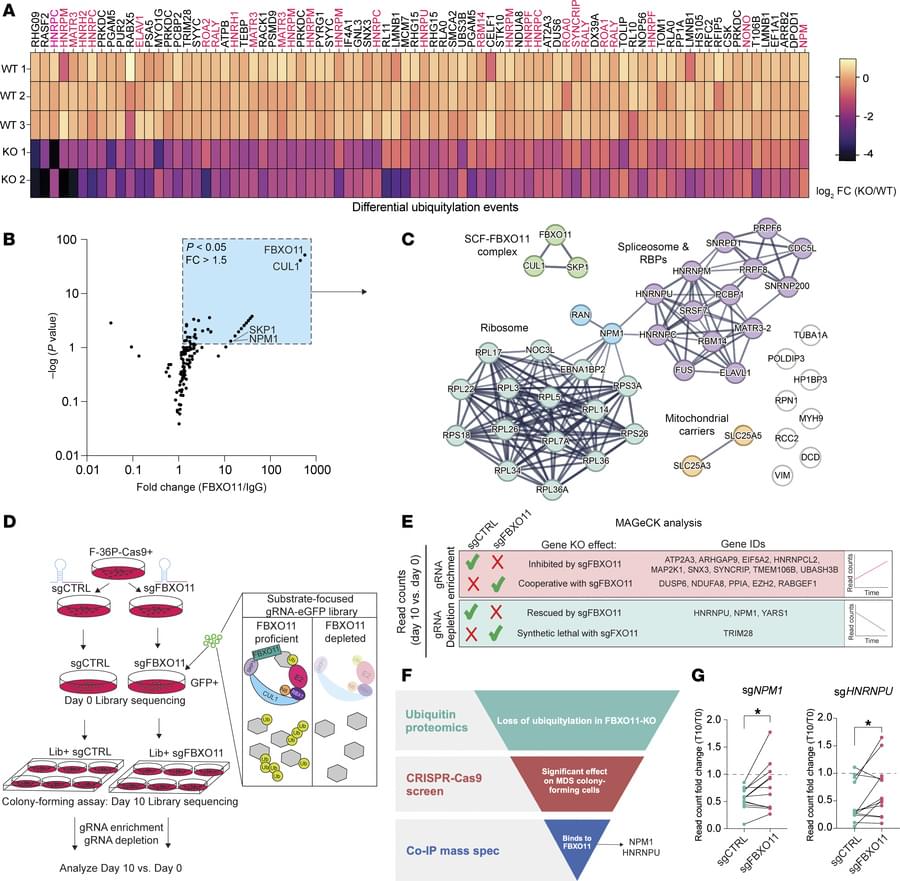
Review: decoding TREM2 signaling pathways—linking macrophage glycolysis to inflammatory diseases in the CNS.
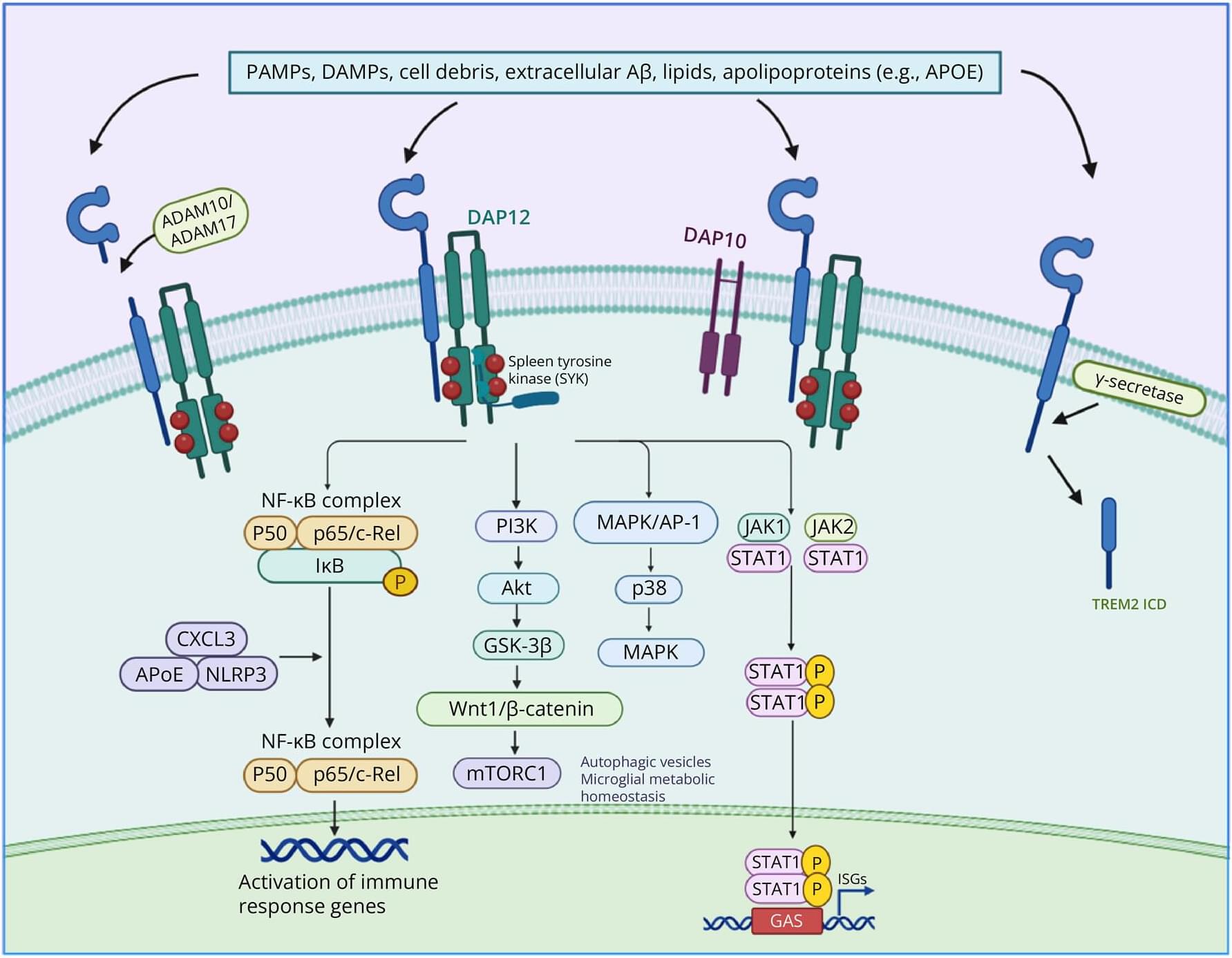
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) is a key immunomodulatory receptor broadly expressed on myeloid cells such as macrophages and microglia. It plays versatile roles in neurodegenerative diseases, tissue repair, and tumor immunity by orchestrating glucose metabolism and inflammatory responses. This review systematically summarizes the structural characteristics of TREM2, its ligand-binding mechanisms, and downstream signaling pathways—including the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B(PI3K/Akt), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) cascades—with a particular focus on its central role in macrophage metabolic reprogramming.
In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer disease, TREM2 contributes to the attenuation of neuroinflammation and slows disease progression by promoting β-amyloid (Aβ) clearance, inhibiting tau hyperphosphorylation, and modulating microglial polarization. Loss-of-function sequence variants, such as R47H, disrupt lipid metabolism, impair phagocytic activity, and destabilize immune homeostasis, thereby significantly increasing disease susceptibility. Furthermore, by enhancing glycolysis and suppressing fatty acid oxidation, TREM2 facilitates macrophage polarization toward a reparative M2 phenotype, promoting neuroregeneration and remyelination in conditions such as spinal cord injury and multiple sclerosis.
Within the tumor microenvironment, TREM2 influences tumor progression and therapeutic resistance by modulating the metabolic reprogramming of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)—notably through activation of pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme M2 (PKM2)–dependent glycolysis—and promoting an immunosuppressive phenotype. In metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity, TREM2 exerts protective effects by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and maintaining lipid homeostasis, highlighting its therapeutic potential.