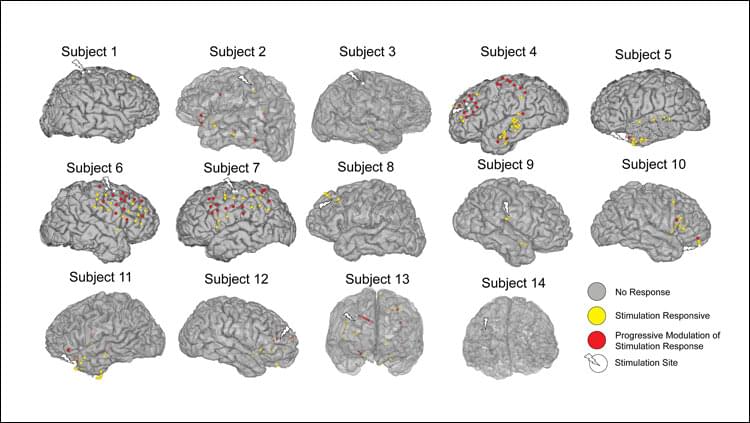
Despite having remarkable utility in treating movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, deep brain stimulation (DBS) has confounded researchers, with a general lack of understanding of why it works at some frequencies and does not at others. Now a University of Houston biomedical engineer is presenting evidence in Nature Communications Biology that electrical stimulation of the brain at higher frequencies (100Hz) induces resonating waveforms which can successfully recalibrate dysfunctional circuits causing movement symptoms.
“We investigated the modulations in local field potentials induced by electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) at therapeutic and non-therapeutic frequencies in Parkinson’s disease patients undergoing DBS surgery. We find that therapeutic high-frequency stimulation (130−180 Hz) induces high-frequency oscillations (~300 Hz, HFO) similar to those observed with pharmacological treatment,” reports Nuri Ince, associate professor of biomedical engineering.
For the past couple of decades, deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been the most important therapeutic advancement in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, a progressive nervous system disorder that affects movement in 10 million people worldwide. In DBS, electrodes are surgically implanted in the deep brain and electrical pulses are delivered at certain rates to control tremors and other disabling motor signs associated with the disease.