Researchers from Harvard Medical School found that it is the changes that affect the expression of the DNA — called epigenetics — that affect aging. The discovery may pave the way for more insights into how humans age.


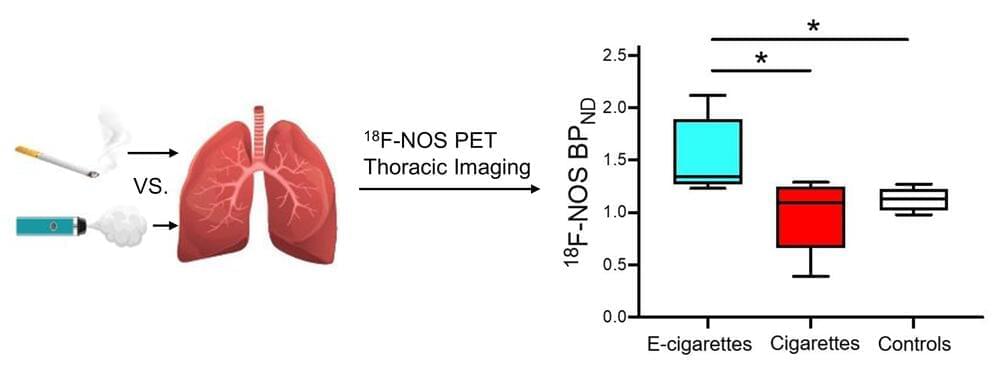
Electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) users have greater lung inflammation than cigarette smokers and non-smokers, according to a new study published online in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. This study is the first to provide evidence that vaping e-liquids with e-cigarettes creates a unique inflammatory response in the lungs that is different from cigarette smoking.
E-cigarette usage has increased dramatically in the past several years, particularly among adolescents and young adults. While many people assume that e-cigarettes are safer than conventional cigarettes, e-cigarettes can cause pulmonary inflammation and increase the risk of lung disease. In addition, their long-term safety has not been rigorously evaluated.
This is the first PET study to use a novel radiotracer, 18 F-NOS, to compare lung inflammation between cigarette and e-cigarette users in vivo. Although PET imaging with 18 F-FDG has been used in the past to investigate inflammation in smokers and vapers, its conclusions were limited.
A monoclonal antibody treatment was found to be safe, well tolerated, and effective in protecting against malaria in a small group of healthy volunteers who were exposed to malaria in a challenge study, according to new research published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM).
“The study demonstrates the feasibility of using monoclonal antibody therapies to help prevent malarial infection and holds promise for deployment to places where the disease is endemic,” said Kirsten Lyke, MD, Professor of Medicine and Director of the Malaria Vaccine and Challenge Unit in the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD) at UMSOM. “This may allow us to revisit malaria eradication efforts.”
There were 241 million malaria cases and 627,000 deaths reported worldwide in 2020 alone, which is a 12 percent increase from 2019. Public health experts contend new strategies are urgently needed to achieve the United Nation’s sustainable development goal of 90 percent reduction in malaria incidence and mortality by 2030. Scientists have tried for decades to develop a highly effective malaria vaccine without much success.

A novel virus, potentially fatal to whales and dolphins, has been discovered by researchers at the University of Hawaiʻi Health and Stranding Lab. Prior to its discovery in 10 whale and dolphin host species across the Pacific, the virus was found in only a single marine mammal worldwide, a Longman’s beaked whale stranded on Maui in 2010. The findings are published in Frontiers in Marine Science.
The discovery of beaked whale circovirus (BWCV) in whales and dolphins expands the knowledge of marine mammal species that can become infected with the disease. Circoviruses are DNA viruses that cause disease in birds, pigs and dogs, and in severe cases can become fatal.
“Our study found Cuvier’s beaked whales tested positive for BWCV in Saipan and American Samoa, nearly 4,000 miles away from the first discovered case,” said Kristi West, director of the UH Health and Stranding Lab. “The positive cases found outside of Hawaiʻi were surprising, and indicates that this virus is spread across the Central and Western Pacific and may have a global presence in marine mammals.”

The last few years have exceeded all expectations in terms of investment activity in longevity, but much more is needed to push the field forward. With more than 40 investments in the longevity field over the past three years, LongevityTech.fund is one of the world’s most active longevity investment funds. The fund’s wide-ranging investment portfolio includes companies like BrainKey, Gerostate Alpha and Occuity.
LongevityTech.fund is now accepting new investors for its second fund, with a target fund size of $50 million up to a maximum of $100 million USD.
Longevity. Technology: LongevityTech.fund has built an impressive company portfolio that has seen no failures to date, with one IPO (longevity biotech Genflow Biosciences) and one company (longevity risk management firm Vesttoo) recently becoming the fund’s first unicorn (valued at more than $1 billion). To learn more about his views on the longevity market, we spoke to serial entrepreneur and investor Petr Sramek, LongevityTech.fund’s co-founder and managing partner.
Health care integration has long been touted as a panacea for reining in health care costs and boosting quality of care.
But integrated health systems appear to be failing on both fronts, according to the results of a new nationwide study led by researchers at Harvard and the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER).
Instead, the analysis finds marginally better care at significantly higher costs for patients seen in health systems, compared to those at independent practices or hospitals.
Cancer cells can shrink or super-size themselves to survive drug treatment or other challenges within their environment, researchers have discovered.
Scientists at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, combined biochemical profiling technologies with mathematical analyses to reveal how genetic changes lead to differences in the size of cancer cells—and how these changes could be exploited by new treatments.
The researchers believe smaller cells could be more vulnerable to DNA-damaging agents like chemotherapy combined with targeted drugs, while larger cancer cells might respond better to immunotherapy.

The hypertension drug rilmenidine has been shown to slow down aging in worms, an effect that in humans could hypothetically help us live longer and keep us healthier in our latter years.
Rilmenidine was picked for this latest study because past research has shown it mimics the effects of caloric restriction on a cellular level. Reducing available energy while maintaining nutrition within the body has been shown to extend lifespans in several animal models.
Whether this translates to human biology, or is a potential risk to our health, is a topic of ongoing debate. Finding ways to achieve the same benefits without the costs of extreme calorie cutting could lead to new ways to improve health in old age.