British scientists are optimistic that they might be on the way to finding a cure for HIV after a promising clinical trial, in which a test patient was shown to have no symptoms of the virus following treatment.



Nice POV read.
We know that emerging innovations within cutting-edge science and technology (S&T) areas carry the potential to revolutionize governmental structures, economies, and life as we know it. Yet, others have argued that such technologies could yield doomsday scenarios and that military applications of such technologies have even greater potential than nuclear weapons to radically change the balance of power. These S&T areas include robotics and autonomous unmanned system; artificial intelligence; biotechnology, including synthetic and systems biology; the cognitive neurosciences; nanotechnology, including stealth meta-materials; additive manufacturing (aka 3D printing); and the intersection of each with information and computing technologies, i.e., cyber-everything. These concepts and the underlying strategic importance were articulated at the multi-national level in NATO’s May 2010 New Strategic Concept paper: “Less predictable is the possibility that research breakthroughs will transform the technological battlefield … The most destructive periods of history tend to be those when the means of aggression have gained the upper hand in the art of waging war.”
As new and unpredicted technologies are emerging at a seemingly unprecedented pace globally, communication of those new discoveries is occurring faster than ever, meaning that the unique ownership of a new technology is no longer a sufficient position, if not impossible. They’re becoming cheaper and more readily available. In today’s world, recognition of the potential applications of a technology and a sense of purpose in exploiting it are far more important than simply having access to it.
While the suggestions like those that nanotechnology will enable a new class of weapons that will alter the geopolitical landscape remain unrealized, a number of unresolved security puzzles underlying emerging technologies have implications for international security, defense policy, deterrence, governance, and arms control regimes.
Still keeping my optics working looking for news to apply to your cyberpunk games and writings.
A way to defend against counterfeit drugs and maybe food too, miniature edible barcodes. Inexpensive, practical and readable with a slight modification of a smart phone.
For some reason, the idea of edible food wrappers just seems very cyberpunk to me. Full of advertising and nutrition!
How we can use CRISPR/Cas9 to treat the processes of aging.
Oliver Medvedik, Cofounder of the Life Extension Advocacy Foundation and the Lifespan.io Crowdfunding platform, discusses the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system in depth and highlights how it may be used to help overcome the diseases and disabilities of aging. He also gives an overview of other promising areas in aging research, such as senescent cell-clearing drugs, or “senolytics”, and “augmentive” compounds that may help restore the body to youthful functionality.
Support our campaigns: https://www.lifespan.io/

Phototactic behaviour directs some bacteria towards light and others into darkness: This enables them to utilize solar energy as efficiently as possible for their metabolism, or, otherwise, protects them from excessive light intensity. A team of researchers headed by Clemens Bechinger from the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems and the University of Stuttgart, as well as colleagues from the University of Düsseldorf have now found a surprisingly simple way to direct synthetic microswimmers towards light or darkness. Their findings could eventually lead to minuscule robots that seek out and treat lesions in the human body.
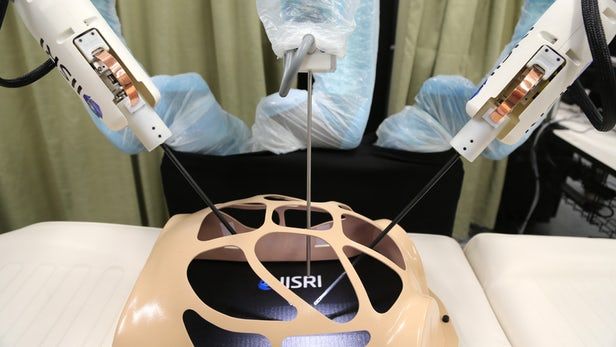
A new system called HeroSurg, developed by researchers at Deakin and Harvard Universities, is set to increase what surgeons can achieve via robotic surgery, using a haptic feedback system to provide a sense of touch. It also brings other improvements over existing tech, such as collision avoidance, to make robotic surgery safer and more accurate.
Robotic surgery, wherein human-controlled robots perform delicate surgical tasks, has been around for a while. One great example of the tech is the da Vinci robotic surgical system from Intuitive Surgical – a setup made up of numerous robotic arms, a console to operate the instruments, and an imaging system that shows the surgeon what’s happening in real time. In 2008, Professor Suren Krishnan, a member of the team behind HeroSurg, became the first surgeon to perform ear, throat and nose operations using the da Vinci robotic surgical system.
Since then, we’ve seen numerous breakthroughs, including improvements to the original da Vinci system, and other robots emerging capable of achieving impressive tasks, such as performing surgery on a beating heart, or successfully stitching soft tissue.

Boston-based startup completes $23 million Series A financing to leverage novel imaging platform of gene locations towards gaining diagnostic insights and delivering therapeutics for cancer, immuno-oncology, infectious diseases, neurological and neuromuscular diseases, brain function and cognitive disorders
BOSTON—(BUSINESS WIRE)—ReadCoor, Inc., today announced completion of an oversubscribed $23 million Series A financing round and its concurrent launch from Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering. ReadCoor will commercialize the Wyss Institute’s FISSEQ (fluorescent in situ sequencing) technology.
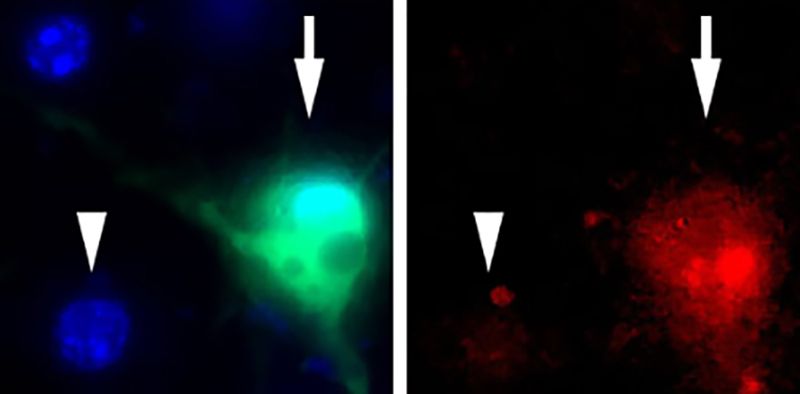
MIT researchers have designed nanosensors that can profile tumors and may yield insight into how they will respond to certain therapies. The system is based on levels of enzymes called proteases, which cancer cells use to remodel their surroundings.
Once adapted for humans, this type of sensor could be used to determine how aggressive a tumor is and help doctors choose the best treatment, says Sangeeta Bhatia, the John and Dorothy Wilson Professor of Health Sciences and Technology and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and a member of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research.
“This approach is exciting because people are developing therapies that are protease-activated,” Bhatia says. “Ideally you’d like to be able to stratify patients based on their protease activity and identify which ones would be good candidates for these therapies.”

A Northwestern Engineering research team has developed a 3D printable ink that produces a synthetic bone implant that rapidly induces bone regeneration and growth. This hyperelastic “bone” material, whose shape can be easily customized, one day could be especially useful for the treatment of bone defects in children.
Bone implantation surgery is never an easy process, but it is particularly painful and complicated for children. With both adults and children, often times bone is harvested from elsewhere in the body to replace the missing bone, which can lead to other complications and pain. Metallic implants are sometimes used, but this is not a permanent fix for growing children.
“Adults have more options when it comes to implants,” said Ramille N. Shah, who led the research. “Pediatric patients do not. If you give them a permanent implant, you have to do more surgeries in the future as they grow. They might face years of difficulty.”