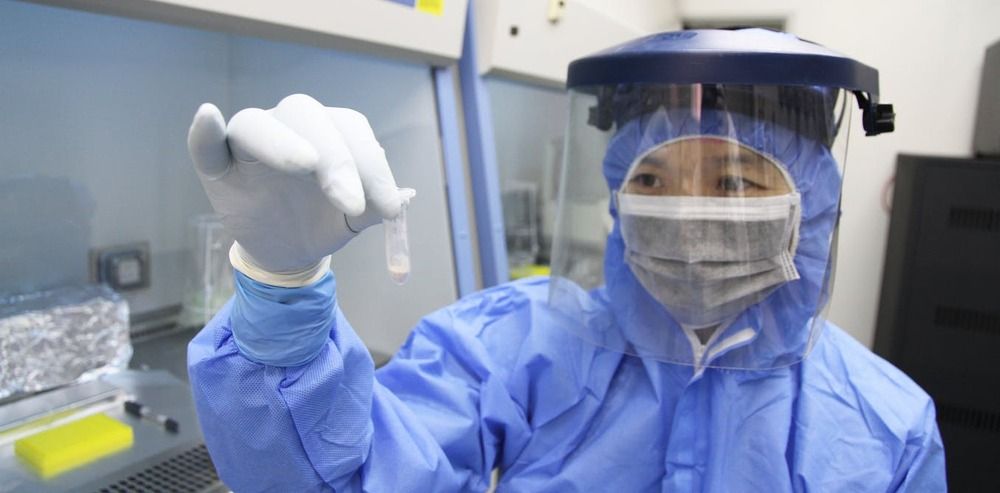


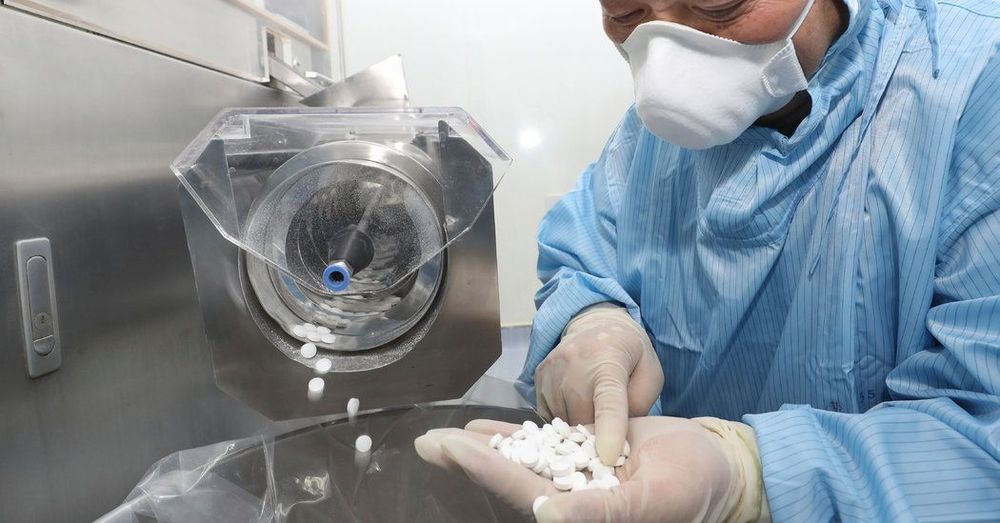
Scientists at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine have isolated “the smallest biological molecule” that “completely and specifically neutralizes” the virus that causes COVID-19.
The antibody component is 10 times smaller than a full-size antibody, and has been used to create the drug Ab8, shared in the report published by the researchers in the journal Cell on Monday. The drug is seen as a potential preventative against SARS-CoV-2.
According to the report, the drug has been “highly effective in preventing and treating” SARS-CoV-2 infections in mice and hamsters during tests. The drug also reportedly does not bind to human cells, which suggests it will not have negative side effects in people.
Gold isn’t just a pretty face – it’s shown promise in fighting cancer in many studies. Now researchers have found a way to grow gold nanoparticles directly inside cancer cells within 30 minutes, which can help with imaging and even be heated up to kill the tumors.
Gold isn’t just a pretty face – it’s shown promise in fighting cancer in many studies. Now researchers have found a way to grow gold nanoparticles directly inside cancer cells within 30 minutes, which can help with imaging and even be heated up to kill the tumors.
In previous work, gold nanostars, nanotubes and other nanoparticle structures have been sent into battle against cancer, but one of the main hurdles is getting the stuff inside the tumors. Sometimes they’re equipped with peptides that hunt down cancer, while others sneak in attached to white blood cells.
For this new study, researchers instead found a way to grow the gold directly inside the cancer cells. The advantage is that it doesn’t require as high a concentration of gold in the cell, and it can be done much quicker than other methods.
The is a multi-sport event, an international competition in which people with physical disabilities compete against each other to complete everyday tasks using state-of-the-art technical assistance Systems (“pilots”). Besides the actual competition, the offers a platform to drive forward research on assistance systems for everyday use, and to promote dialogue with the public.
The first organised by the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich (ETH Zurich) took place in the Swiss Arena in Kloten north of Zurich in Switzerland on 8 October 2016 and was the first international competition of this kind.[1][2][3] 66 pilots from 25 nations competed in front of a stadium with approximately 4600 spectators.
The next takes place on 13–14 November 2020 in a new format at the teams’ home base instead of in the Swiss Arena in Kloten, Zurich as it had been planned[4]. This is due to the COVID-19 pandemic which requires measures such as social distancing to be adhered. Termed the “Global Edition”, teams will set up their infrastructure for the competition at their home base and capture their races on video instead of competing physically next to each other in Zurich. officials will supervise the pilots which will start individually [5].

