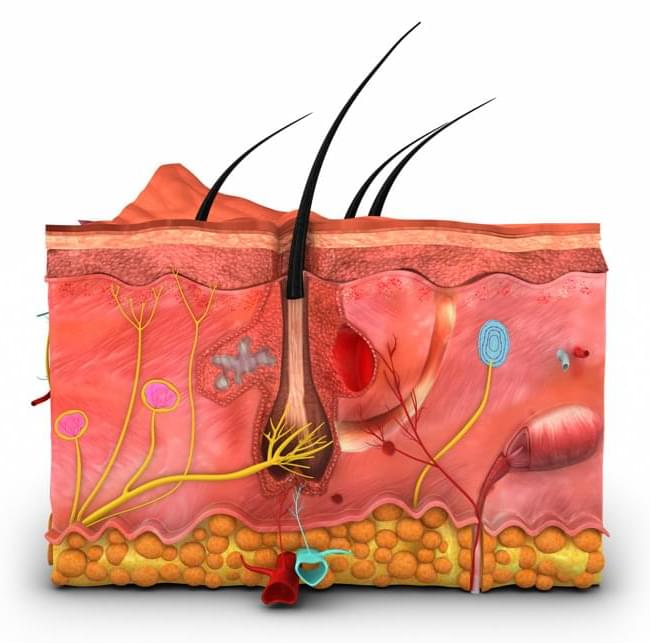
PHILADELPHIA – Treating obese mice with the cytokine known as TSLP led to significant abdominal fat and weight loss compared to controls, according to new research published Thursday in Science from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Unexpectedly, the fat loss was not associated with decreased food intake or faster metabolism. Instead, the researchers discovered that TSLP stimulated the immune system to release lipids through the skin’s oil-producing sebaceous glands.
“This was a completely unforeseen finding, but we’ve demonstrated that fat loss can be achieved by secreting calories from the skin in the form of energy-rich sebum,” said principal investigator Taku Kambayashi, MD, PhD, an associate professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine at Penn, who led the study with fourth-year medical student Ruth Choa, PhD. “We believe that we are the first group to show a non-hormonal way to induce this process, highlighting an unexpected role for the body’s immune system.”
The animal model findings, Kambayashi said, support the possibility that increasing sebum production via the immune system could be a strategy for treating obesity in people.