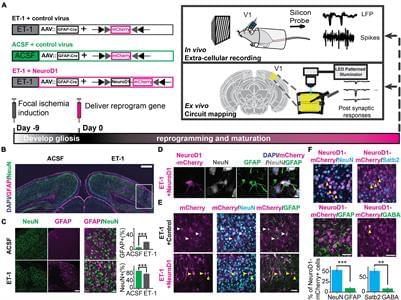
Neural circuits underlying brain functions are vulnerable to damage, including ischemic injury, leading to neuronal loss and gliosis. Recent technology of direct conversion of endogenous astrocytes into neurons in situ can simultaneously replenish the neuronal population and reverse the glial scar. However, whether these newly reprogrammed neurons undergo normal development, integrate into the existing neuronal circuit, and acquire functional properties specific for this circuit is not known. We investigated the effect of NeuroD1-mediated in vivo direct reprogramming on visual cortical circuit integration and functional recovery in a mouse model of ischemic injury. After performing electrophysiological extracellular recordings and two-photon calcium imaging of reprogrammed cells in vivo and mapping the synaptic connections formed onto these cells ex vivo, we discovered that NeuroD1 reprogrammed neurons were integrated into the cortical microcircuit and acquired direct visual responses. Furthermore, following visual experience, the reprogrammed neurons demonstrated maturation of orientation selectivity and functional connectivity. Our results show that NeuroD1-reprogrammed neurons can successfully develop and integrate into the visual cortical circuit leading to vision recovery after ischemic injury.
Functional circuit impairment associated with neuronal loss is commonly seen in patients with brain injuries, such as ischemia. Though neural stem cells (NSCs) exist in the subventricular zone (SVZ) in the adult brain, they are found to differentiate mainly into astrocytes when they migrate to injured cortex (Benner et al., 2013; Faiz et al., 2015), and their neurogenesis capacity is too limited to compensate for the neuronal loss. Currently, it still remains a challenge to generate neurons in adults and functionally incorporate them into the local circuits. Several strategies have shown the capability to induce neurogenesis and lead to some behavioral recovery. One promising approach is to transplant stem cell-derived neurons or neural progenitor cells (Tornero et al., 2013; Michelsen et al., 2015; Falkner et al., 2016; Somaa et al., 2017). Yet, there are concerns about graft rejection and tumorigenicity of the transplanted cells (Erdo et al., 2003; Marei et al., 2018).