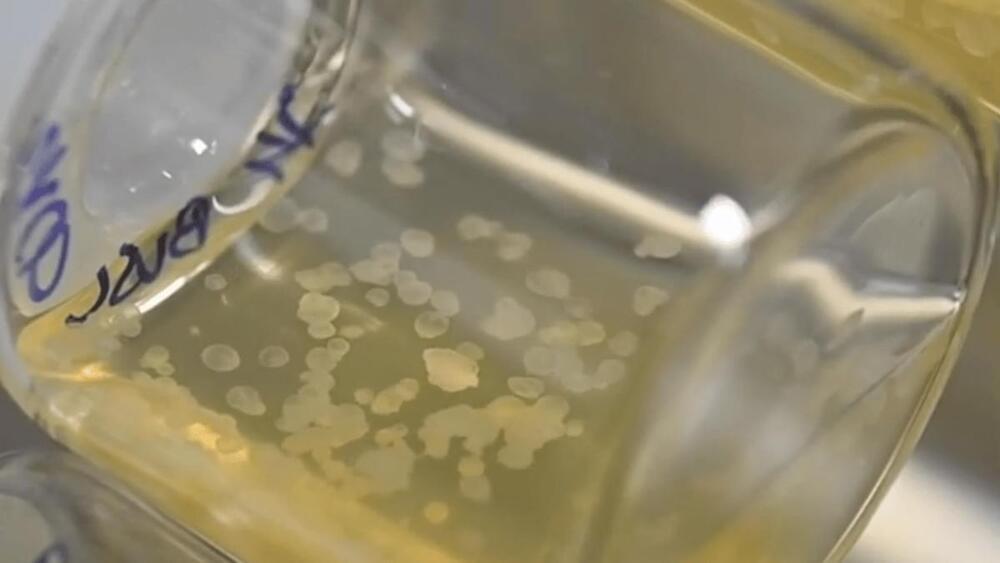
Researchers have created synthetic mouse embryos out of stem cells, removing the need for sperm, eggs and even a womb. They were then grown to almost half the entire gestation period, at which point they had all of the organ progenitors, including a beating heart. The tech could eventually be used to grow organs for transplant.
The new study, from researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, built on two branches of the team’s previous research. The first involved reprogramming stem cells into a “naive” state that allows them to differentiate into all other cells, including other stem cells. The other work focused on developing a device that could grow embryos more effectively outside of the womb.
By combining the two techniques, the team has now grown some of the most advanced synthetic mouse embryos to date. They started with naive mouse stem cells, which had been cultured in a Petri dish for several years prior. These were separated into three groups that would play key roles in the embryo development.