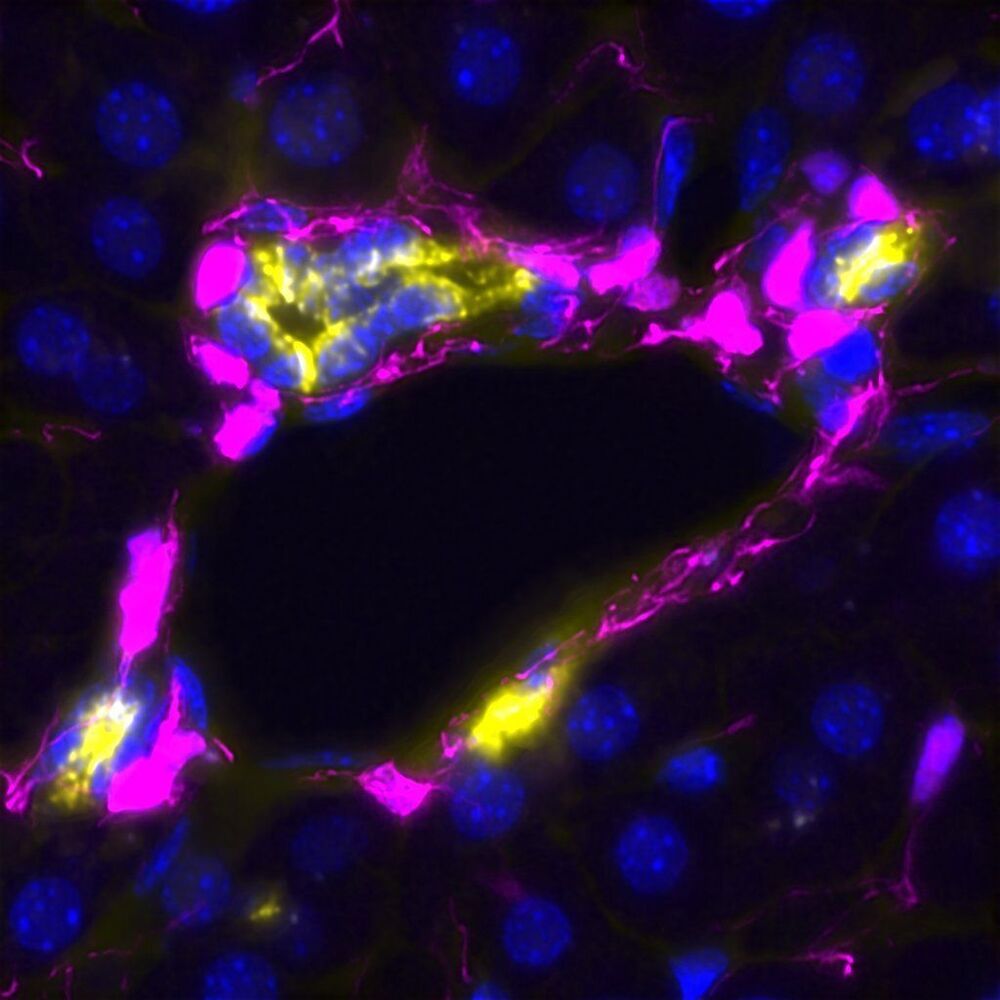
From the time of Aristotle, it has been known that the human liver has the greatest regenerative capacity of any organ in the body, being able to regrow even from a 70% amputation, which has enabled live-donor transplants. Although the liver regenerates fully upon injury, the mechanisms that regulate how to activate or stop the process and when regeneration is terminated, are still unknown. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in Dresden (Germany), at the Gurdon Institute (Cambridge, UK) and at the University of Cambridge (Biochemistry Department) have now found that a regulatory cell type—mesenchymal cell—can activate or stop liver regeneration. The mesenchymal cells do so by the number of contacts they establish with the regenerating cells (epithelial cells). This study suggests that mistakes in the regeneration process, which can give rise to cancer or chronic liver diseases, are caused by the wrong number of contacts between both populations. The work is described in a paper published in the journal Cell Stem Cell on 2nd August 2021.
The molecular mechanisms by which adult liver cells trigger the regenerative response remain largely unknown. Approximately 29 million people in Europe suffer from a chronic liver condition such as cirrhosis or liver cancer. They are a major cause of morbidity and mortality with liver diseases accounting for approximately two million deaths per year worldwide. Currently, there is no cure and liver transplants are the only treatment for liver failure. Scientists are therefore exploring new options for how to trigger the regenerative capacity of the liver as an alternative means to restore function.