Pfizer Inc said on Tuesday participants were showing mild-to-moderate side effects when given either the company’s experimental coronavirus vaccine or a placebo in an ongoing late-stage study.
(Reuters) — Pfizer Inc PFE.N said on Tuesday participants were showing mostly mild-to-moderate side effects when given either the company’s experimental coronavirus vaccine or a placebo in an ongoing late-stage study.
The company said in a presentation to investors that side effects included fatigue, headache, chills and muscle pain. Some participants in the trial also developed fevers — including a few high fevers. The data is blinded, meaning Pfizer does not know which patients received the vaccine or a placebo.
Kathrin Jansen, Pfizer’s head of vaccine research and development, stressed that the independent data monitoring committee “has access to unblinded data so they would notify us if they have any safety concerns and have not done so to date.”

Myotonic dystrophy type I is the most common type of adult-onset muscular dystrophy. People with the condition inherit repeated DNA segments that lead to the toxic buildup of repetitive RNA, the messenger that carries a gene’s recipe to the cell’s protein-making machinery. As a result, people born with myotonic dystrophy experience progressive muscle wasting and weakness and a wide variety of other debilitating symptoms.
CRISPR-Cas9 is a technique increasingly used in efforts to correct the genetic (DNA) defects that cause a variety of diseases. A few years ago, University of California San Diego School of Medicine researchers redirected the technique to instead modify RNA in a method they call RNA-targeting Cas9 (RCas9).
In a new study, publishing September 14, 2020 in Nature Biomedical Engineering, the team demonstrates that one dose of RCas9 gene therapy can chew up toxic RNA and almost completely reverse symptoms in a mouse model of myotonic dystrophy.

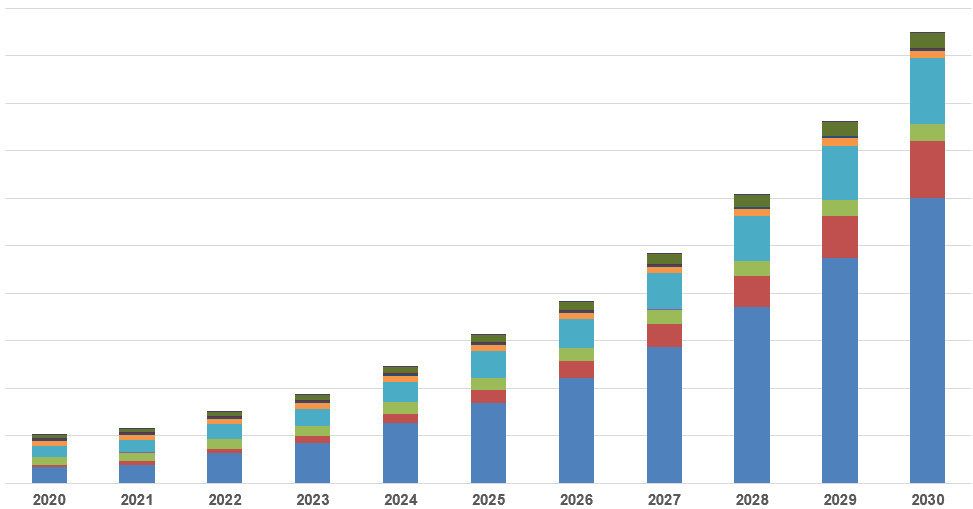
BOSTON, July 27, 2020 /PRNewswire/ — Solid-state batteries keep on attracting tremendous attention and investment with the maturing technologies and closeness to mass production. Even with the influence of COVID-19, the potential market size is expected to grow to over $6 billion by 2030, according to IDTechEx’s report “Solid-State and Polymer Batteries 2020–2030: Technology, Patents, Forecasts, Players.”
A Chinese virologist who has alleged that COVID-19 was human-made in a lab in China released a report on Monday that she says backs up her explosive claim.
Dr. Li-Meng Yan, a former researcher at the Hong Kong School of Public Health, posted a paper on the open-access repository website Zenote, that she claims shows how SARS-CoV-2 could be “conveniently created” in a laboratory setting in six months.
The paper, co-authored with two others, is titled “Unusual Features of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome Suggesting Sophisticated Laboratory Modification Rather Than Natural Evolution and Delineation of Its Probable Synthetic Route.”
