AI is all that matters now, and reaching Agi before 2030 is all that matters for this decade.
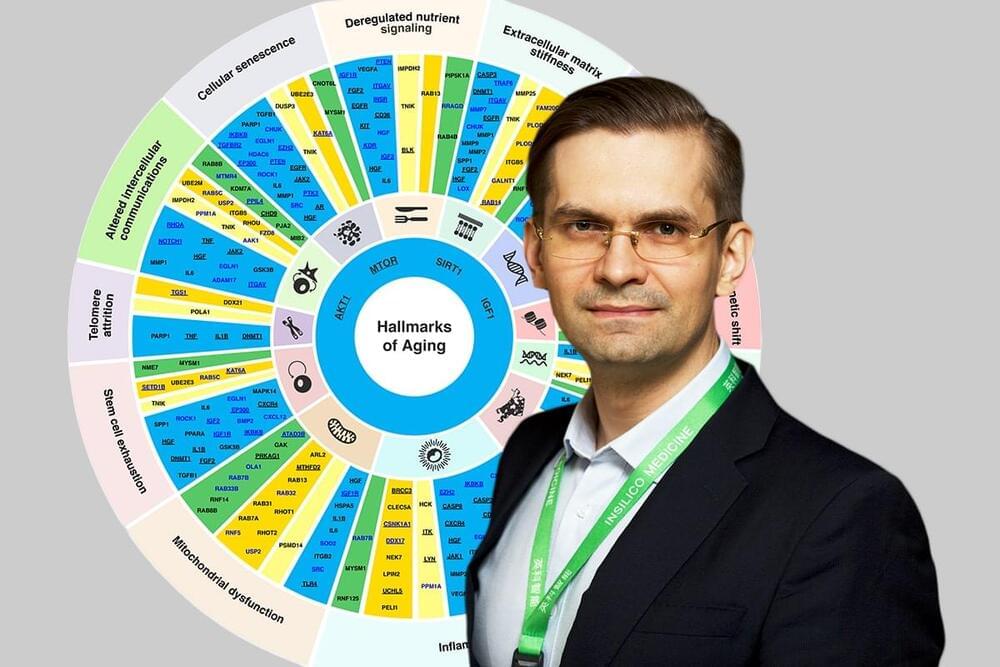
A substantial percentage of the human clinical trials, including those evaluating investigational anti-aging drugs, fail in Phase II, a phase where the efficacy of the drug is tested. This poor success is in part due to inadequate target choice and the inability to identify a group of patients who will most likely respond to specific agents. This challenge is further complicated by the differences in the biological age of the patients, as the importance of therapeutic targets varies between the age groups. Unfortunately, most targets are discovered without considering patients’ age and being tested in a relatively younger population (average age in phase I is 24). Hence, identifying potential targets that are implicated in multiple age-associated diseases, and also play a role in the basic biology of aging, may have substantial benefits.
Identifying dual-purpose targets that are implicated in aging and disease at the same time will extend healthspan and delay age-related health issues – even if the target is not the most important in a specific patient, the drug would still benefit that patient.
“When it comes to targets identification in chronic diseases, it is important to prioritize the targets that are implicated in age-associated diseases, implicated in more than one hallmark of aging, and safe,” said Zhavoronkov. “So that in addition to treating a disease, the drug would also treat aging – it is an off-target bonus.”